What are the elements of augmented reality?
Augmented reality is brought to life by the dynamic integration of hardware and software. There are three core elements that define AR and make it unique.
Fusion of physical and virtual elements
Digital content overlay on the user’s real-world perspective is one of the main characteristics of augmented reality. All one needs to get an immersive experience is a display device, such as smartphones or head-mounted displays (HUD’s) integrated with AR technology.
Tracking and registration
Augmented reality uses a computer vision algorithm called SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) to achieve reliable tracking. It maps visual details and keeps track of the environment using cameras and sensors, such as a gyroscope and accelerometer.
Real-time interaction
What makes AR technology stand out is having interactive digital elements in the real world. With immersive types of AR, such as superimposition-based, marker-based or marker-less AR, users can interact live with digital elements using simple touch or hand gestures, voice commands, or gaze tracking.
How does augmented reality work?
Augmented reality works by combining physical and virtual elements to create an immersive experience for the user. Here are the underlying processes in an AR system.
Collect, process, and analyze visual data
AR systems collect environmental data and recognize visual markers with sensors and algorithms. By processing this data, it determines the user’s location and context in the environment, preparing itself to position virtual elements in it.
Register and render digital elements
With the AR system prepped, it’s time to generate the digital content (images or text), register its position, scale and orient it in the real-world view, and render it onto the mapped environment.
Update virtual content with each interaction
With the user’s every movement and gesture, the AR system accurately adjusts and updates the digital content in real time to provide the best immersive experience.
What’s the difference between AR and VR?
The difference between AR and VR lies in the way it works and the processes that are needed to emulate that type of reality.
Real-time overlay of digital content onto the physical world
Supported or enabled on most devices like smartphones, tablets, HUDs
Dynamic and simultaneous interaction in the physical and digital world
Partial immersive experience where the user is aware of the physical world
Computer-generated simulation of an entirely artificial environment
Supported only on dedicated devices like a VR headset
Interaction in only one medium, the simulated virtual world
Complete immersive experience where the user can only see the virtual world
Top 5 reasons why augmented reality is better
- Minimal cost to set up
- Accessibility
- Safety
- Real-world integration
- Broader applications
What is augmented reality used for?
Augmented reality (AR) has a wide range of applications across individuals and industries. It creates a significant impact on our society by transforming the way we interact with each other and the environment. Here are a few examples of augmented reality in industrial applications.
Maintenance and repair
Diagnose issues in any equipment or system, troubleshoot, and fix them remotely using an AR software.
Customer service
Allow client-facing teams to improve customer service operations by solving issues remotely through live video streaming and augmented reality technology.
Real-time collaboration
Change the way you collaborate with AR collaboration tools that empower you to visualize complex workflows and interact with experts from anyplace in the world.
Field service
Equip technicians to complete work orders faster, reduce travel times, and manage assignments right from their desk.

How can augmented reality be used in industries?
AR technologies are currently trending in manufacturing and service industries that aim for efficiency within the available time and resources. As it becomes more widespread, accessible, and advanced, it will become the go-to solution for enterprises and SMBs alike.
- Automobile
- Aviation
- Healthcare
- Insurance
- Retail
- Warehousing
Automobile
Supervisors can conduct periodical checks on a live camera stream and provide visual remote support to engineers in their manufacturing plant and service centers by guiding them with visual pointers and annotations.
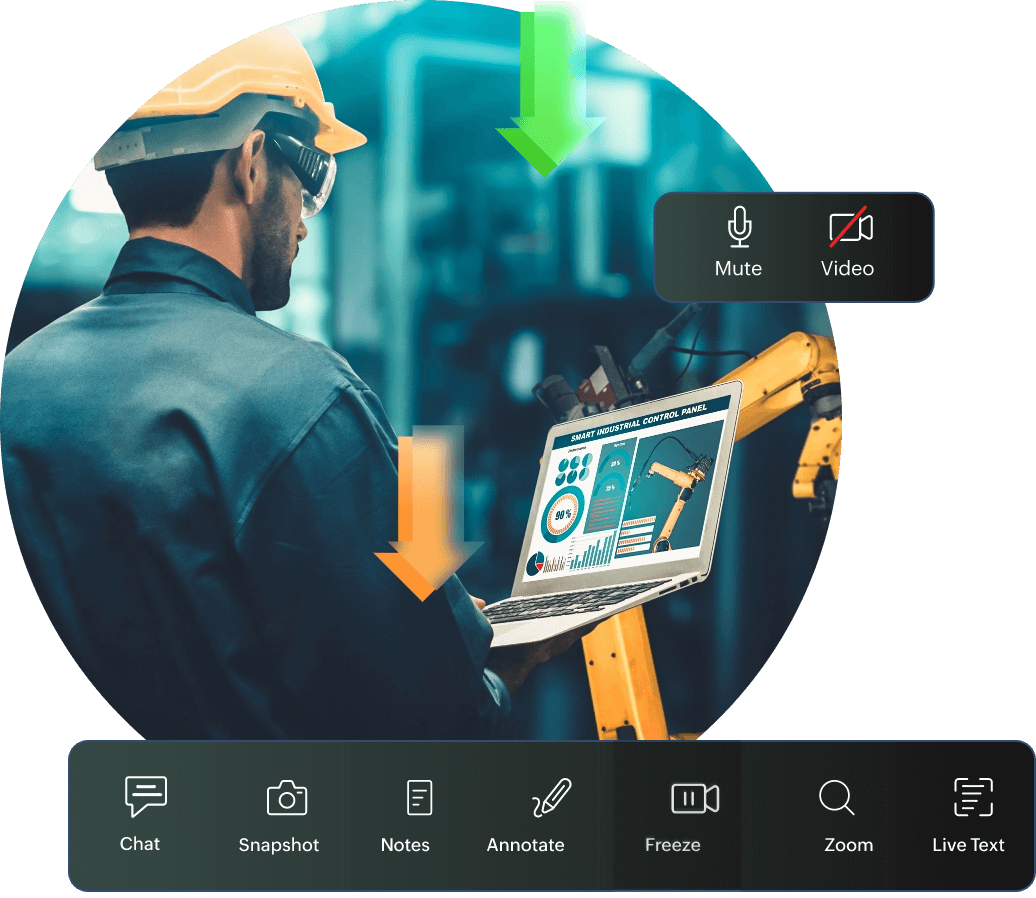
Aviation
Chief engineers can establish a visual connection with their ground crews in any location to manage aircraft assembly and ramp operations, like cargo handling, fueling, and aircraft marshaling, in real time.

Healthcare
Healthcare professionals can share timely medical information with patients and nursing staff and receive remote assistance during the repair or use of medical devices.
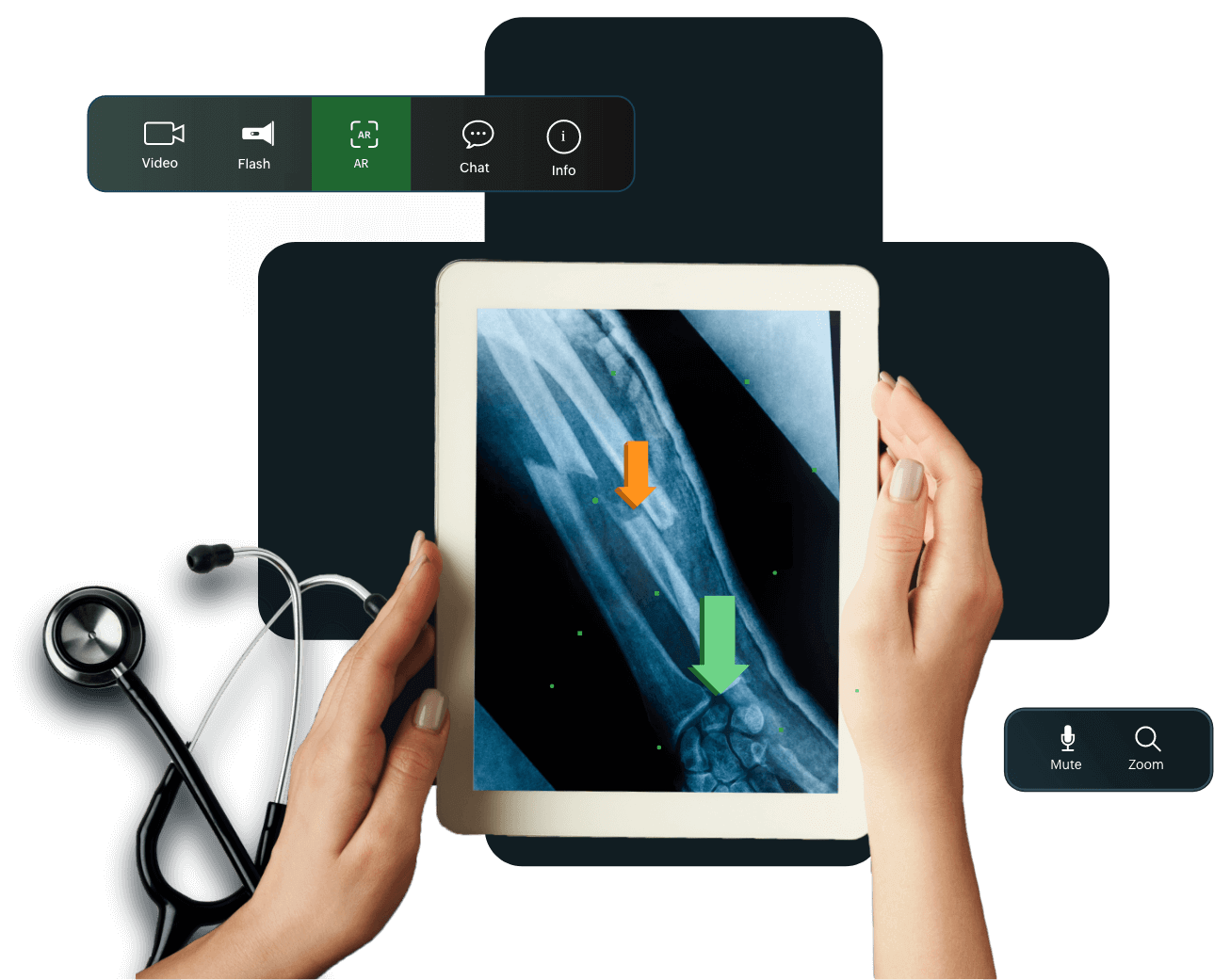
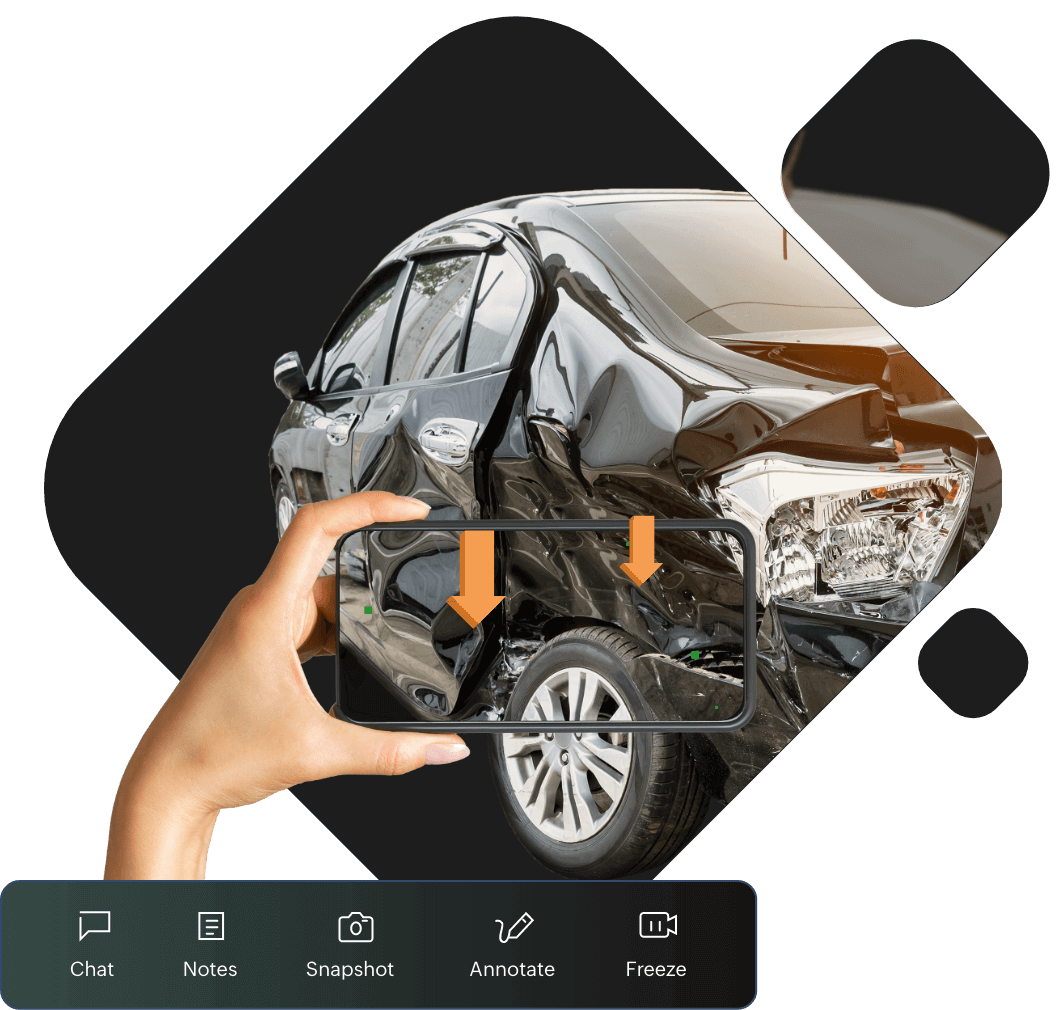
Insurance
With AR usage, claim adjusters can reduce insurance cycle times by replacing onsite visits with remote assistance sessions

Retail
Store managers can manage supply chains in real time, reduce maintenance downtime for machine-handling equipment, and improve customers’ post-purchase experience.

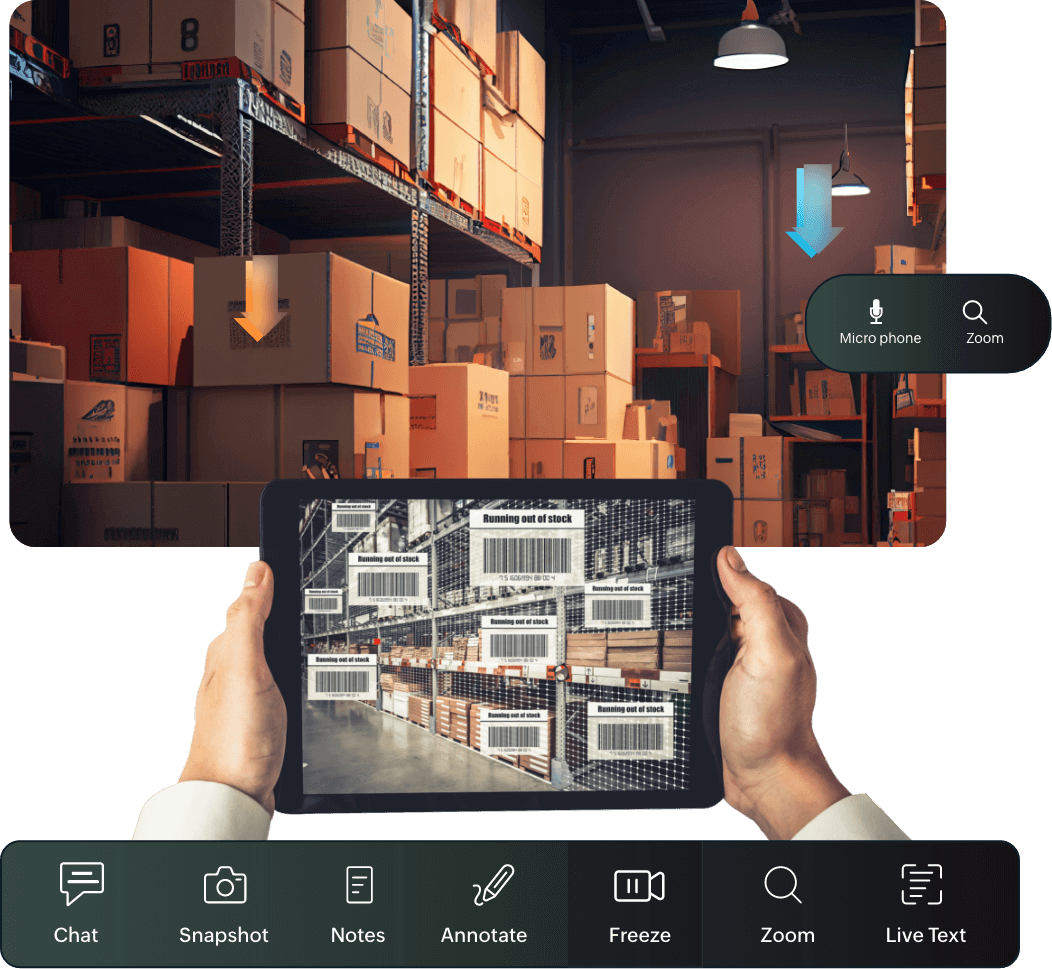
Warehousing
Logistics staff can annotate to draw attention to specific handling units during order picking and scan product labels for quicker dispatch.

