- What is augmented reality?
- What is virtual reality?
- How does augmented reality work?
- How does virtual reality work?
What is augmented reality?
Augmented reality (AR) is a type of technology that blends the physical and digital worlds seamlessly by adding an overlay of digital elements like images or text onto the physical environment. It enhances a user's perception of the real world with contextual visual, auditory, or haptic information.
What is virtual reality?
Virtual reality (VR) is different from AR, where it isolates the physical world from the user completely with a simulation of a digital environment. It provides a three-dimensional experience for the user, where they can view, interact, and control the elements in the virtual world only.
In essence, both AR and VR are a part of the extended reality (XR) spectrum, where AR seamlessly integrates with the real world, while VR completely cuts off the real-world view.
How does augmented reality work?
AR technology requires a camera, a few sensors, and the right software to map the physical world, process spatial information, and show the synthesized result to the user via a display. With this technology, users can view their environment while getting real-time feedback on their digital interactions.
How does virtual reality work?
VR technology runs on high-powered computer systems to simulate entire virtual worlds that can be viewed in specialized devices like a head-mounted display (HMD). With this technology, users are submerged into a virtual space, where they are free to interact and move around in the simulated world.
Types of augmented reality
Augmented reality technology can be broadly classified in two ways: marker-based and marker-less.
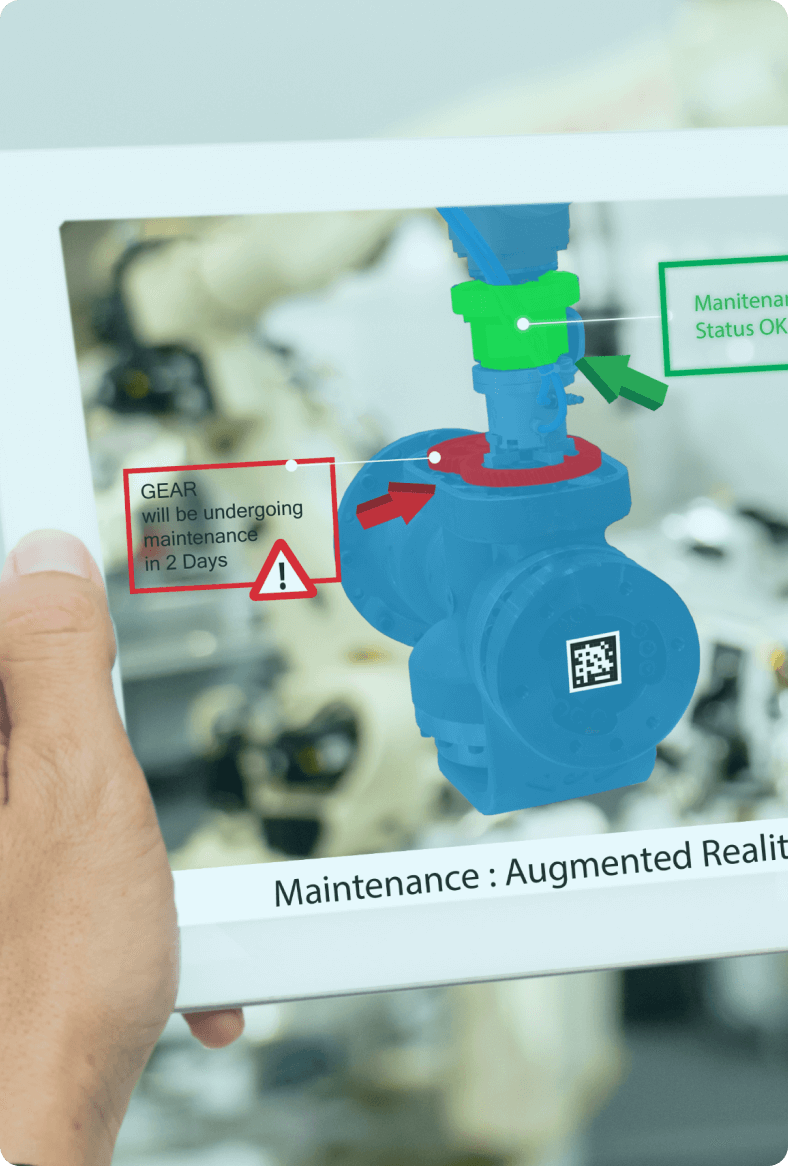
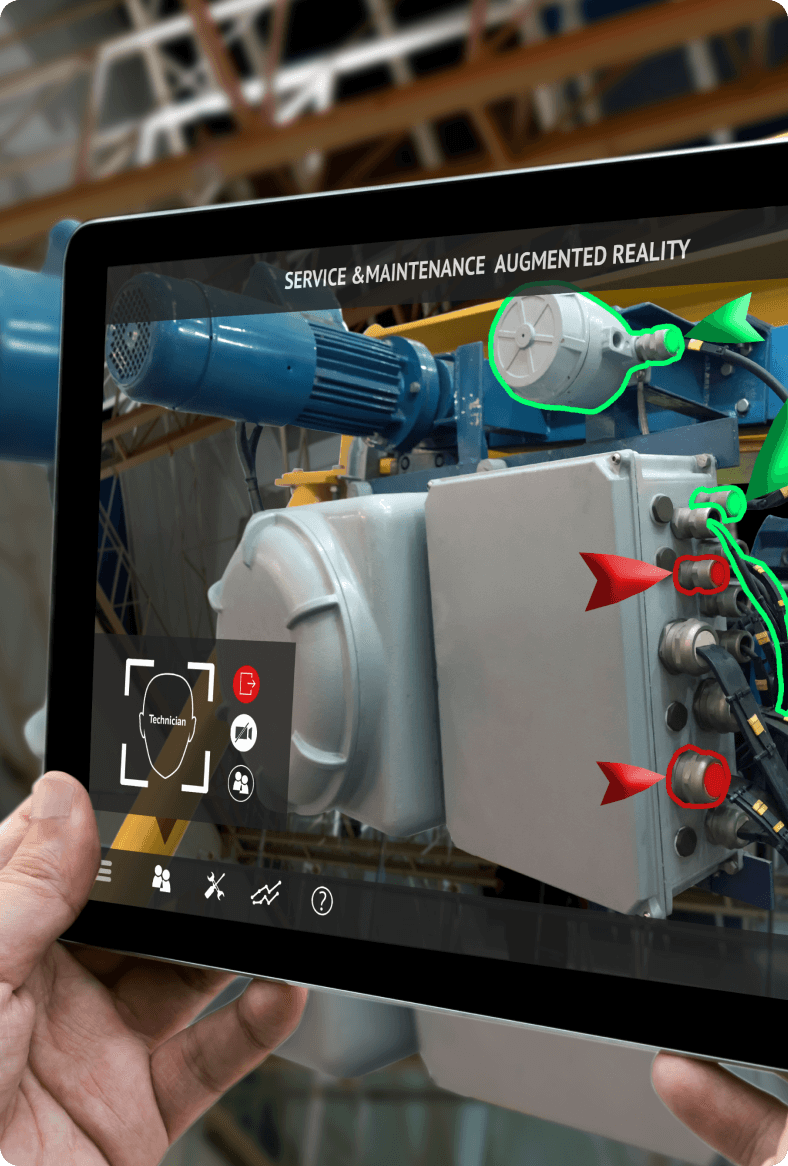
Marker-based AR
Marker-based AR is also known as recognition-based AR or image recognition AR. It uses a target image known as a marker to anchor the digital content on that marker. An example of marker-based AR would be to use QR codes as markers, which the user can scan on their device to trigger the mixed reality experience. This can be extended to images on posters or greeting cards, which can then be scanned with a dedicated AR app to bring those images to life.
Marker-less AR
Marker-less AR goes beyond the constraints of markers and can display digital content anywhere in the user's environment. It uses a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm to map the physical environment around the user with the help of the device's camera, GPS, accelerometers, and other sensors.
The most popular applications of marker-less AR are real-world mobile games like Pokemon Go, social media filters such as the ones we see on Instagram or Snapchat, and online shopping features on IKEA and Amazon that allow users to place the digital version of furniture in their homes to see how it looks and fits into that space.
It can be further classified into four types.
- Location-based AR
- Projection-based AR
- Contour-based AR
- Superimposition or overlay-based AR
- User-defined AR
Types of virtual reality
Based on the immersion levels, VR technology can be classified into three types:
Non immersive VR
Users can view and interact with the virtual environment through their computer display. Third-person simulation games are the most common form of non-immersive VR.
Fully-immersive VR
It gives maximum immersion through headsets and allows users to interact and affect the virtual world with body connectors and sense detectors. First-person flight or driving simulations are great applications for fully-immersive VR.
Semi-immersive VR
Using a phone or a VR box, users can only see the virtual world and affect their perspective by swiping the screen or turning their head. The devices use a gyroscope to determine the user's direction.
Differences between AR and VR
The difference between AR and VR lies in the way it works, its availability, versatility, and the emulation processes involved.
- Real-time digital overlay of elements onto the physical world
- Supported or enabled on most devices like smartphones, tablets, head-up displays (HUDs)
- Simultaneous, dynamic interaction in the physical and digital world
- Low to medium immersion levels where the user is aware of the physical world
- Isolated from the real world with the simulation of virtual environments
- Supported only on specialized devices like HMDs or VR headsets
- Interaction reflected in only one medium, the simulated space
- High immersion levels where the user can only see the virtual world
Augmented reality at Zoho Lens
Zoho Lens is an AR remote assistance software that helps technicians view hardware and equipment issues via live camera stream and solve them using AR tools. It uses marker-less AR (specifically user-defined AR) along with spatial tracking and depth mapping to create an immersive experience. This gives more freedom to end users to place digital content anywhere on the camera stream while working in an augmented environment.
Applications of AR technology in the industrial landscape
AR technology has the power to transform the way industries operate by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and customer interactions. Take a look at the industries that are benefiting significantly from augmented reality:
Manufacturing
AR technology helps in streamlining your manufacturing processes and scaling your operations to the next level, where you can visualize assembly instructions, conduct quality inspections, and monitor machinery health in real time.
Learn moreAutomobile
With AR technology, automobile manufacturers can expand on their product visualization methods, optimize assembly workflows, and enhance maintenance procedures for increased throughput and even incorporate these technologies in their customer's post-purchase engagement.
Learn moreAviation
Augmented reality can simplify complex engineering and aircraft assembly processes by empowering chief engineers to conduct regular checks from remote locations and manage ramp operations, like cargo handling, fueling, and aircraft marshaling, all in real time.
Learn moreHealthcare
AR applications in healthcare are numerous, ranging from enhanced visualization of diagnostic procedures, live remote consultations, and receiving remote assistance during the repair or use of medical devices.
Learn moreInsurance
Claim adjusters can use augmented reality to communicate effectively with the person on the ground and gather more information accurately, thereby reducing insurance cycle times.
Learn moreRetail
AR finds its most popular applications in the retail industry, such as virtual try-ons and interactive digital stores. Store managers can use it to remotely manage supply chains, speed up dispatches, and improve customers' post-purchase experience.
Learn moreConstruction
The use of AR in construction is becoming widespread due to its two-fold benefit of enhanced workforce safety and faster implementation of construction projects. Architects and engineers can leverage AR technology to collaborate from remote locations, and conduct live training sessions and safety checks with ease.
Learn moreCustomer service
Innovative approaches can elevate the customer support infrastructure of an enterprise. Augmented reality technology allows client-facing teams to solve issues remotely with efficiency and precision through live video streaming and powerful virtual tools.
Learn moreIndustrial applications of VR technology
The immersive nature of VR transforms how industrial tasks are approached, fostering innovation and improving industrial operations. In the realm of training and safety, VR simulations provide realistic environments for practicing equipment operation, emergency response, and maintenance procedures, minimizing risks and downtime. VR is instrumental in product design and prototyping, allowing engineers to visualize and interact with 3D models, improving the design process.
The future of AR and VR
AR and VR technologies are at the forefront of innovations in Industry 4.0. The dynamic nature of these technologies will transform business operations at every level and deliver the best customer experiences. With ongoing technological advancements in hardware and software, it will become more user-friendly and affordable, maximizing user and enterprise adoption in the upcoming years. Artificial intelligence (AI) will play a crucial role in enhancing AR and VR experiences by contributing to better object recognition, natural language processing, and the generation of realistic virtual environments.
