- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- BPM vs workflows: What's the difference?
BPM vs workflows: What's the difference?
- Last Updated : March 17, 2025
- 881 Views
- 6 Min Read
Choosing between business process management (BPM) and workflows can be challenging, as they both have very similar goals. So before diving in to the comparison between BPM and workflows, it's essential that we understand their roles in improving organizational efficiency.
Businesses are always looking to improve how they operate, and aim to enhance process modeling, reduce costs, and provide better service. BPM and workflows are two approaches that support these goals in different ways.
Differences between BPM & workflows
So how exactly are BPM and workflows different from each other, and which one might suit your business needs? Before we dig deeper, here's a short look at the main differences:
| BPM | Workflows |
Definition | A strategic approach that focuses on optimizing and improving the overall processes within an organization | A sequence of steps or tasks that needs to be completed to achieve a specific goal |
Goal | Improve and automate business processes | Automate specific tasks within a process |
Complexity level | High | Low to medium |
Scalability | Suitable for handling high-volume processes and large datasets | Scalable only within specific tasks or departments |
Preferred user | Ideal for organizations with complex, interconnected processes that span multiple departments | Ideal for small- to medium-sized businesses, departments within larger organizations, and teams that handle similar tasks at high volume |
Business process management involves analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and refining processes to ensure they're as efficient and effective as possible.
Whereas, workflows are more about the operational side of things, detailing how tasks move from one stage to another. Workflows are usually simpler and can often be automated using workflow management software.
Objectives and goals
BPM and workflows have different aims that make them suitable for various tasks. BPM's main goal is to improve and automate business processes, making them more efficient and aligned with company goals and customer needs. It focuses on constant improvement and innovation, aiming to streamline processes across the organization.
BPM will help with your business process automation and make it more agile and better at handling changes in the market. It also helps foster a culture of continuous improvement and integrate processes with technology, which enhances decision-making.
A workflow, on the other hand, is more about automating specific tasks within a process. Its objective is to make sure these tasks are done in a set order and follow certain rules, which reduces the need for manual work and minimizes errors.
Workflows aim to simplify your task management, increase the speed and accuracy of task completion, ensure compliance with standards, and improve coordination among your team members. Essentially, workflows enhance productivity and consistency in task execution.
Levels of complexity
The complexity of BPM and workflows is quite different. BPM is generally more complex, as it manages whole processes that may involve several departments. It requires a deep understanding of how these processes fit into the larger goals of your organization and how they interact with each other.
BPM involves continuously monitoring, analyzing, and improving processes, often integrating with other business systems, like enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM).
Examples of BPM use cases include supply chain management, customer service management, and financial process management—all areas where coordination and optimization across various functions are crucial.
Workflows, though, operate at a low- to medium-complexity level. They focus on automating specific, well-defined tasks within a process, making things easier to design and manage. Compared to BPM, workflows are typically linear, following a set sequence and involving fewer integrations.
Examples of workflows include document approval processes, employee onboarding, and invoice processing. These tasks are straightforward and follow a predefined path, managing specific, routine tasks, which makes them perfectly suited to workflows.
Scalability and flexibility
When it comes to scalability and flexibility, BPM and workflows differ significantly. As BPM is designed to scale across your entire organization, it's more suitable for handling growth and changing business needs. It's capable of managing complex, high-volume processes and large datasets, supporting enterprise-wide standardization and optimization. BPM also enables continuous process improvement and can be customized to meet your specific business requirements.
For example, a multinational supply chain company can use BPM to standardize processes across global offices, ensuring consistency while allowing for regional differences.
In contrast, a workflow is scalable within specific tasks or departments, but may not be as effective for managing processes across the whole organization.
Workflows can be replicated in other areas, but they have limitations. Such systems are less flexible than BPM, because they follow strict rules and are often rigidly defined. Changing workflows usually means redesigning the tasks and sequences. Workflows are usually best for stable, repetitive tasks that don't vary much.
For instance, a marketing team at the above-mentioned supply chain company might use workflow automation to manage campaign approvals, ensuring tasks are completed on time and following guidelines, while an IT department could use workflows to automate help desk ticket management, improving response times and reducing manual effort.
Benefits and challenges
Below are the few common benefits:
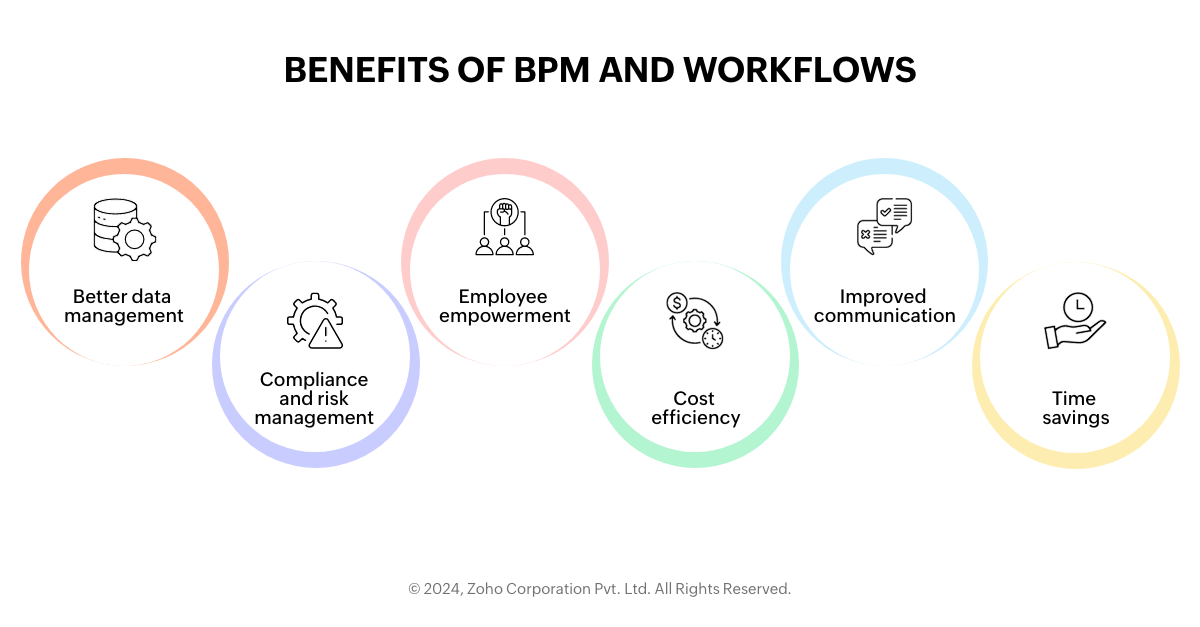
Better data management: They often include features for better data tracking and reporting, which can help you make more informed decisions.
Compliance and risk management: By standardizing processes, BPM and workflows help ensure compliance with industry regulations and reduce the risk of human errors.
Employee empowerment: They can help employees understand their roles within a process, which can lead to increased job satisfaction and productivity.
Cost efficiency: Automating tasks with BPM and workflow tools can significantly reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for manual labor.
Improved communication: These tools also include features for better communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Time savings: By automating repetitive tasks and processes, workflows and BPM free up time for employees to focus on more strategic work.
While BPM and workflow management offer numerous benefits, there are also challenges to consider. Implementing BPM can be time-consuming and may require significant changes to existing processes.
It often demands substantial resources, including personnel and technology investments, which can be a hurdle for some organizations. Additionally, BPM initiatives require continuous monitoring and refinement, which can strain resources further.
On the other hand, workflow management systems also come with their own set of challenges. Workflow automation typically has a limited scope, focusing on specific tasks rather than addressing broader process inefficiencies. This narrow focus may not resolve larger systemic issues within an organization.
Furthermore, once a workflow is defined, making changes can be difficult and may require redesigning the entire workflow, which can be a complicated process.
Who needs BPM?
BPM is ideal for organizations with complex, interconnected processes that span multiple departments. It’s beneficial for industries like manufacturing, finance, healthcare, and logistics, where process efficiency is crucial.
If your business goals include reducing costs, improving customer satisfaction, and enhancing overall operational efficiency, BPM will be a powerful tool.
BPM helps you take a broad view of your business, identify areas for improvement, and implement changes that have a lasting impact. It's particularly useful for large organizations or ones undergoing significant digital transformation.
For example, a national bank might use BPM to improve its customer service processes. By analyzing the entire customer journey, from opening an account to resolving issues, the bank will be able to identify areas for improvement and implement changes that enhance the customer experience.
Who needs workflows?
Workflow management system is suitable for businesses that need to improve the efficiency of specific tasks or processes. They're beneficial for automating repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency and reducing errors. Workflow tools are ideal for small to medium-sized businesses, departments within larger organizations, and for teams that handle similar tasks in high volume.
Workflows are particularly useful for processes like document approval, customer service ticket handling, and routine HR tasks. They help you streamline operations and improve task management.
For instance, your marketing team could use workflow tools to manage content creation. The workflow might include steps like drafting, editing, approving, and publishing content. Automating these workflows ensures that each piece of content goes through the necessary steps efficiently and consistently.
Conclusion
Choosing between BPM and workflow management depends on your business needs and goals. BPM offers a strategic approach to optimizing entire processes within your organization, making it ideal for complex and interconnected operations. Whereas, workflow management focuses on improving specific tasks and sequences, providing a simpler solution for routine processes.
The best thing is that the choice between BPM and workflow is not always mutually exclusive. Many organizations use both approaches together to address different needs within their operations. For example, you might use BPM to optimize your overall supply chain while using workflow tools to manage specific tasks within that chain.
Low-code platforms, like Zoho Creator are capable of enabling both BPM and workflows, as they're designed to help you create process-based applications, as well as automate routine tasks.
Ultimately, no matter what you choose, the goal is to facilitate business process improvement, enhance efficiency, and help you achieve better outcomes.
 Ann Elizabeth Sam
Ann Elizabeth SamHey! I'm Ann, and I work as a content writer at Zoho Creator. I'm exploring the SaaS world through various forms of content creation. Outside of work, I love dancing and would give up anything to read a good murder mystery.