- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- What is workflow technology, and how does it work?
What is workflow technology, and how does it work?
- Last Updated : November 30, 2025
- 270 Views
- 11 Min Read
Your purchase order has been “pending approval” for 48 hours. No one knows whose desk it's on. You have the right people and the right tools, but work still gets stuck. Sound familiar?
The bottleneck isn’t your team. It's the manual handoffs between each step. Workflow technology automates those connections so tasks move forward based on conditions you set, not on who remembers to follow up.
Highlights
Workflow technology is about turning logic, data, and ownership into systems that run without supervision.
Mapping workflows before automating them helps avoid gaps, missed steps, and inconsistent execution across teams.
Technologies like AI, RPA, and low-code tools are shifting workflows from static rule-based flows to adaptive, decision-ready systems.
Teams don’t need a stack of tools. They need one platform that lets them design, run, and scale workflows where the work happens.
This guide breaks down what workflow technology is, which types fit different business needs, and how teams across industries use it to get work done faster without adding complexity.
What is workflow technology?
Workflow technology solves this problem by structuring how tasks are triggered, routed, and tracked automatically.
Every business process runs through a series of steps. Information moves, decisions happen, and actions follow. That sequence is called a workflow.
When those steps are manual, tasks fall through the cracks. Teams lose visibility. Each step in the flow depends on clear conditions. One action triggers the next. Data moves from form to system to user without delays or duplication.
Workflow technology creates a controlled environment for repeatable processes. That’s why, by 2027, the global workflow management market is projected to reach USD 26.8 billion. It replaces scattered handoffs with rule-based execution. How those flows are structured depends on the type of workflow, and that’s where distinctions begin to matter.
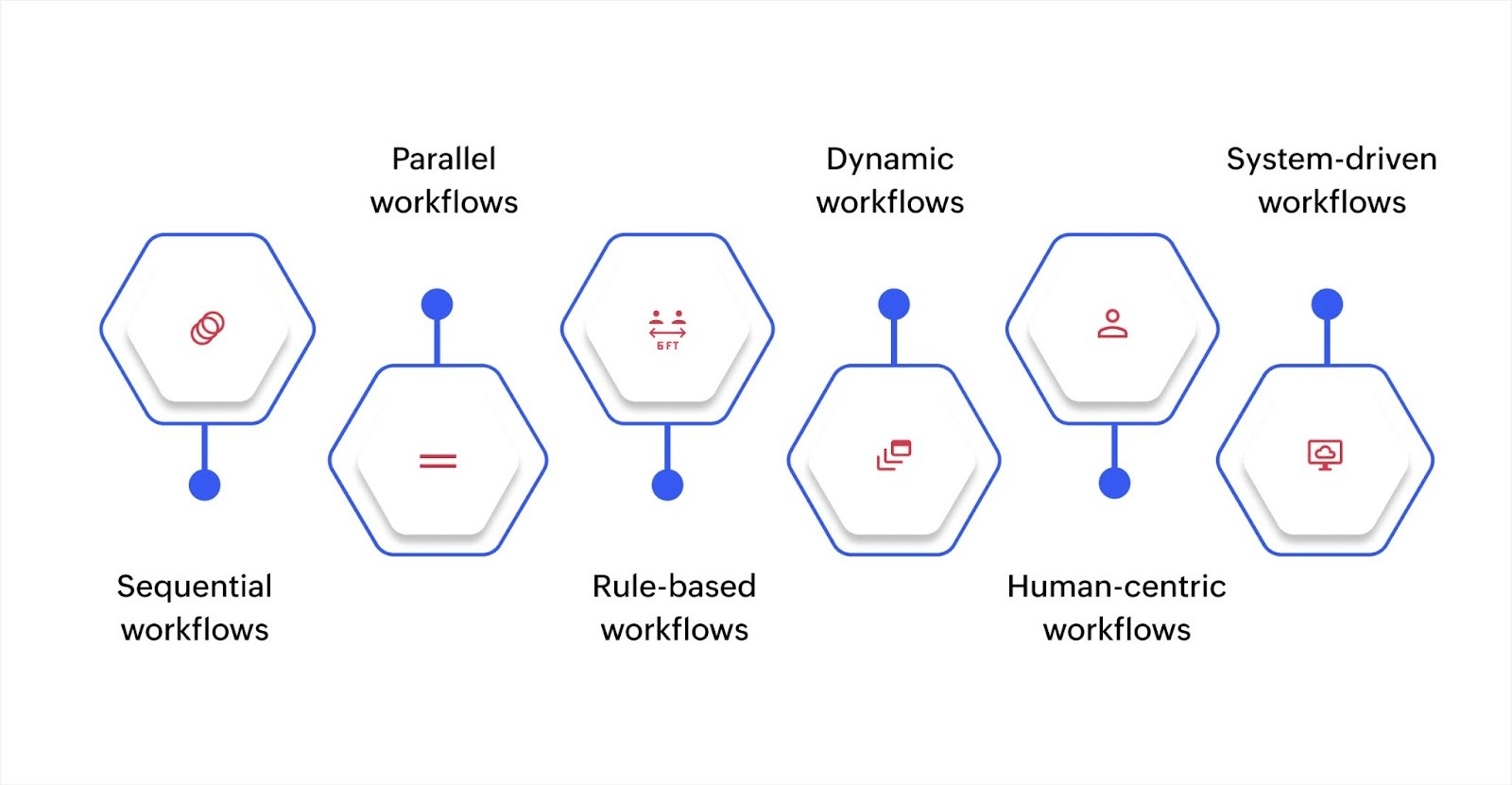
Types of workflows
Workflow type | Best for | How it works | Key benefit |
Sequential | Leave approvals, compliance checks | Each task begins only after the previous one is completed | Clear, predictable process flow |
Parallel | Onboarding, multi-team projects | Multiple tasks run simultaneously | Faster completion times |
Rule-based | Customer support, procurement | Conditions determine how steps proceed | Smart routing based on criteria |
Dynamic | IT operations, customer service | Adapts in real time to variables | Flexible response to changing conditions |
Human-centric | HR processes, procurement approvals | Requires input, review, or approval from people | Human judgment where needed |
System-driven | Notifications, data transfers | Runs automatically based on triggers | Zero manual intervention |
Workflow mapping and design process
Clear design lays the foundation for every successful workflow. Automation only speeds up broken processes. That's why every successful workflow starts with a clear design. Before adding automation, you need to map out how work actually flows, and who does what, when, and why. This stage helps you define each step, eliminate ambiguity, and build a foundation for reliable execution.
Identify the process to map
Start with a specific, repetitive process that causes friction. It could be a delayed approval chain, a missed follow-up, or manual handoffs across teams. Avoid broad workflows. Focus on a single process with clear boundaries and outcomes.
Break it into repeatable steps
List every step from start to finish. Who starts the process? What inputs are required? Who approves or acts next? Use plain language to describe each step. Avoid skipping actions that feel “implied,” as those are often the source of confusion.
Build a visual flow
Create a diagram that outlines the full flow. Include start and end points, inputs, outputs, task owners, and decision nodes. Show where the process might branch into alternate paths. This clarity prevents rework when building the logic.
Validate the workflow with users
Share the draft with stakeholders. Ask how they handle exceptions. Confirm whether the diagram reflects what actually happens, not what’s written in a policy document. These conversations reveal missing conditions and fix assumptions early.
Prepare it for automation
Once the structure holds up, define triggers, rules, and dependencies. Identify which steps can run automatically and which require user input. Once your workflow design is finalized, it's time to move from planning to implementation.
When workflows involve multiple steps, a business process automation platform can help you turn mapped processes into working automation with visual workflow builders and structured data models that match how your business operates.
If you stop only after designing the process manual, handoffs will create room for error. To fix that, you need a system that runs the workflow once it’s designed.
How does workflow automation work?
Let's see how workflow automation works with an example of automating a leave approval process. Here’s how it would work:
Trigger: The workflow starts when an employee submits a leave request form.
Rule: If the leave duration is under three days, it routes automatically to the team lead for quick approval. If it exceeds three days, it goes to the manager.
Task execution: Once approved, the system automatically updates the employee's leave balance, notifies HR, and sends a confirmation email.
Exception handling: If a mandatory field (like leave dates) is missing, the workflow flags it and notifies the employee to correct the form.
Visibility: Both the requester and the approver can track the request status in real time, without follow-ups or emails.
Automation solves execution gaps, but its impact goes far beyond faster task completion. For example, 77% of marketers who utilize automation have seen an increase in digital engagement. This demonstrates how workflow automation benefits teams by scaling their work more efficiently.
Benefits of automating workflows
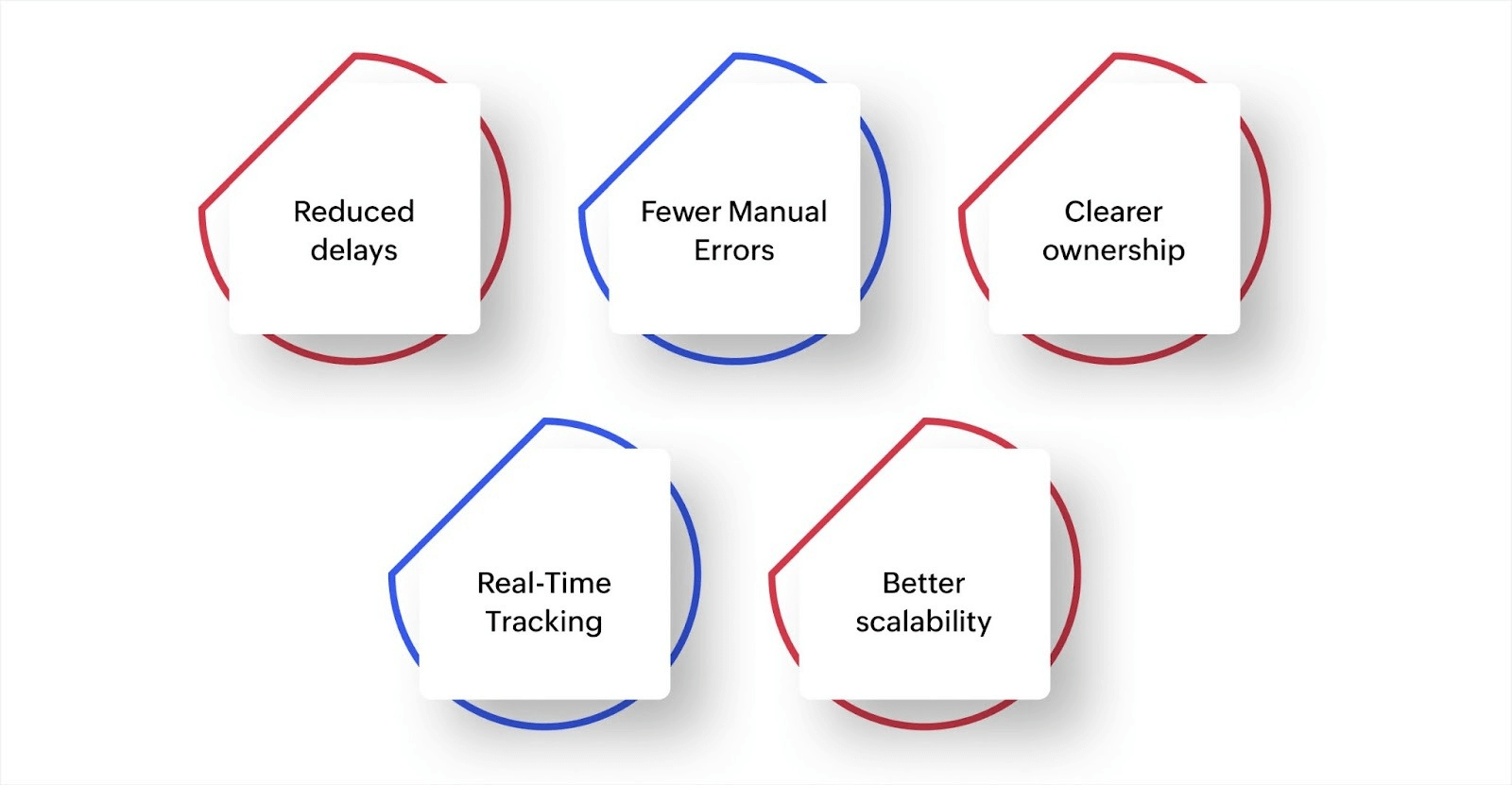
Reduced delays: When steps are automated, there’s no lag between completion and handoff. This shortens cycle times and improves response rates.
Fewer manual errors: Defined rules limit common errors like skipped steps, missed approvals, or duplicated entries.
Clearer ownership: Because everyone knows what’s next, who’s responsible, and what’s pending, people show accountability.
Real-time tracking: You can track performance and review past activity without chasing updates for compliance-heavy processes.
Better scalability: As operations grow, automated rules adapt to volume without increasing complexity.
9 common use cases across teams
Workflow automation adapts to different industries by fitting the way work actually flows. Each sector faces conditional decisions and delays. Here's a look at how different industries use workflow technology to fix real execution problems.
Human resources
HR teams handle repetitive processes that involve multiple steps and approvals. Delays in onboarding can push back a new hire's productivity by days or even weeks. When a candidate accepts an offer, an automated workflow handles contract signing, account creation, and task assignments across departments without manual coordination.
For instance, HR automation can instantly create email accounts, assign training modules, and notify managers the moment someone joins, significantly reducing onboarding time.
Finance
Finance teams spend significant time chasing approvals and tracking down missing documents. When purchase requests sit in email threads, projects get delayed and budgets become hard to track.
An automated approval workflow routes requests based on amount and department, attaches required documents, and syncs approved purchases directly to accounting systems. Financial automation ensures compliance at every step while moving transactions through approval chains faster, giving finance teams real-time visibility into spending.
Customer support
Support teams lose valuable time manually sorting through tickets and figuring out who should handle each issue. By the time a ticket reaches the right person, customers have often been waiting too long.
When a customer submits a request, automated systems analyzes the content, categorizes the issue, and routes it to the appropriate team based on keywords and urgency. Customer service workflows can escalate unresolved tickets automatically and ensure nothing gets missed, improving response times without adding headcount.
Sales
Sales reps waste hours qualifying leads manually, often following up on prospects that aren’t ready to buy. Automated lead qualification scores and filters incoming leads based on budget, timeline, and fit.
Sales workflows assign high-priority leads to the right representatives immediately and trigger personalized follow-up sequences, so your team focuses energy where it matters most.
Marketing
Marketing campaigns involve creative approvals, asset coordination, and precise timing across multiple channels. Manual handoffs create bottlenecks that delay launches and cause teams to miss deadlines.
Automated campaign workflows move content through approval stages, segment audiences, and publish assets on schedule without manual intervention. Marketing automation keeps campaigns on track and ensures that content reaches the right audience at the right time, even when teams work across time zones.
Retail operations
Retail businesses struggle to maintain the right inventory levels across multiple locations. Too much stock ties up cash, while too little means lost sales. Automated inventory workflows monitor stock levels in real time and trigger reorder requests when items fall below thresholds.
Retail management systems can route purchase requests through pricing and vendor approval automatically, then adjust ordering patterns based on sales trends to keep shelves stocked without overbuying.
Healthcare administration
Healthcare facilities process high volumes of patient information under tight regulatory requirements. Manual data entry slows down registration and increases the risk of errors that can affect patient care.
When a patient registers, automated workflows verify insurance coverage, check for missing information, and route patients to the correct department based on their needs. Healthcare workflows reduce wait times and free staff to focus on patient interactions rather than paperwork.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing operations require constant quality monitoring to catch defects before they reach customers. When quality checks are done manually, problems can go unnoticed until an entire batch is affected.
Automated quality workflows assign inspection checklists, capture defect data, and alert supervisors immediately when issues are detected. Manufacturing workflows provide real-time visibility into production quality, allowing teams to address problems on the line rather than after products have shipped.
Education
Educational institutions manage complex enrollment processes that involve verifying documents, assigning courses, and coordinating across multiple departments. During peak registration periods, manual processing creates long wait times and frustrated students.
When a student registers, automated workflows assign them to course batches, notify instructors, generate access credentials, and route approvals based on program requirements. Educational management systems handle hundreds of enrollments simultaneously, cutting processing time and reducing administrative burden when it matters most.
Across industries, workflows may look different on the surface, but they share the same foundation. It’s the scalable technology that keeps processes connected and efficient.
Modern and emerging workflow automation technologies

Big data integration
Workflow engines now connect directly with large, real-time datasets to provide context at the right moment. Instead of manually pulling reports or switching between systems, workflows can auto-generate the information decision-makers need and surface it at the exact step where it matters.
For example, a capital expenditure approval process can pull financial data from your ERP, generate a budget impact report, and attach it to the approval request automatically. This gives approvers complete context without delays or back-and-forth emails.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI helps workflows make smarter decisions when simple rules aren’t enough. It can analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and route tasks based on context rather than fixed logic.
For instance, in lead management, AI scores incoming leads by analyzing historical conversion data, behavior signals, and engagement patterns. High-value leads get routed to senior sales reps immediately, while lower-priority ones follow a different nurture path. This means your team focuses on the right opportunities without manually sorting through every entry.
Machine learning (ML)
Machine learning improves workflows by learning from historical data and adjusting over time. It identifies patterns that humans might miss and uses them to make better predictions.
For example, a customer support team can use ML to predict ticket volume based on product release schedules, past support patterns, and seasonal trends. When the system forecasts a surge in incoming requests, it automatically triggers workflows to bring in additional staff or redistribute workloads across teams. The more data it processes, the more accurate the predictions become.
Natural language processing (NLP)
NLP extracts structured information from unstructured text like emails, chat messages, and support tickets. This allows workflows to act on information that would otherwise require manual reading and data entry.
For instance, when a customer emails about a delayed shipment, NLP can identify the order number, detect the issue type, and automatically create a support ticket with all of the relevant details filled in. The workflow then routes it to the logistics team without anyone manually reading and categorizing the email.
Computer vision
Computer vision allows workflows to process and act on visual information. Systems can analyze images or video feeds and trigger actions based on what they detect.
For instance, in manufacturing, cameras on the production line scan each finished product for defects. When the system spots a flaw, it flags the item, pauses that section of the line, and creates a quality control task for the supervisor. This catches problems immediately rather than after an entire batch has been produced.
Low-code and no-code platforms
Low-code and no-code platforms let business users build and modify workflows without writing extensive code. These tools use visual builders, drag-and-drop interfaces, and prebuilt logic blocks to make automation accessible to teams outside IT.
For example, with Zoho Creator, an operations manager can design an approval workflow using a visual workflow builder, set conditional rules based on department or budget thresholds, and connect it to existing systems through prebuilt integrations.
Changes can be tested and deployed within hours rather than weeks. This puts workflow control in the hands of people who know the process best, speeding up implementation and reducing dependency on development resources.
Robotic process automation (RPA)
RPA handles repetitive, rule-based tasks that involve copying data between systems. It mimics human actions like clicking buttons, filling forms, and moving information from one application to another.
For example, when a supplier sends an invoice by email, RPA can extract the invoice details, enter them into your accounting system, match them against purchase orders, and flag any discrepancies for review. This removes manual data entry from high-volume processes and reduces errors caused by typos or missed fields.
The evolution continues: Hyperautomation and intelligent orchestration
Hyperautomation connects entire business functions end-to-end, linking workflows with AI, RPA, and analytics to create seamless operations across departments. Instead of isolated automation, systems now work together to handle complex processes that span multiple teams and tools.
Intelligent orchestration takes this further by adding adaptive decision-making. Workflows don't just follow fixed rules anymore. They respond to real-time conditions, learn from outcomes, and adjust routing based on context. For instance, a workflow may reroute an approval based on current workload, flag exceptions that fall outside normal patterns, or suggest process improvements based on bottleneck analysis.
These evolving capabilities are shifting workflows from static systems that execute predefined steps to dynamic operations that adapt, learn, and optimize themselves.
Start building workflows that scale with Zoho Creator
Workflow technology has moved beyond automating simple tasks. Today, businesses need systems that can handle complex, multi-step processes while adapting to how different teams actually work. The challenge is finding a platform that offers both power and accessibility without forcing you to choose between flexibility and ease of use.
Zoho Creator is an AI-powered, low-code application development platform that helps you design and run workflows tailored to your operations. You can automate approvals, connect data across systems, and scale processes without heavy coding or managing multiple disconnected tools.
Here's how Zoho Creator helps you build workflows that scale:
AI-powered workflow automation: Use AI to suggest logic, predict outcomes, and automate decision-making within your workflows.
Custom data models: Structure your data the way your business works, then connect it to workflows that enforce consistency.
Mobile-ready workflows: Deploy workflows that work on web, iOS, and Android, so teams stay connected from anywhere.
Real-time analytics and dashboards: Track workflow performance, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven improvements.
Role-based access controls: Define who can view, edit, or approve at each workflow stage, ensuring security and compliance.
Scalable deployment options: Host workflows in the cloud, on-premise, or hybrid environments based on your requirements.
The fastest-growing companies are already using workflow automation to gain a competitive advantage. Every day without automation means more time spent on manual tasks and fewer resources for strategic work. Sign up for a 15-day free trial and see how Zoho Creator can enhance your business processes.
FAQ
What’s the difference between workflow automation and workflow technology?
Workflow automation focuses on removing manual steps in a process. Workflow technology refers to the full set of tools that let you design, run, and manage those automated workflows across systems.
How do I know if my business is ready for workflow automation?
If you’re repeating the same tasks, chasing approvals, or relying on spreadsheets to track progress, you’re ready. Even small teams benefit from automation when delays and errors start to affect execution.
Can non-developers build workflows using modern tools?
Yes. With low-code platforms like Zoho Creator, users with no coding background can use visual builders and prebuilt logic to design. In this way, anyone can quickly launch workflows.
What’s the first step in implementing workflow technology?
Start by mapping one core process that slows your team down. Break it into steps, define triggers and outcomes, and identify where delays happen. Then use a tool that supports both design and automation in one place.
 Ann Elizabeth Sam
Ann Elizabeth SamHey! I'm Ann, and I work as a content writer at Zoho Creator. I'm exploring the SaaS world through various forms of content creation. Outside of work, I love dancing and would give up anything to read a good murder mystery.