- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Low-code governance: Key components and best practices
Low-code governance: Key components and best practices
- Last Updated : February 2, 2026
- 221 Views
- 8 Min Read
Low-code platforms help businesses build applications faster and reduce IT dependency. The low-code approach means teams can create solutions quickly, solving problems without waiting months for development resources. But as more applications appear across departments, questions can emerge about security, compliance, and who's building what.
Highlights
- Low-code governance establishes policies and controls for managing platform usage, covering access permissions, security standards, and deployment processes across your organization.
- Role-based access control restricts platform capabilities based on user roles, preventing unauthorized changes while enabling appropriate teams to build solutions.
- Security controls and compliance checks ensure applications meet regulatory requirements like GDPR and HIPAA throughout the development lifecycle.
- Audit trails track all modifications, showing who changed what and when to maintain accountability and support compliance requirements.
- AI-powered governance automation handles real-time compliance monitoring, security testing, and risk assessment without manual oversight for every application change.
Without clear oversight, rapid application development creates risks. Security gaps emerge when applications handle sensitive data without proper controls, and compliance violations occur when apps don't follow regulatory requirements.
This blog post explains low-code governance fundamentals and practical implementation best practices. You'll learn how to maintain development speed while ensuring applications meet security standards, stay compliant, and align with business objectives.
What is low-code governance?
Low-code governance is the strategic framework of policies and tools used to manage how applications are created and deployed within an organization. It ensures that applications are secure, compliant, scalable, and well-managed throughout their lifecycle.
Rather than acting as a barrier, low-code governance provides guardrails that ensure every custom-built tool aligns with broader business objectives and IT security standards.
Why is low-code governance important?
Without proper governance, apps can be built outside the security team's view. Also, you might face fragmented development, with different departments building unnecessary tools, resulting in wasted resources. Here’s why low-code governance is essential:
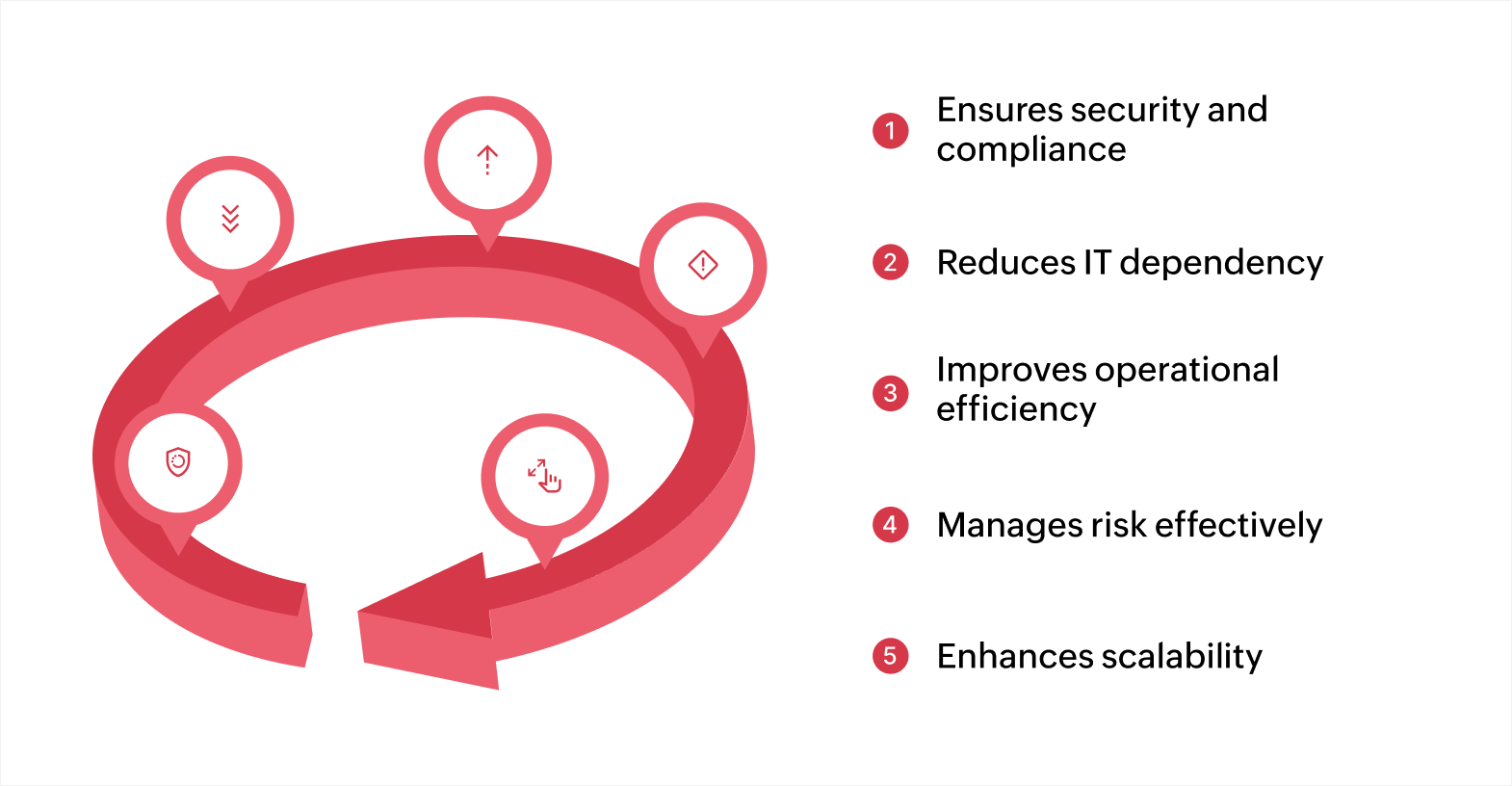
Ensures security and compliance
Low-code platforms often allow non-technical users to build applications, which may lead to security risks and compliance issues. Governance ensures that security protocols, such as role-based access control, encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA), are consistently applied throughout the development lifecycle.
It also ensures that applications meet regulatory requirements, such as GDPR or HIPAA, helping avoid legal complications.
Reduces IT dependency and promotes business agility
One of the main advantages of low-code platforms is reducing IT’s involvement in app development. However, without governance, this can lead to fragmented or inconsistent development.
Low-code governance provides a structure that empowers business users to create apps independently while still ensuring that IT standards are met. This balance increases efficiency and allows IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
Improves operational efficiency and collaboration
Low-code governance helps standardize development practices across teams, ensuring consistency in app quality. It also fosters collaboration between business users and IT departments by aligning both sides on key objectives and governance policies. This reduces siloed development, encouraging teams to work together more effectively toward business goals.
Manages risk effectively
Uncontrolled app creation may introduce significant risks, including security breaches, operational disruptions, and compliance failures. Governance helps mitigate these risks by enforcing security checks, conducting vulnerability assessments, and ensuring that disaster recovery plans are in place. With governance, potential risks are identified early, preventing major issues down the line.
Enhances scalability
As your organization grows, so does the need for scalable solutions. Low-code governance ensures that applications are designed with scalability in mind. Governance provides the structure needed to handle growing demands, ensuring that your apps remain efficient and adaptable to changing business requirements.
Implementing low-code governance, you create a balanced framework that enhances both the speed and security of app development. This approach not only reduces risks but also ensures that your low-code platform can scale effectively as your business evolves.
Key components of low-code governance
The global market for low-code development platforms reached $6.78 billion in 2022 and is expected to hit $35.22 billion by 2030, with a 22.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). This highlights the increasing adoption of low-code platforms.
As businesses make greater use of these platforms, strong governance becomes necessary to ensure that applications are developed, deployed, and maintained effectively. Below are the key components of low-code governance:
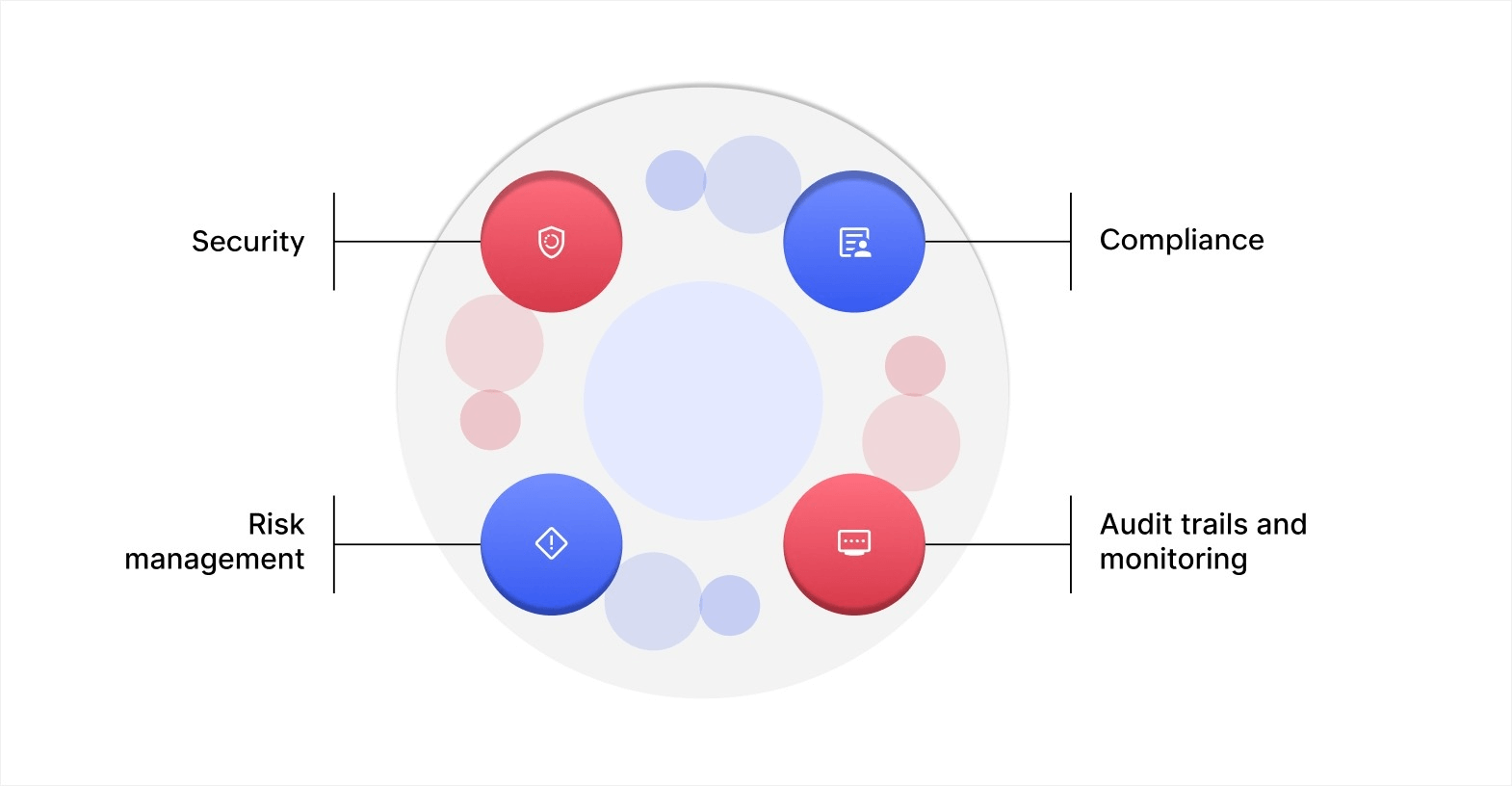
Security
Security is a key element of low-code governance, especially as applications are built by users without extensive technical knowledge.
- User access control: Role-based access management ensures that only authorized individuals can access certain features or data.
- Data protection: Encrypting data during transfer and while stored helps safeguard sensitive business information.
- Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) ensures only legitimate users can access applications and platform features.
These security measures must be integrated into every stage of the application lifecycle to minimize the risk of vulnerabilities.
Compliance
Compliance ensures that low-code applications adhere to necessary legal and regulatory standards, particularly when dealing with sensitive data.
- Regulatory adherence: Applications must meet the requirements of laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, which govern how data is collected, processed, and stored.
- Audit readiness: Low-code platforms should be able to generate reports and logs that demonstrate compliance whenever required.
By embedding compliance checks throughout the development process, businesses can avoid potential legal consequences.
Risk management
Risk management in low-code governance involves identifying and addressing potential challenges that could affect the application or business operations.
- Vulnerability assessments: Regular testing for security weaknesses helps identify and fix risks before they escalate into bigger issues.
- Operational continuity: Building applications with fail-safes and disaster recovery options ensures smooth business operations during unforeseen disruptions.
- Continuous monitoring: Ongoing tracking of performance and security activities helps spot potential risks and resolve them quickly.
A proactive approach to risk management helps ensure that low-code applications run securely and effectively.
Audit trails and monitoring
Audit trails and monitoring provide transparency and accountability, enabling businesses to track changes and detect irregularities in low-code applications.
- Change tracking: Keeping a detailed log of changes helps businesses maintain visibility into who made what changes and when.
- Real-time monitoring: Monitoring applications for security threats and performance issues allows businesses to address problems before they affect operations.
- Compliance audits: Audit trails simplify compliance audits by providing a clear record of all actions taken within the application.
These tools support transparency, compliance, and help in troubleshooting when issues arise.
As the low-code development platform market continues to expand, maintaining effective low-code governance is essential for securing applications, ensuring compliance, and minimizing risks.
Best practices for building a low-code governance framework
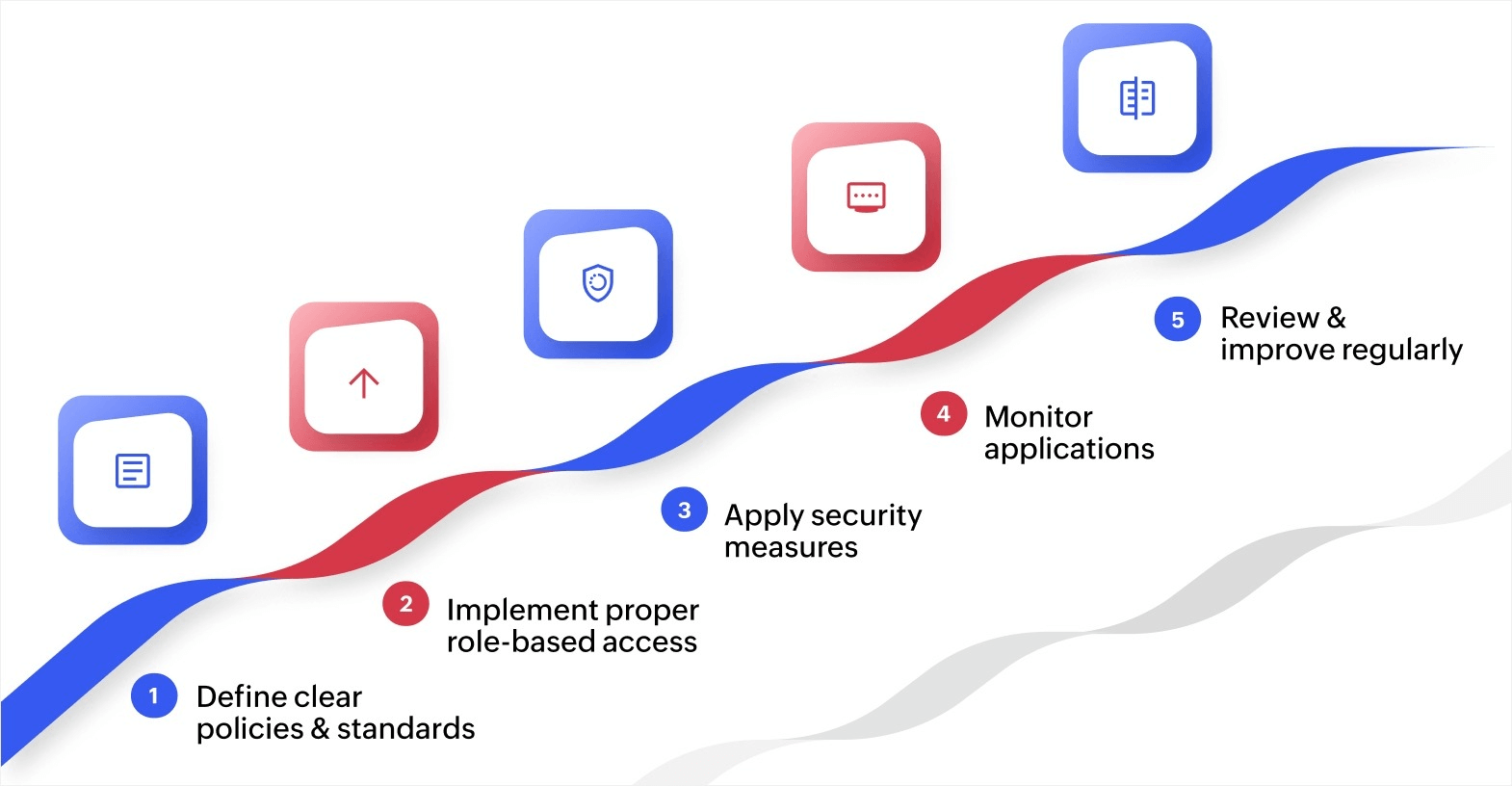
Creating effective governance requires clear policies and consistent processes. Here's how to build a framework supporting both speed and control:
1. Start with clear policies and standards
Define specific rules covering application development, data access, security requirements, and approval processes. Document what application types require IT review, which data sources business users can access, and what security measures apply to different categories. Clear policies give teams confidence to build solutions knowing exactly what standards apply to their work.
2. Implement proper role-based access
Assign platform permissions matching organizational roles and responsibilities. For instance, business analysts might create forms and reports, but not access production databases directly. Developers get broader technical capabilities while maintaining appropriate restrictions. Review access levels regularly as team members change roles or join new projects.
3. Apply security measures and maintain compliance
Protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements throughout the application lifecycle. Implement encryption for data during transfer and storage, use secure API integrations protecting data exchanges, and conduct security reviews identifying vulnerabilities before deployment. Regular compliance audits verify applications continue meeting legal and regulatory standards as requirements change.
4. Monitor applications and track changes
Track applications continuously to identify performance issues, security concerns, or usage patterns indicating problems. Real-time monitoring catches issues like unexpected data access, performance drops, or integration failures before they significantly affect operations. Maintain detailed audit trails showing who modified applications, what changes occurred, and when modifications happened.
5. Review and improve regularly
Schedule periodic reviews of your governance framework, examining what works well and what needs adjustment. Gather feedback from IT teams and business users building applications. Update policies as your organization grows, new regulations emerge, or technology capabilities change. Continuous improvement keeps governance effective without creating unnecessary obstacles.
Regular monitoring ensures that your low-code environment remains secure and compliant as it grows. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your low-code governance framework remains strong, enabling both innovation and security.
Key trends shaping low-code governance
Governance approaches continue advancing as technology capabilities improve and organizations gain experience managing platforms at scale. Several trends are reshaping how companies implement governance:
AI-powered governance automation
Artificial intelligence now handles many governance tasks previously requiring manual review. AI systems analyze applications automatically, checking for security issues, compliance violations, and quality problems.
Machine learning models improve over time, learning from past issues to identify similar problems in new applications. For instance, AI can detect when applications access data inappropriately or violate established architectural patterns, flagging issues before deployment.
Real-time compliance monitoring
Modern platforms provide continuous compliance checking instead of periodic audits. Systems monitor applications constantly, verifying they meet current regulatory requirements and alerting teams immediately when changes create compliance risks.
This shift from periodic checking to continuous monitoring helps organizations maintain compliance more reliably while reducing audit preparation time.
Integrated security testing
Security testing happens automatically throughout development rather than as separate steps before deployment.
Platforms scan code continuously, check dependencies for known vulnerabilities, and validate security configurations as developers build applications. This integration catches security issues early when they're easier and less expensive to fix.
Predictive risk management
Analytics systems analyze application portfolios to predict where problems might occur. By examining patterns across many applications, these systems identify high-risk areas requiring attention before issues affect operations.
For example, predictive analytics might flag applications likely facing performance problems under increased load, letting teams address capacity issues proactively.
As the low-code market continues to grow, governance models will become more advanced. Automation will play a larger role in enforcing governance rules in real time, and AI will provide predictive insights to address potential security and performance issues before they arise.
By adopting strong low-code governance frameworks, businesses can manage risks and ensure long-term success while still enabling fast application development.
Implementing secure low-code governance in your organization
Generic software forces your processes to match its limitations. When you need custom approval workflows, specific security controls, or integration with specialized systems, standard packages require workarounds and compromises.
Zoho Creator is an AI-powered low-code application development platform that lets you build governed applications matching your exact requirements. You can design custom forms, automated workflows, and integrated solutions with built-in security and compliance features.
- The platform's user management capabilities include role-based access controls, determining who can build applications and access specific data.
- Application security features protect sensitive data with encryption, authentication controls, and automated security monitoring throughout the lifecycle.
- Integration flows connect applications to existing systems without compromising security boundaries.
- Multi-environment deployment options separate development, testing, and production, so applications move through proper validation.
- Monitoring tools track application performance and usage patterns, identifying issues before they affect operations.
Building on a platform with integrated governance gives you control without sacrificing development speed. Sign up for free today to see how built-in governance features support secure application development.
FAQ
How does low-code governance improve collaboration between business users and IT teams?
Low-code governance sets clear roles and approval processes, promoting collaboration and ensuring applications align with business goals and security standards.
What risks arise from not implementing low-code governance?
Without governance, businesses face security breaches, compliance issues, and inconsistent app quality, leading to potential legal and operational problems.
How does low-code governance help scale applications?
Governance provides guidelines for app design, performance monitoring, and infrastructure, ensuring applications scale smoothly as the business grows.
Can low-code governance be automated?
Yes, automation can simplify approval workflows, access control, and compliance checks, making governance more efficient and reducing manual errors.
 Rohith Krishnan S
Rohith Krishnan SRohith is a product marketer at Zoho. He writes about low-code, workflow automation and follows the latest digital transformation trends. Outside work he enjoys spending time with family, watching football matches and reading about futuristic trends, in no specific order.