- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Understanding process flows: A comprehensive guide
Understanding process flows: A comprehensive guide
- Last Updated : December 1, 2025
- 568 Views
- 7 Min Read
Feeling stuck in a tangle of tasks that never seem to flow right? Many teams face the same challenge. Inefficient workflows, repetitive tasks, and unclear responsibilities can slow progress and frustrate everyone involved. If projects constantly hit roadblocks, or if your team spends more time fixing mistakes than moving forward, chances are your process flows need attention.
Highlights
Process flows are a series of steps that define how tasks are completed, helping businesses improve efficiency and reduce errors.
Types of process flows include linear, branching, and parallelflows, each serving different needs based on task complexity.
Mapping process flows using tools like BPMN, UML, and flowcharts helps visualize tasks and identify inefficiencies.
Automating and optimizing processes using RPA and BPM systems can improve performance, reduce manual tasks, and ensure smooth operation.
The truth is, most workflow problems aren’t caused by people. They’re caused by processes that no longer serve your team well.
That's where understanding and visualizing your process flows can make all the difference. When you map out how work gets done, it becomes easier to identify delays, eliminate waste, and streamline the process of tasks from start to finish.
This guide breaks down process flows in detail, including visualization tools and automation strategies.
What are process flows?
A process flow is a series of steps that a system follows to complete a specific task or reach a desired outcome. These steps are often shown through diagrams or flowcharts, allowing engineers and developers to visualize, understand, and improve operations.
In technology, process flows help clarify how systems function, allowing for smoother operations and more efficient task completion. By defining each task and its sequence, process flows reduce the risk of errors and help teams stay organized.
Types of process flows in technology
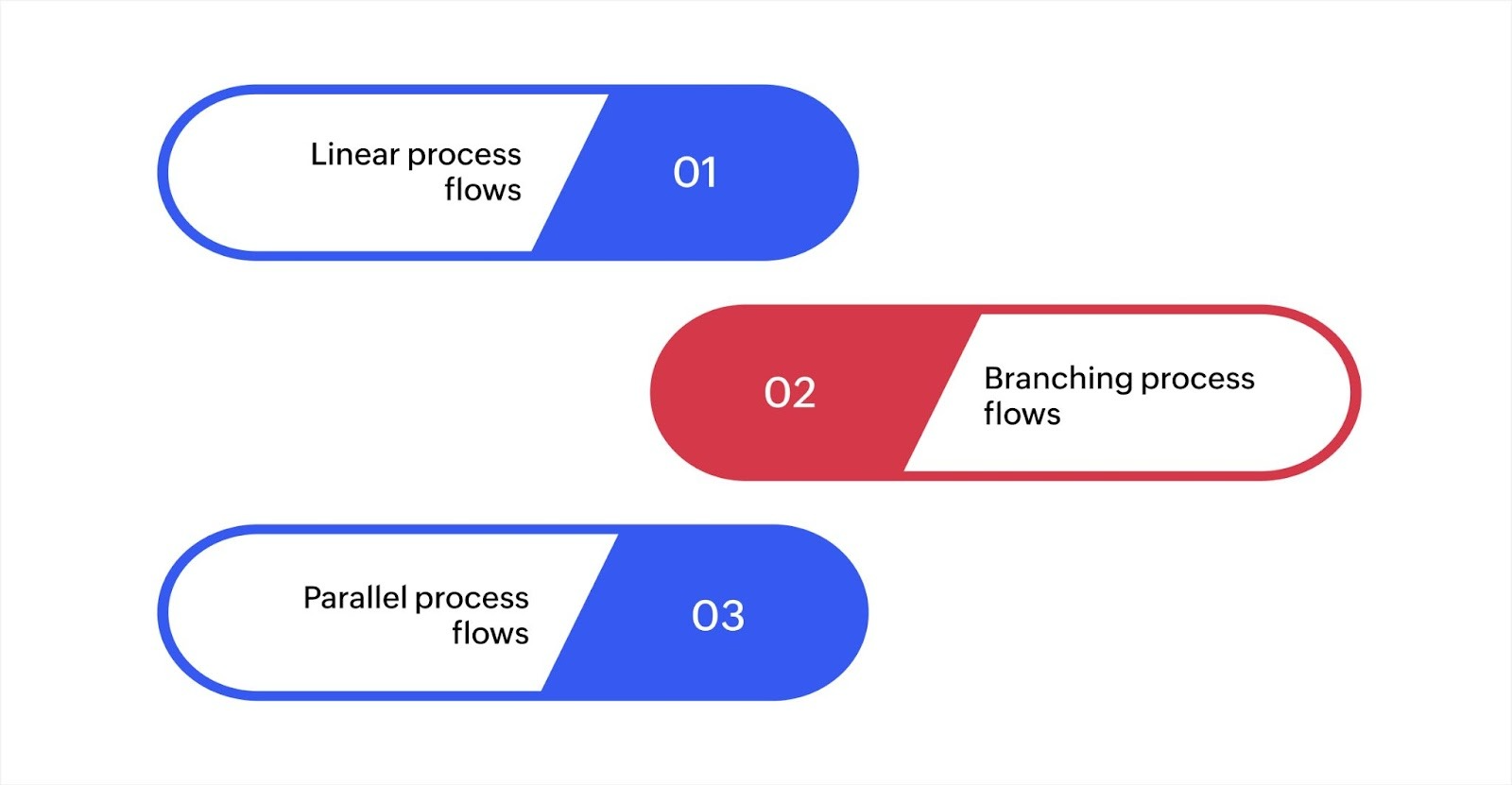
Process flows come in different types, each serving a particular purpose based on the task's complexity and requirements. Understanding which type to use can help optimize workflows and improve system efficiency.
1. Linear process flows
Linear process flows are simple and follow a straight, sequential order. These flows are used when each step needs to be completed in a specific order, without deviations. Linear flows are often applied to repetitive tasks or basic operations, such as automation scripts or batch processes.
For example, a data processing task where data is extracted, processed, and then loaded follows a clear, linear flow.
Best for: Simple tasks with a fixed sequence.
Example: Automated tasks like sending emails or data imports.
Linear flows are easy to set up and work well for tasks that require little to no decision-making. They ensure that each action happens in the right order, which is especially helpful for tasks that need to be performed in a predictable and repeatable manner.
2. Branching process flows
Branching process flows are used when decisions need to be made at certain points during a task. These flows split into different paths based on specific conditions or inputs, allowing flexibility within the process.
In software development, branching is commonly implemented with if-else statements, where the workflow changes based on the conditions provided.
For example, a customer support process might branch based on the issue type, like billing vs. technical support, leading to different teams or actions.
Best for: Tasks requiring decisions based on input or conditions.
Example: Customer service workflows where different types of issues are handled by different departments.
Branching process flows add adaptability to systems by allowing different paths depending on specific variables. They are effective when a task involves several possible outcomes, making them ideal for workflows with dynamic inputs or multiple scenarios.
3. Parallel process flows
Parallel process flows allow multiple tasks to be executed at the same time. These flows are particularly useful for systems that need to perform several tasks simultaneously, such as in cloud computing or when managing distributed systems.
In a parallel flow, tasks are divided into smaller, independent processes that can be handled concurrently.
For example, in large-scale data processing, different parts of the data can be processed in parallel to speed up the overall workflow.
Best for: Tasks that can be run at the same time.
Example: Systems like data processing frameworks, where data is split across multiple processors.
Parallel process flows help improve system performance by enabling simultaneous task execution, which reduces the time required to complete processes and makes better use of available resources.
Visualizing and optimizing process flows for better efficiency
The process optimization market is rapidly growing, projected to reach USD 113.1 billion by 2034. This highlights the increasing importance of automating workflows and enhancing efficiency across industries. Understanding your process flows and making improvements can dramatically boost your team's productivity, reduce errors, and streamline operations.
The journey to process flow optimization begins with visualization, which allows you to identify inefficiencies in your workflows. Once visualized, the next step is optimization, where you address redundant tasks. Finally, automation helps eliminate manual processes and enhances consistency, ensuring smoother and more efficient operations. Below, we break down the key stages in the process flow optimization journey.
Visualizing process flows
The first step to improving your workflows is visualizing the process flows. Mapping the steps, tasks, and decisions that occur within your system can help you spot areas where delays or inefficiencies may arise.
Key tools for visualization include:
BPMN (business process model and notation): A standardized method for representing business processes using specific symbols for tasks, decision points, and interactions between systems. It provides clarity and ensures consistency across teams.
UML (unified modeling language): It is used in software development to map out how different parts of a system connect and work together.
Flowcharts: A simple and widely used tool to map out processes. Flowcharts allow you to easily visualize the sequence of steps and identify where tasks begin, progress, and end.
Visualizing process flows provides a clear understanding of how tasks move through the system, enabling you to pinpoint where improvements are needed and which processes need more attention.
Optimizing process flows
Once you've visualized your process flows, the next step is to identify inefficiencies and optimize them. Inefficiencies often occur due to redundant tasks, manual handoffs, or outdated systems. By addressing these issues, you can enhance your workflows and make your operations more efficient.
Common inefficiencies to look for:
Redundant tasks: Repetitive tasks that don't add value to the process. Identifying these helps in eliminating unnecessary steps.
Manual data entry: Tasks that require human input for data processing. Automation of these tasks can save time and reduce errors.
System integration issues: If your systems aren't integrated properly, manual data transfers and delays can occur. Integration helps streamline data flow and ensures consistency across the system.
Optimizing your process flows involves addressing these inefficiencies. By removing bottlenecks and automating repetitive tasks, you can significantly improve workflow speed and reduce operational costs.
Automating process flows
The final stage in process flow optimization is automation. By automating certain tasks, you can eliminate manual processes, increase consistency, and free up your team’s time for higher-value work. Automation not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error.
Key tools for automation include:
RPA (robotic process automation): RPA is designed to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, such as data entry, transaction processing, or report generation. It significantly reduces human error and saves time on low-value tasks.
BPM systems: Business process management (BPM) systems help monitor, manage, and optimize business processes. These systems provide real-time insights into workflows, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and consistently.
Together, RPA and BPM systems allow businesses to automate workflows, improve data consistency, and minimize manual interventions. This not only boosts operational efficiency but also ensures smoother and more reliable processes.
Visualising, optimizing, and automating process flows are key to improving efficiency and consistency. To ensure lasting improvements, continuous optimization and monitoring are essential. Next, let's explore the best practices that will help maintain smooth operations and enhance workflow performance.
Best practices for improving process performance and data consistency
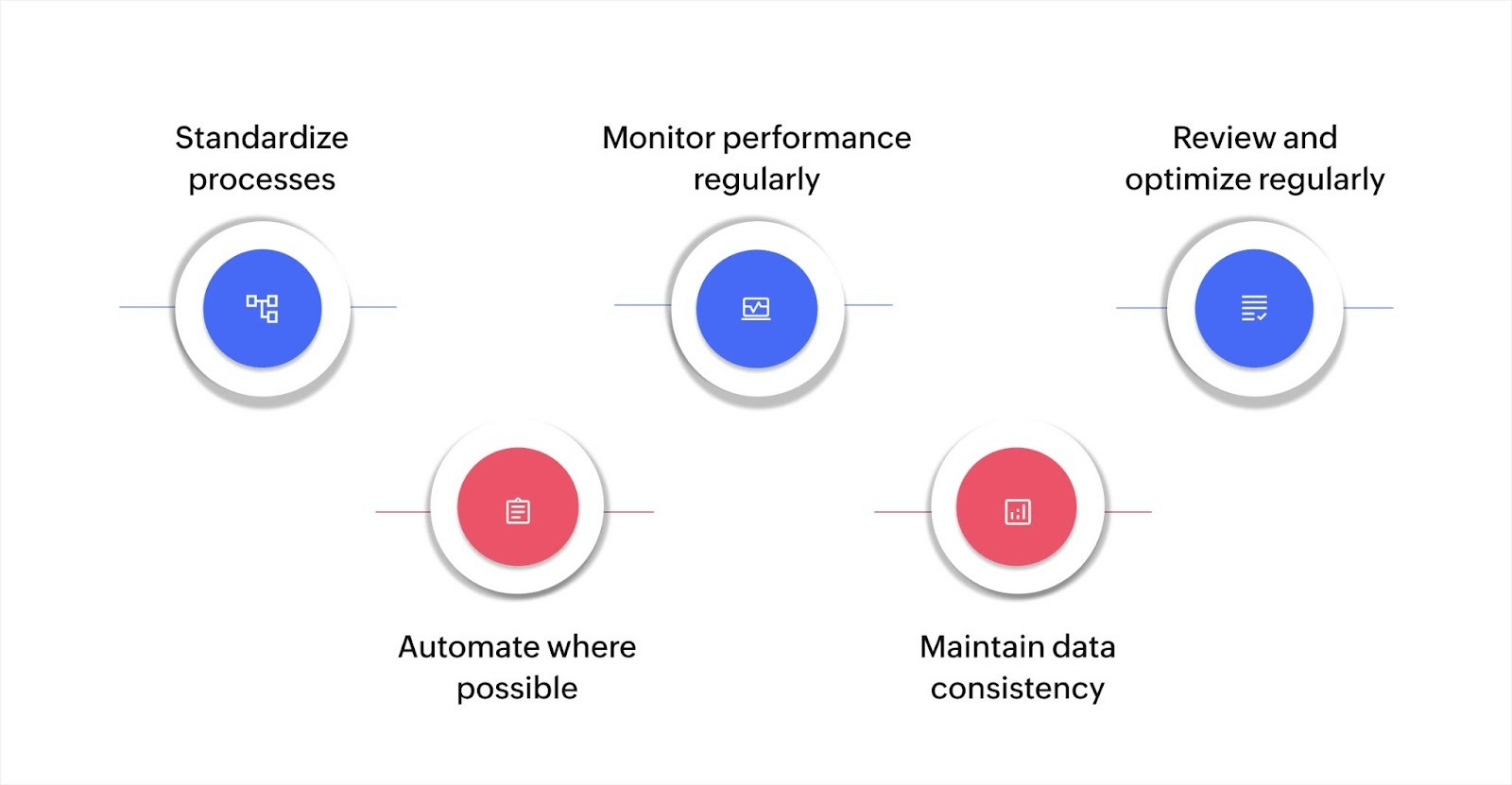
Improving process performance and ensuring data consistency are key to optimizing workflows. These practices reduce inefficiencies, errors, and delays, making operations smoother and more reliable.
Standardize processes
Standardizing workflows ensures consistency and reduces errors. When processes are uniform, it’s easier to troubleshoot issues and maintain efficiency. Clear naming conventions and data formats help with system integration.
Automate where possible
Automation with RPA and BPM reduces manual work and errors. RPA handles repetitive tasks, while BPM systems ensure tasks are completed in the correct order, improving task execution speed and accuracy.
Monitor performance regularly
Monitoring key performance metrics helps identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Tracking completion times and task efficiency allows for proactive adjustments, ensuring optimal workflow performance.
Maintain data consistency
Data consistency across systems is crucial for smooth operations. Integrate systems to prevent discrepancies and automate data validation to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Review and optimize regularly
Regularly reviewing and optimizing processes helps keep them aligned with business needs and industry changes. Continuous improvements prevent stagnation and help adapt to evolving challenges.
By standardizing, automating, monitoring, ensuring data consistency, and reviewing regularly, you can enhance process performance, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. These best practices help maintain smooth and scalable operations.
Optimize your process flows with workflow automation
Understanding and optimizing process flows is crucial for improving efficiency, reducing errors, and ensuring smoother operations. By mapping and automating workflows with tools like BPMN, UML, and flowcharts, you can identify inefficiencies and improve your processes.
Zoho Creator offers an effective solution to help businesses design, automate, and optimize their process flows. With Zoho Creator, you can build custom applications with minimal coding, enabling your team to automate tasks, track progress, and manage data all in one place. The platform provides a simple interface to create and customize workflows based on your specific needs.
To begin, you can easily create a flow solution from your Zoho Creator. This allows you to automate tasks, monitor process flows, and integrate various systems to improve the overall efficiency of your operations.
Start optimizing your process flows with Zoho Creator today and take control of your business processes.
FAQ
How do I start mapping process flows in my business?
To start mapping process flows, identify the key tasks and decisions in your operations, and choose the right tools (like BPMN, UML, or flowcharts) to visualize the steps in a clear, sequential manner.
What role do process flows play in digital transformation?
Process flows are crucial in digital transformation because they help businesses standardize tasks, automate workflows, and reduce manual errors, enabling smoother transitions to digital systems.
Can process flows be integrated with existing software tools?
Yes, process flows can be integrated with various business software tools, like CRM or ERP systems, to ensure data consistency and workflow automation, streamlining business operations.
How can I track and measure the effectiveness of process flow improvements?
You can track and measure effectiveness by using performance metrics such as task completion time, error rates, and system response times, while regularly reviewing and adjusting process flows as needed.
 Ann Elizabeth Sam
Ann Elizabeth SamHey! I'm Ann, and I work as a content writer at Zoho Creator. I'm exploring the SaaS world through various forms of content creation. Outside of work, I love dancing and would give up anything to read a good murder mystery.