- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Digital transformation maturity model: 5 essential stages
Digital transformation maturity model: 5 essential stages
- Last Updated : November 17, 2025
- 480 Views
- 13 Min Read
You've invested in new tools, launched digital initiatives, and encouraged teams to use the latest technology. But how do you know if these efforts are actually moving you forward? Recent studies indicate 90% of companies around the world are going through digital transformation efforts right now. This shows that an increasing number of companies are making moves to become more digital every day.
Highlights:
- Structured assessment framework: Digital transformation maturity models provide a systematic way to evaluate your organization's digital capabilities across technology, processes, culture, and strategy.
- Five progression stages: Most organizations move through stages like Initial, Emerging, Defined, Managed, and Optimized, each of which represents deeper digital integration.
- Multiple dimensions evaluated: Maturity models assess strategy alignment, cultural readiness, technology infrastructure, process automation, data capabilities, and customer engagement.
- Effective roadmap creation: Assessment results help build data-driven plans with clear goals, timelines, and priorities for digital advancement.
- Continuous improvement focus: Digital maturity is not a one-time achievement, but rather an ongoing journey that requires periodic reassessment and adaptation.
But even though many organizations have the technology, they lack a clear view of their digital capabilities. That's why they need a digital transformation maturity model, which provides a structured way to assess where they stand, identify gaps, and create a roadmap to reach higher levels of digital maturity.
Let's explore in detail what digital transformation maturity models are, the stages organizations typically progress through, how to assess your current maturity level, and some tips to advance your digital capabilities.
What is a digital transformation maturity model?
A digital transformation maturity model is a framework that helps you assess how advanced your organization is in using and integrating digital technologies. Most maturity models break digital evolution into distinct stages.
Organizations typically start with few digital processes and limited strategies—and then progress through stages in which digital initiatives become more defined, standardized, and ultimately embedded into the company culture.
Each stage represents a higher level of digital integration and sophistication. For example, a company in the early stages might use spreadsheets and email for most workflows, with disconnected systems across departments, while a digitally mature company has integrated platforms, automated workflows, data-driven decision making, and digital innovation baked into daily operations.
Why do you need a digital transformation maturity model?
Studies indicate that 87% of top-level business leaders consider digital transformation an important focus area for their organization. With so many leaders focused on digital change, it's clear why having a digital transformation strategy in place is crucial.
However, before you invest more time and money in digital initiatives, you need to know if you're moving in the right direction; you need a way to track if your efforts are actually working. A maturity model gives you that clarity.
Here's what a structured assessment framework provides:
Clear baseline measurement: You get an honest view of your current digital capabilities rather than relying on assumptions or fragmented observations from different teams.
Gap identification: The model highlights specific areas where you lag behind, whether it's outdated technology, manual processes, poor data management, or resistance to change.
Prioritization guidance: Not everything can be fixed at once. Maturity models help you identify which improvements will have the biggest impact and should be tackled first.
Stakeholder alignment: When you can show the leadership team exactly where the organization stands and what the path forward looks like, it becomes easier to secure buy-in and budget for digital projects.
Competitive benchmarking: Many frameworks include industry comparisons that show you how your digital maturity stacks up against peers and competitors.
Progress tracking: Periodic reassessments show whether your digital investments are working. You can measure improvement over time and adjust strategies based on what's actually moving the needle.
Risk reduction: By identifying weak spots early, you avoid costly mistakes like investing heavily in technology your culture is not ready to adopt or building on infrastructure that cannot scale.
Organizations use a maturity model approach to digital transformation strategically, rather than reactively. They stop throwing technology at problems and start building capabilities in a structured, measurable way.
What are the stages of digital transformation maturity?
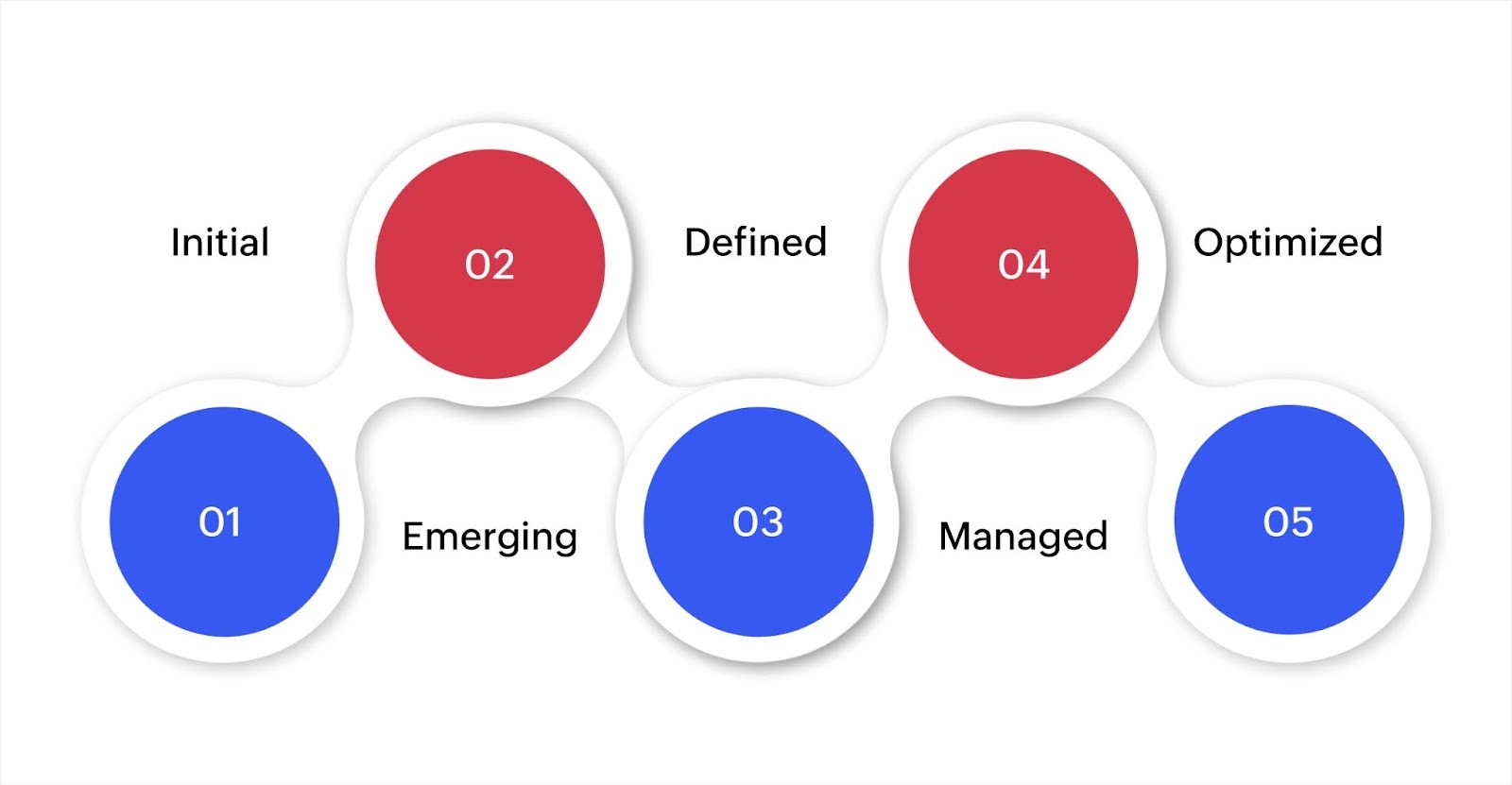
Digital transformation maturity models typically have five key stages through which organizations progress through as they deepen their digital integrations and capabilities. Here's how these maturity stages compare:
| Stage | Digital strategy | Technology use | Process maturity | Data capabilities | Cultural readiness |
| Initial | No formal strategy | Disconnected tools | Manual, ad hoc | Data silos | Low awareness |
| Emerging | Strategy being developed | Some digital adoption | Inconsistent implementation | Basic analytics | Growing interest |
| Defined | Documented strategy | Standardized systems | Consistent processes | Organized data management | Active engagement |
| Managed | Aligned with business goals | Integrated platforms | Automated workflows | Data-driven decisions | High collaboration |
| Optimized | Innovation-focused | Advanced tech stack | Continuous improvement | Predictive analytics | Digital-first culture |
Let's break down what each stage looks like in practice.
Stage 1: Initial
At this level, digital transformation is barely underway. Your organization has a few digital processes and no real strategy guiding technology adoption. Different departments use their own tools, without integrations. Data sits in isolated spreadsheets and systems that don't talk to each other.
For instance, your sales team might use a CRM while your operations team tracks orders in Excel—and your customer service team has its own ticketing system that doesn't connect to either. When someone needs a complete view of customer interactions, they have to pull data from multiple sources manually.
Decision-making relies heavily on intuition or limited data. There's little automation. Most workflows require manual steps and approvals. The culture shows resistance to change and minimal awareness of digital possibilities.
Stage 2: Emerging
You're starting to see the value of digital transformation and to develop a strategy. Leadership is discussing digital initiatives, and some departments are piloting new technologies. However, implementation remains inconsistent across the organization.
For example, you may have launched a project management tool for the IT team and a customer portal for support, but these efforts are not coordinated. Some teams embrace new tools while others stick to old methods. There's no unified approach to measuring success or scaling what works.
Data management improves slightly. You have basic analytics and reporting, but insights are still fragmented. The culture is warming up to digital change, though adoption varies widely by department and individual.
Stage 3: Defined
Now you have a documented digital transformation strategy that the entire organization knows about. Digital initiatives are no longer scattered experiments but planned projects with clear objectives. Processes are standardized and consistently implemented across departments.
For instance, you've established standard workflows for key business processes like order fulfillment, customer onboarding, or inventory management. Everyone follows the same procedures using the same integrated systems. Data is organized with proper governance, and you have reliable dashboards that leaders check regularly.
The culture actively supports digital initiatives. Employees receive training on new tools and processes. There's collaboration between IT and business units to identify improvement opportunities.
Stage 4: Managed
Digital transformation is deeply embedded in operations. Your processes are highly automated, which reduces manual work and errors. Technology platforms are fully integrated, giving you a unified view of business operations. Data-driven decision-making is standard practice.
For example, when a customer places an order, it automatically triggers a series of actions across systems: inventory updates, shipping arrangements, invoice generation, and customer notifications—all without manual intervention. Leaders have real-time dashboards showing key metrics and can quickly respond to issues or opportunities.
The culture shows high engagement with digital tools. Teams proactively suggest improvements. There's strong collaboration between departments using shared platforms and data. Digital capabilities are measured and optimized regularly.
Stage 5: Optimized
At the highest maturity level, digital transformation is part of your company's DNA. Innovation happens continuously. You use advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics to stay ahead of market changes and customer needs.
For instance, you might use AI to predict customer churn and automatically trigger retention campaigns, or rely on machine learning to optimize supply chain operations based on demand forecasts. Your systems adapt and improve themselves based on data patterns.
The culture is fully digital-first. Employees at all levels think about how technology can improve their work. The organization quickly adopts new tools and methods. Continuous improvement is not a project but a mindset embedded in daily operations.
Not every organization needs to reach the Optimized stage immediately. The goal is steady progress through stages that make sense for your business model and industry. What matters is having a clear understanding of where you are and a plan to advance effectively.
How do you assess your digital transformation maturity?
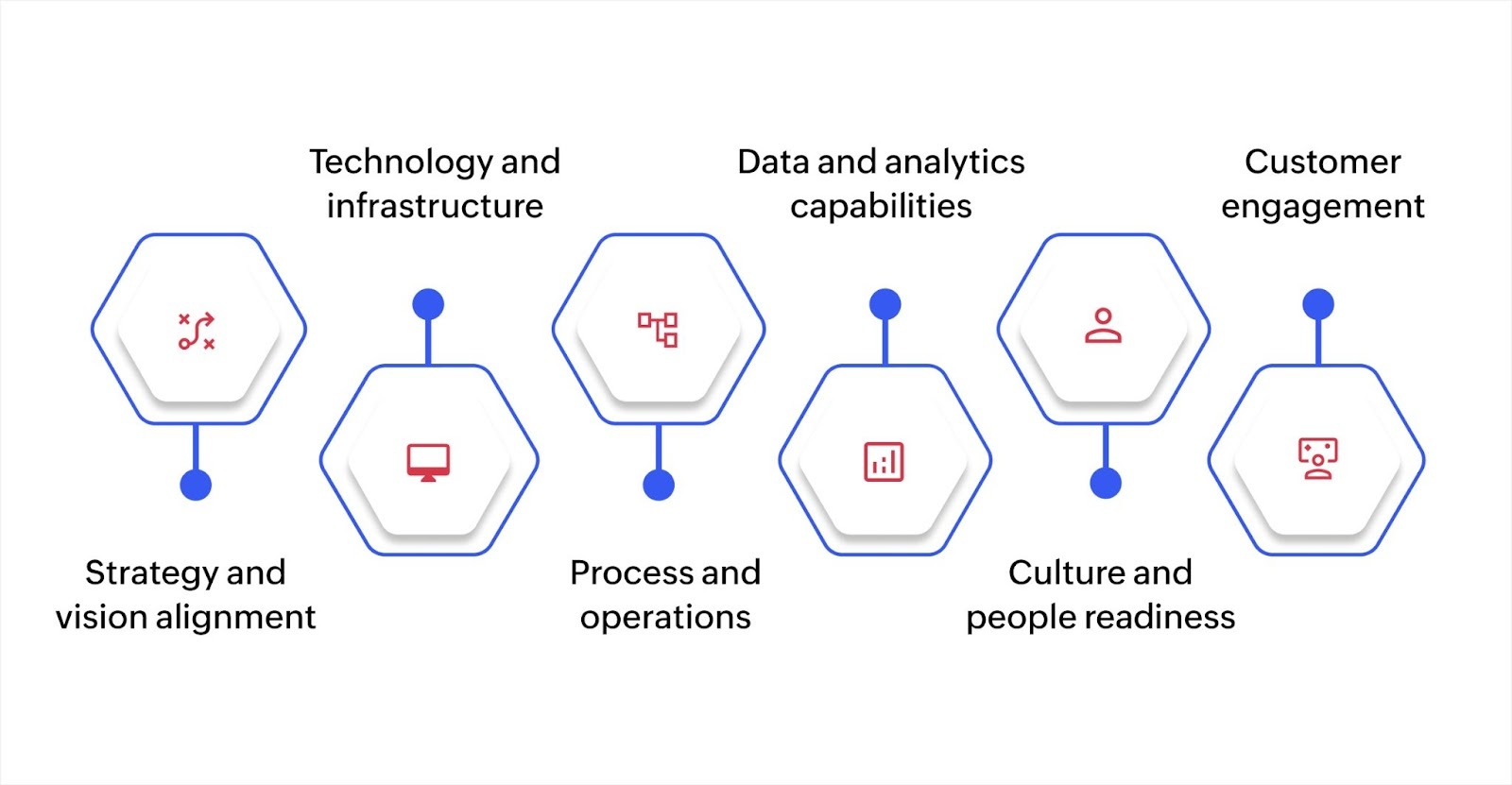
Assessment is the foundation of improvement; you can't build a meaningful digital transformation roadmap without knowing your starting point. Here's how to evaluate your current maturity level across key dimensions.
Strategy and vision alignment
Do you have a documented digital strategy that leadership and employees understand? A written strategy ensures everyone knows the organization's direction. Without documentation, teams work on conflicting priorities and waste resources on initiatives that don't align.
Are digital initiatives directly tied to business objectives like revenue growth, cost reduction, or customer satisfaction? Digital projects should solve real business problems, and not simply involve adopting technology for its own sake. Clear connections to goals help you measure return on investment.
Is there a dedicated budget and are there resources allocated to digital transformation? Organizations that are serious about digital maturity fund it properly. Ad hoc spending or borrowing from other budgets signals that digital transformation is not truly a priority.
Who owns the digital transformation, and do they have executive support? Someone needs clear accountability for driving digital change. Without a dedicated owner backed by leadership, initiatives often face resistance or competing demands and get stalled.
For example, if your company wants to expand into new markets but your digital strategy focuses only on internal efficiency, that misalignment will limit transformation success.
Technology and infrastructure
Evaluate the sophistication of your technology stack and how well systems work together. Consider:
Are your core business applications modern or legacy systems? Older systems often lack flexibility and integration capabilities. Modern applications support rapid changes and connect easily with other tools your business needs.
How integrated are your various software platforms? Data should flow automatically between systems without manual export and import. Poor integration creates data silos and forces employees to duplicate work across multiple tools.
Can data flow seamlessly between systems? When customer information in your CRM updates, does it automatically reflect in your billing, support, and analytics systems? Seamless data flow eliminates errors and saves time.
Do you have cloud infrastructure or are you still primarily on-premise? Cloud platforms offer scalability and accessibility that on-premise systems can't match. They also reduce maintenance overhead and enable remote work more effectively.
How quickly can you deploy new applications or features? Speed of deployment indicates technological agility. Organizations stuck in long development cycles can't respond quickly to market opportunities or customer needs.
For instance, if launching a new customer-facing application requires six months of custom development and infrastructure setup, your technology maturity is lower than an organization that can build and deploy apps in weeks using low-code platforms.
Process and operations
Look at how automated and standardized your business processes are across departments. Review these areas:
What percentage of key workflows are automated versus manual? Manual processes are slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Higher rates of automation indicate more mature operations that can handle growth without proportional staff increases.
Are processes documented and consistently followed? Undocumented processes exist only in people's heads, which creates risks when employees leave. Documented processes ensure consistency and make it easier to identify improvement opportunities.
How long do approval cycles take? Lengthy approval processes slow decision-making and frustrate employees. Quick approvals—enabled by clear rules and automated routing—indicate operational maturity.
Can you easily modify processes when business needs change? Rigid processes that require months to change can't keep up with market demands. Flexible processes that adapt quickly show higher maturity and business agility.
Do you have clear process ownership and governance? Every important process needs an owner responsible for its performance and improvement. Without ownership, processes degrade over time and nobody takes action to fix problems.
For example, if every invoice still requires manual review and approval from multiple people—thereby causing payment delays—your process maturity needs improvement compared to organizations with automated approval workflows based on predefined rules.
Data and analytics capabilities
Assess how well you collect, organize, and use data for decision making. Ask yourself:
Is your data centralized or scattered across disconnected systems? Scattered data makes it nearly impossible to get a complete picture of your business. Centralized data enables better analysis and faster decisions based on complete information.
Do you have a data governance framework? Governance defines who can access what data, how data quality is maintained, and what standards apply. Without it, data becomes unreliable and teams lose trust in reports and analytics.
How accessible is data to people who need it? Employees should be able to access relevant data without submitting IT tickets or waiting days for reports. Self-service access speeds up decision-making at every level.
What analytics capabilities do you have beyond basic reporting? Basic reports show what happened. Advanced analytics reveal why it happened and what might happen next. Predictive and prescriptive analytics indicate higher data maturity.
Are decisions made based on data insights or gut feeling? Data-driven cultures systematically use information to guide choices. Organizations that rely on intuition miss opportunities and make avoidable mistakes that data would prevent.
For instance, if your sales team can't easily access customer purchase histories when making recommendations, or if leadership relies on month-old reports instead of real-time dashboards, your data maturity lags.
Culture and people readiness
Evaluate how prepared your organization's culture and workforce are to embrace digital change. Consider:
- How do employees react to new technology implementations? Positive reactions and quick adoption show cultural readiness. Resistance and slow uptake indicate you need to work on change management and communication before adding more technology.
- Is there active resistance or enthusiastic adoption? Enthusiasm means people see value in digital tools and trust that changes will improve their work. Resistance suggests past implementations failed or people feel left out of decisions.
- Do you have digital skills gaps? Even the best technology fails if people lack the skills to use it effectively. Regular skills assessments and training programs show commitment to building digital capabilities across the workforce.
- Is there collaboration between IT and business units? Digital transformation requires IT and business teams working together, not IT dictating solutions or business units working around IT. Strong collaboration produces better outcomes faster.
- Do leaders champion digital initiatives? Leaders who actively promote and participate in digital change set the tone for the entire organization. Without visible leadership support, employees treat digital transformation as optional.
- Is innovation encouraged and rewarded? Organizations that reward people for trying new approaches and learning from failures build cultures that continuously improve. Punishing mistakes creates risk-averse cultures that resist change.
For example, if every new system rollout faces pushback and low adoption rates because people prefer familiar tools, cultural readiness is a bigger barrier than technology itself.
Customer engagement
Review how digitally enabled your customer interactions and experiences are. Look at:
How many customer touchpoints are digital versus offline? More digital touchpoints provide convenience and generate valuable data about customer behavior. They also reduce costs compared to phone or in-person interactions.
Can customers easily interact with you through their preferred channels? Some customers prefer chat; others prefer email; and still others prefer phone. Mature organizations let customers choose their channels while maintaining consistent service quality across all options.
Do you have a unified view of customer interactions across channels? When a customer contacts you, can support see their recent purchases, previous inquiries, and website activities? Unified views prevent customers from repeating information and enable personalized service.
How personalized are customer experiences? Generic, one-size-fits-all experiences feel impersonal and miss opportunities. Personalization based on customer data shows maturity in using digital capabilities to improve relationships.
Do you proactively reach customers or only react to their inquiries? Reactive organizations wait for customers to report problems. Proactive organizations use data to anticipate needs, prevent issues, and offer relevant suggestions before customers ask.
For instance, if customers have to call or email for basic requests that could be handled through self-service portals, or if your website, app, and support team have different information about the same customer, your customer engagement maturity needs work.
Once you assess these dimensions, you'll see patterns that place you in a particular maturity stage. Some areas might be more advanced than others. That's normal. The goal is to identify where to focus improvement efforts for the biggest impact on overall digital maturity.
Build applications that accelerate digital maturity with Zoho Creator
Moving through the stages of digital transformation maturity requires the right tools. But traditional development approaches are too slow and expensive; you need a faster way to build the custom applications that drive digital operations forward.
Zoho Creator s an AI-powered low-code application development platform that helps organizations rapidly advance their digital capabilities without extensive coding. Whether yours is in the Initial stage, trying to reach Emerging or Defined, or pushing toward Managed, Zoho Creator accelerates progress at every level.
Here's how Zoho Creator helps you build digital maturity:
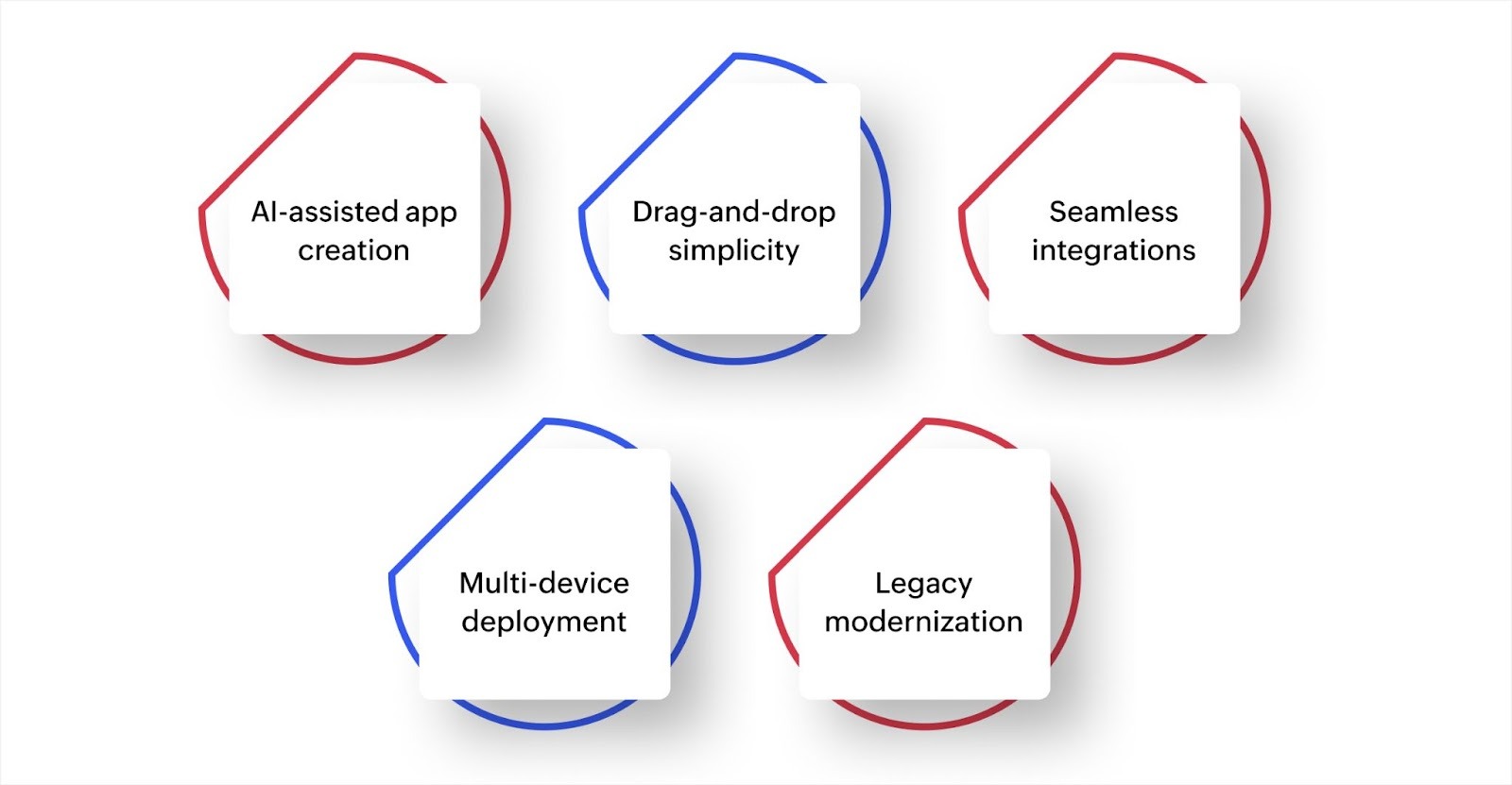
- AI-assisted app creation: Use the CoCreator, powered by Zia, to build applications through simple conversation. Reduce development time from days to a few minutes by describing what you need and letting AI generate forms, workflows, and database structures.
- Drag-and-drop simplicity: Build custom internal tools, customer portals, and core business systems without writing code. IT teams and business users can collaborate to create exactly what the organization needs.
- Seamless integrations: Connect with 1,000+ prebuilt integrations, including CRMs, ERPs, and communication tools. Break down data silos and create the unified systems that higher maturity stages require.
- Multi-device deployment: Applications built on Zoho Creator automatically work on web, iOS, and Android. Reach employees and customers wherever they are with native mobile experiences.
- Legacy modernization: Replace outdated systems that slow you down. Update old applications and move to modern platforms that support growth without starting from scratch.
You can start with a simple task tracker to digitize your first processes or build a complex custom ERP to integrate operations across departments. Zoho Creator meets you where you are and grows with your digital maturity.
FAQ
1. Can you skip maturity stages, or do you have to progress sequentially?
You typically need to progress sequentially, because each stage builds on capabilities from the previous one. For instance, you can't effectively implement advanced analytics if you haven't first organized your data and established data controls, which are lower-stage requirements.
2. What are the biggest barriers to advancing digital maturity?
The biggest barriers are cultural resistance to change, lack of digital skills, insufficient leadership support, disconnected legacy systems, limited budget, and absence of a clear strategy. Many organizations also struggle with data quality and governance issues that block progress.
3. How often should you reassess digital maturity?
Most organizations benefit from annual comprehensive assessments to track progress and adjust strategies. However, you can conduct lighter check-ins quarterly to monitor specific initiatives and ensure you stay on track toward maturity goals.
4. Do different industries have different maturity models?
While the main principles remain similar, some industries have specialized maturity models that reflect sector-specific requirements. For example, healthcare and financial services have compliance-focused models, while manufacturing emphasizes supply chain and operational technology integration.
5. What role does leadership play in digital maturity advancement?
Leadership is critical for digital maturity success. Executives must support transformation efforts, allocate resources, remove organizational barriers, and model digital-first behaviors. Without active leadership support, digital initiatives often stall regardless of technology investments.
 Ashwin Raj S N
Ashwin Raj S NAshwin is a Growth Marketer for Zoho, with a passion for learning new things. In his spare time, he enjoys spending time with his family and friends, watching anime, and travelling.