- HOME
- Industrial IoT
- Smart Manufacturing: Where Machines Learn and Factories Think
Smart Manufacturing: Where Machines Learn and Factories Think
- Last Updated : August 12, 2025
- 427 Views
- 6 Min Read
What is Smart Manufacturing?

Picture a factory where machines don’t just run, they think, communicate, and make decisions. Production lines automatically adjust to new orders. Equipment predicts when it will need maintenance and schedules it before anything breaks. Quality control happens in real time, catching defects before they leave the line. This is not fiction, it’s happening right now in smart factories across the globe.
Smart manufacturing is the transformation of traditional production into a connected, intelligent, and highly adaptable ecosystem. It blends advanced technologies like the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, automation, and big data analytics. Unlike older systems that operate in silos, smart manufacturing creates a seamless flow of information across machines, people, and processes, allowing for faster, more accurate decision-making.
History of Manufacturing: The Transformation from Industry 1.0 to 4.0

The story of manufacturing is one of constant transformation. Industry 1.0, which began in the late 18th century, marked the start of mechanization. The invention of steam engines, power looms, and water-powered machinery allowed production to move from manual, craft-based work to machine-driven processes. This was the era when factories began to take shape, and industries such as textiles and mining expanded rapidly.
Industry 2.0 emerged in the late 19th century with the introduction of electricity. This revolution brought mass production and assembly line techniques to the forefront, dramatically increasing output. Henry Ford’s moving assembly line for automobile production became the defining example of this era, allowing complex products to be built quickly and consistently.
Industry 3.0 took shape in the mid-20th century with the rise of automation and computing. The development of electronics, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and early computer systems enabled precise, consistent production at higher speeds. Processes became more controlled, and efficiency reached new heights.
Today, we are in Industry 4.0, the digital revolution. This phase is characterized by smart, connected systems that integrate cyber-physical infrastructure, IoT devices, artificial intelligence, robotics, and big data analytics. The emphasis is no longer just on efficiency, but on intelligence, adaptability, and real-time responsiveness.
Smart Manufacturing Technologies
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
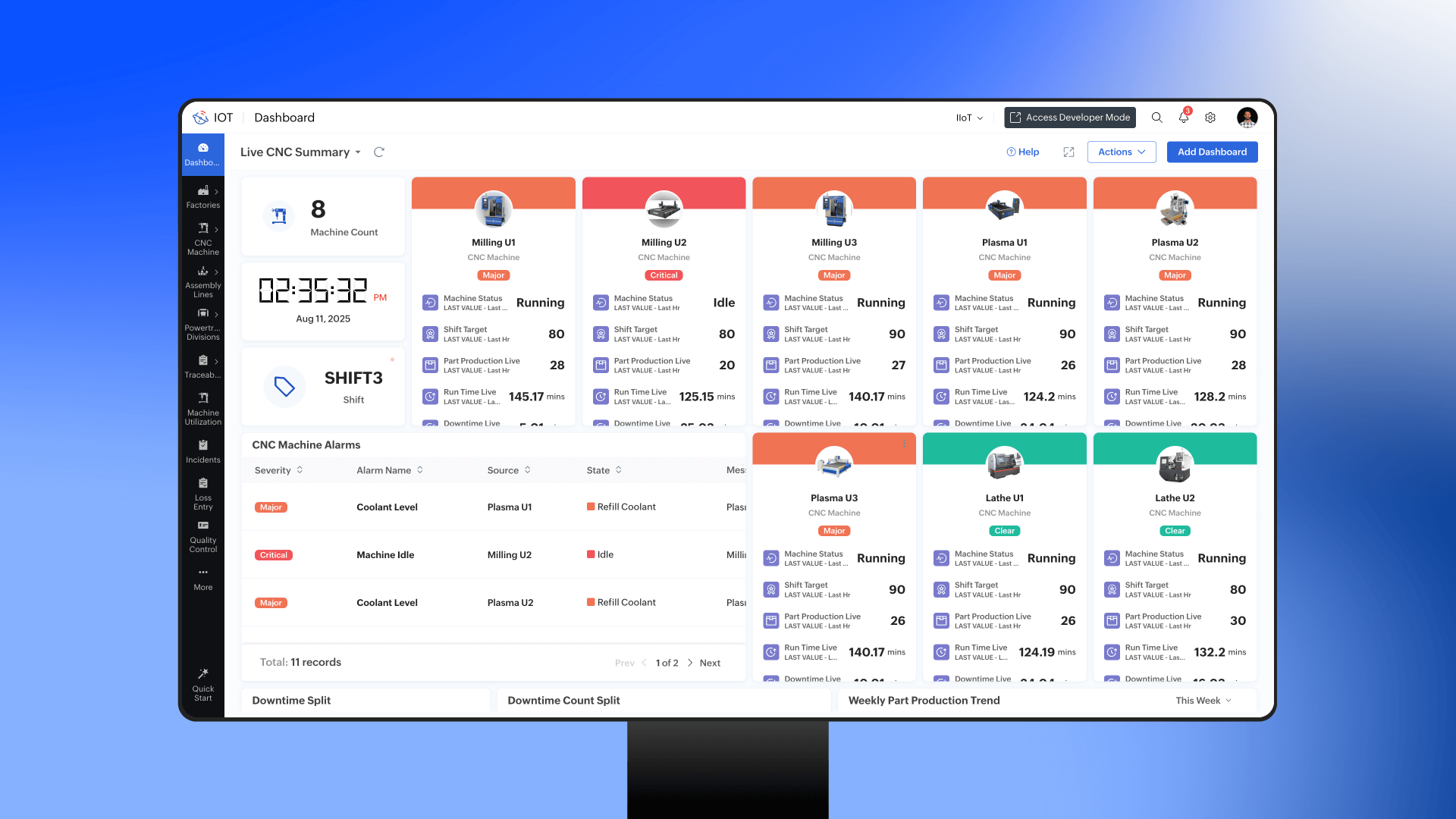
The Industrial Internet of Things is the foundation of smart manufacturing. It involves connecting machines, devices, and sensors across the factory floor to a network that enables seamless data exchange. These sensors can monitor critical parameters in real time. The collected data is transmitted to edge/cloud, where data is processed to identify patterns and anomalies. IIoT enables predictive maintenance, quality monitoring, asset tracking, and more.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence adds decision-making intelligence to the manufacturing environment. AI algorithms can process vast amounts of production data to identify trends, predict anomalies, outcomes, and make real-time recommendations. AI can forecast material requirements based on historical data and market demand, reducing shortages and overstock situations.
Robotics
Robotics plays a central role in smart manufacturing, specially the fully automated robots. Modern robots can perform tasks with high precision, speed, and consistency, whether it is assembling components, welding, or packaging products.
Digital Twin
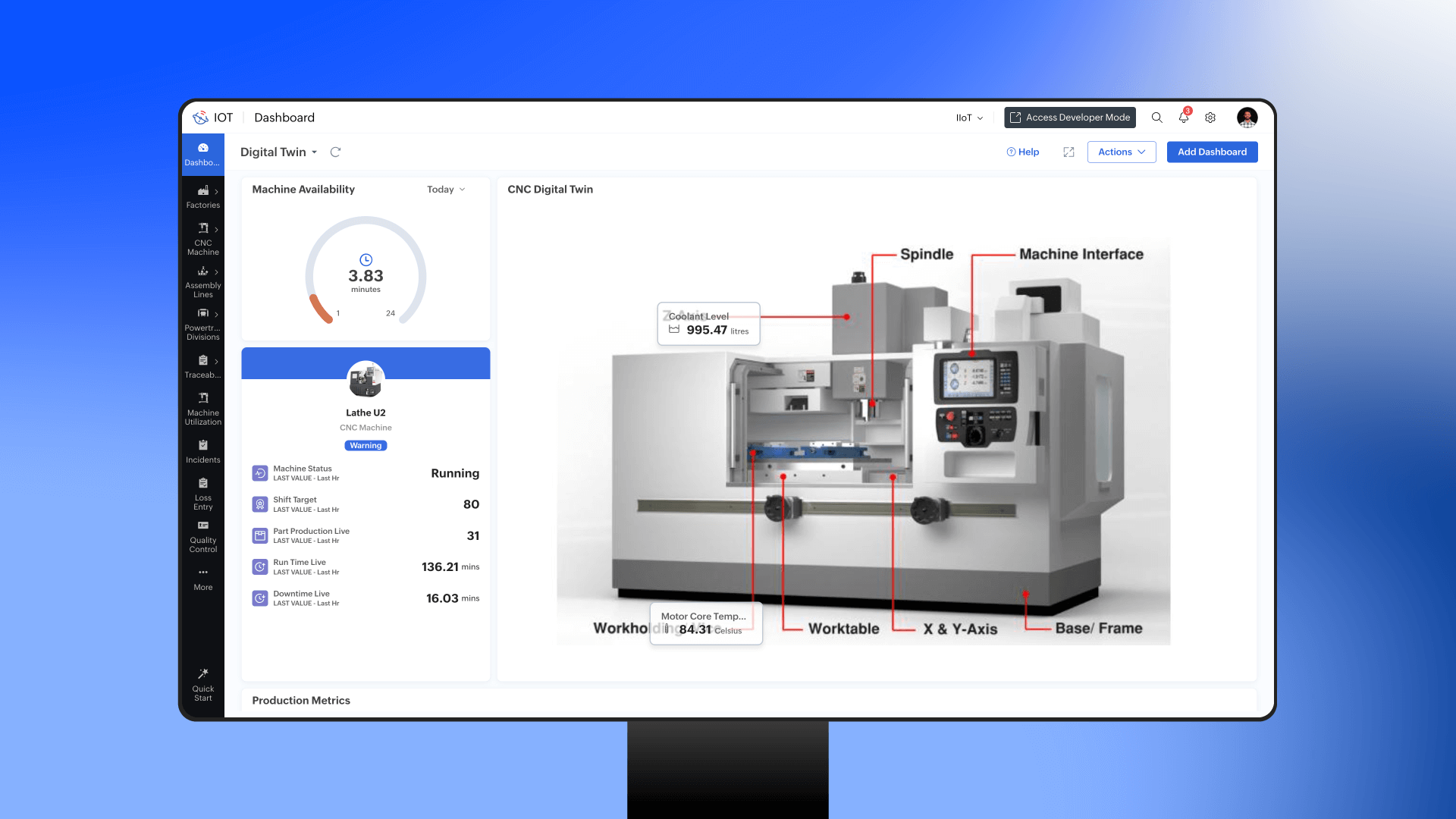
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, process, or system. It mirrors the real-world object in real time, allowing manufacturers to simulate changes, test scenarios, and monitor performance without disrupting actual operations.
Automation
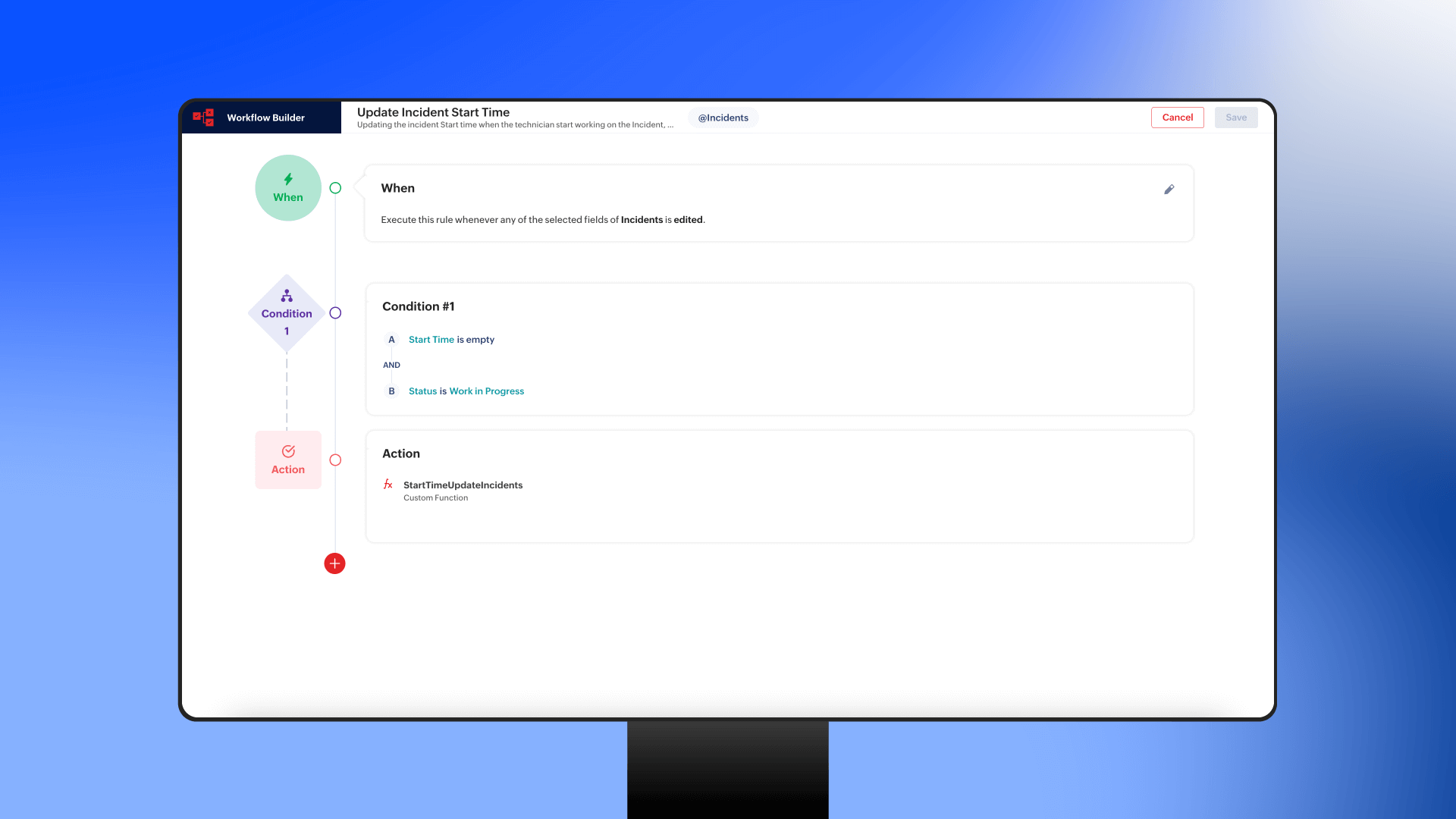
Automation in smart manufacturing goes beyond repetitive motion control. Automated systems can adjust production parameters in response to real-time feedback, enabling mass customization without slowing down operations. For instance, an automated packaging line can instantly switch between product sizes and configurations based on incoming orders, reducing setup time and increasing efficiency.
Edge Computing
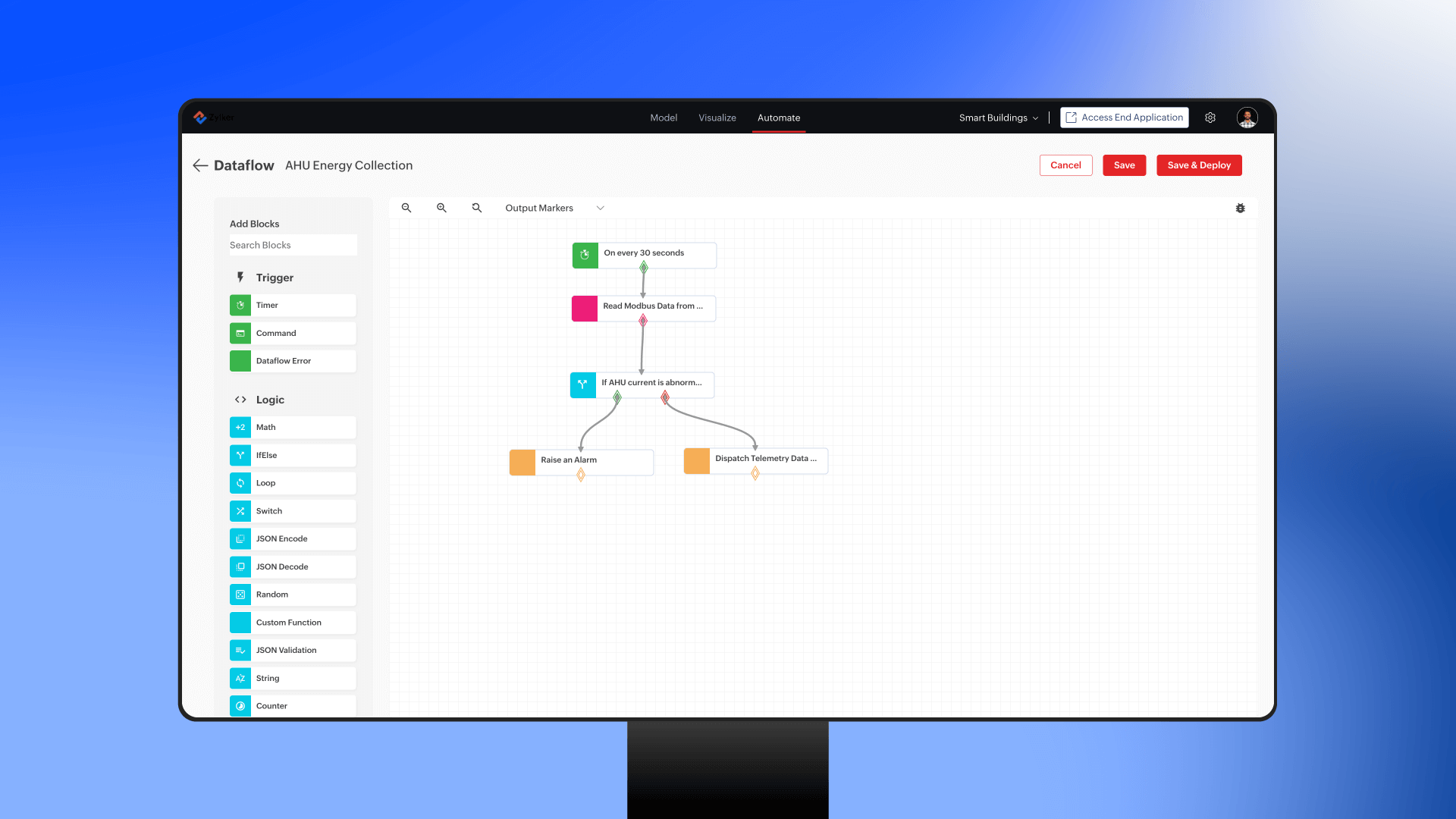
While cloud computing processes data in centralized servers, edge computing brings processing closer to the data source. This is especially important in manufacturing environments where milliseconds can make a difference. Edge computing reduces latency, enabling faster responses to equipment malfunctions or quality issues. It also helps maintain operational continuity in situations where cloud connectivity is unreliable.
Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
- Increased Productivity: Automation and real-time optimization streamline processes, allowing manufacturers to produce more in less time without sacrificing quality.
- Improved Quality Control: Advanced monitoring systems like IoT enabled vision system can detect defects early, ensuring consistent product standards and reducing waste.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance helps avoid unexpected breakdowns, keeping machines running longer and more reliably.
- Lower Operational Costs: Efficiency gains from optimized processes and reduced waste translate into significant cost savings.
- Greater Flexibility: Smart manufacturing allows quick adjustments to production lines, supporting customization and rapid market response.
- Enhanced Worker Safety: Robotics, security, and automation handle hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
- Sustainability: Real-time asset and energy monitoring enables optimized resource usage and waste reduction to help meet environmental goals.
- Competitive Advantage: Manufacturers that adopt smart technologies can deliver better products faster, securing a stronger position in the market.
Smart Manufacturing and IoT Use Cases
These scenarios show how smart manufacturing powered by IoT is not just theoretical, but it is delivering measurable results today.
Predictive Maintenance for fault detection
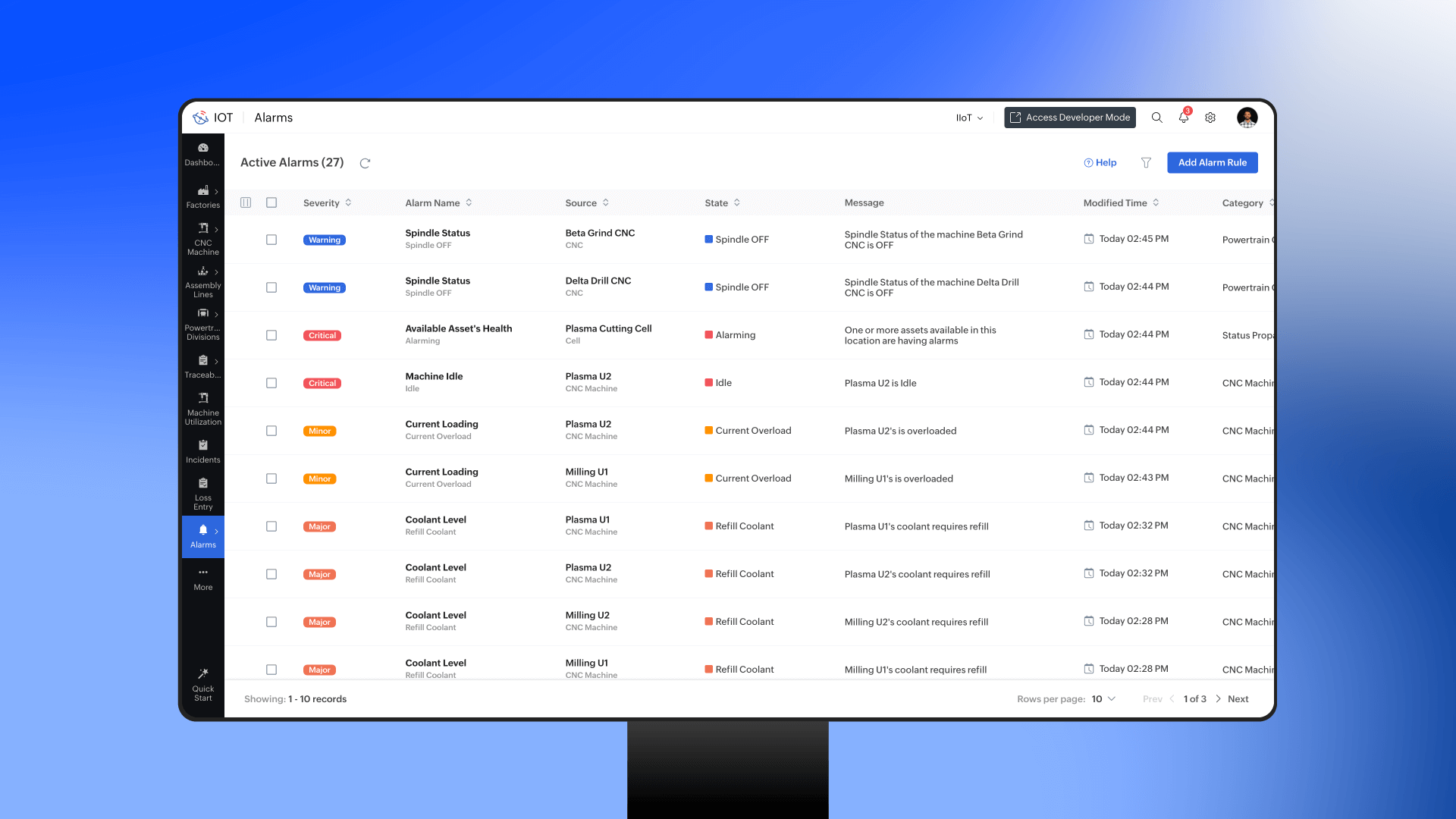
Imagine a large automotive manufacturing plant. On the factory floor, IoT sensors are embedded in every major machine. One morning, the predictive analytics system detects unusual vibrations in a robotic welding arm. Based on historical data, it predicts that the welding head will fail within 48 hours. An automated alert is sent to the maintenance team, which schedules a quick replacement during the next production. This prevents a major line stoppage that could have cost the company thousands of dollars in lost production.
Cold storage monitoring for process manufacturing industries
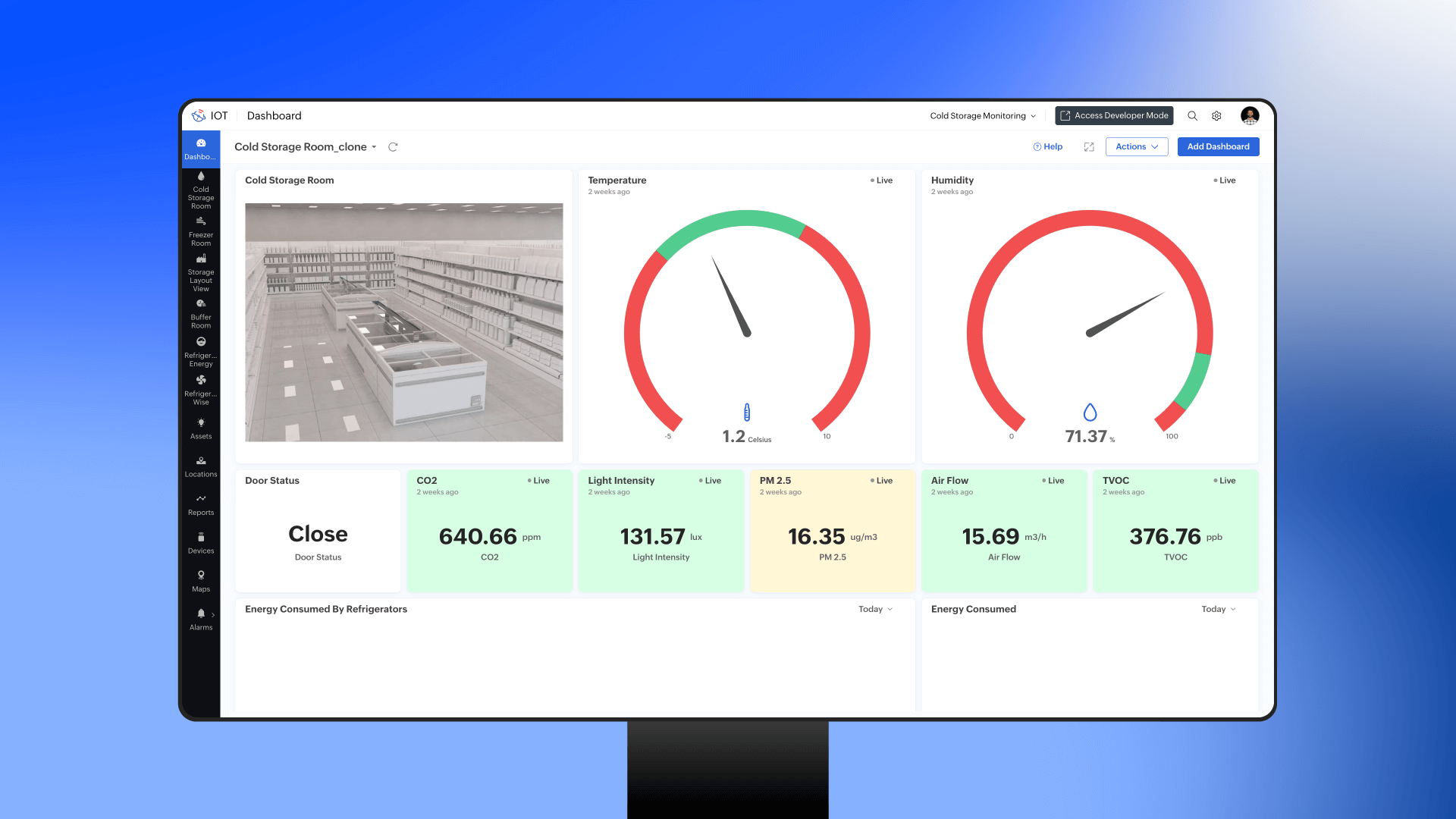
A food processing facility uses IoT-enabled temperature and humidity sensors in its storage rooms. These sensors continuously stream data to an AI-powered quality control system. When the system notices that a refrigeration unit is not cooling to its set point, it automatically adjusts the system and notifies the operator. This rapid response prevents spoilage, ensuring product safety and compliance with food safety regulations.
The ROI of Smart Manufacturing: Numbers That Matter
Manufacturers adopting Zoho IIoT are seeing measurable business benefits across the board:
| Benefit Area | Measurable Impact |
|---|---|
| Downtime Reduction | ↓ 20–40% |
| Maintenance Costs | ↓ 15–30% |
| Energy Bills | ↓ 10–25% |
| Quality Defects | ↓ 15–35% |
| Productivity | ↑ 25–50% |
| Time to Deploy | ↓ 60% (with low-code) |
These gains translate directly into higher profit margins, greater sustainability, and long-term competitive advantage.
The Zoho IoT Edge: End-to-End Manufacturing Intelligence on One Platform
Zoho IoT's Industrial IoT solution is tailor-made for industry, from single-line discrete manufacturing to complex, multi-site process enterprises. IIoT is transforming the manufacturing industry by enabling real-time visibility, data-driven decision-making, and agile operations.
Zoho IIoT brings this transformation to your factory floor with an affordable, powerful, and scalable platform that empowers both technical and non-technical teams to innovate quickly and integrate seamlessly with Zoho’s extensive cloud and industrial app ecosystem.\
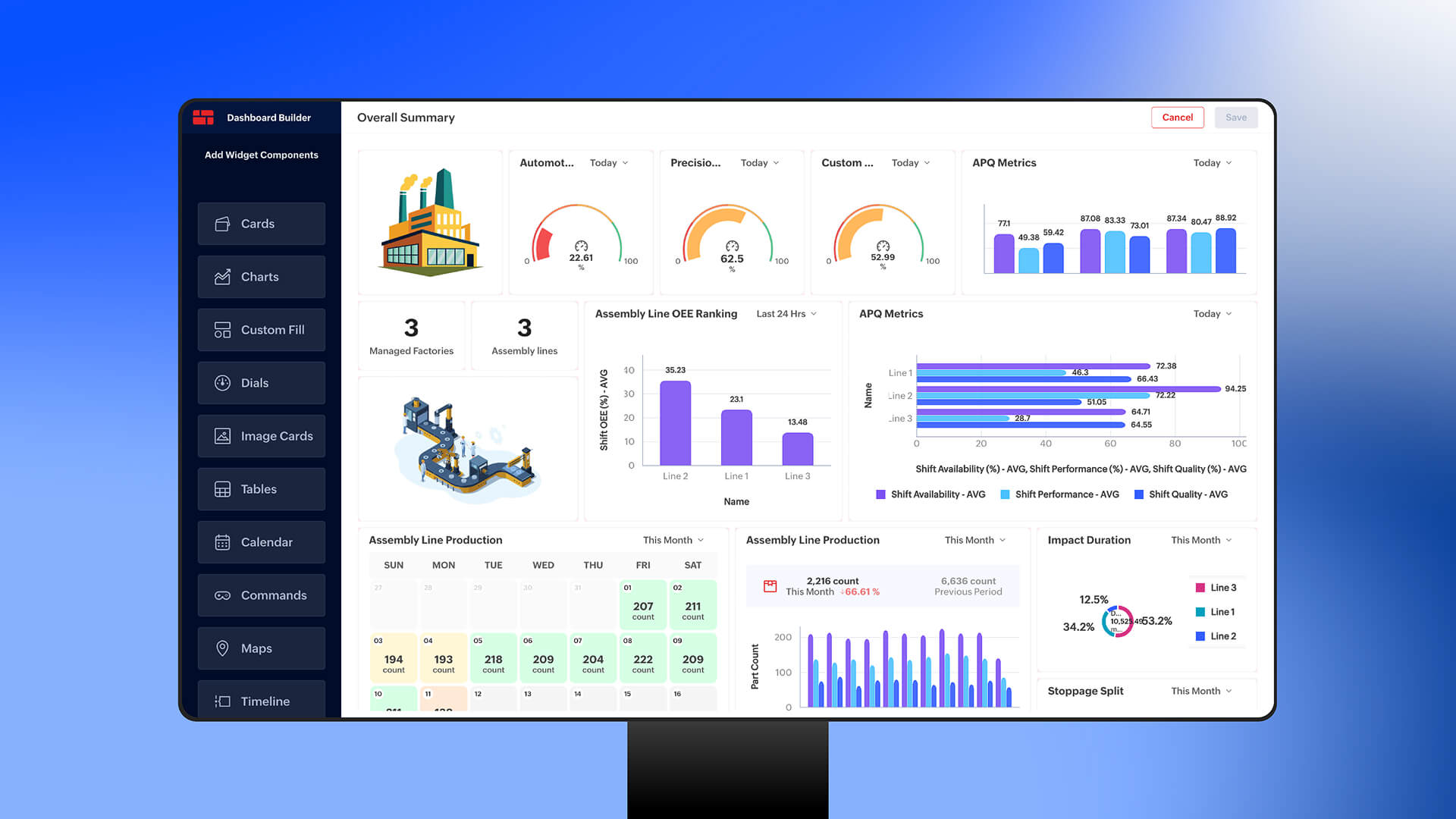
What Makes Zoho IoT Unique?
Your Industrial IoT journey’s success depends heavily on selecting a platform that aligns with your business goals, scales with your growth, and integrates seamlessly with your existing systems. While Zoho IIoT checks all these boxes, it’s important to understand what factors truly make an IoT platform the right fit for your operations.
- Unified Device Monitoring: Seamlessly connect machines, sensors, energy meters, and PLCs for centralized oversight, eliminating silos and enabling unified data-driven decision-making.
- Low-Code Flexibility: Build sophisticated workflows, set up complex alerts, and create impactful dashboards, all visually, without requiring a team of specialists.
- AI and ML Analytics: Harness powerful analytics to predict failures, uncover hidden inefficiencies, and fine-tune throughput, leveraging both machine learning and traditional data science.
- Edge-to-Cloud Architecture: Capture and process critical data locally for instant insight and use the cloud for deep-dive, enterprise-wide intelligence.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: Protect intellectual property and sensitive factory data with role-based access, industry-leading encryption, and support for compliance requirements.
Zoho IoT's Automation-Ready Features
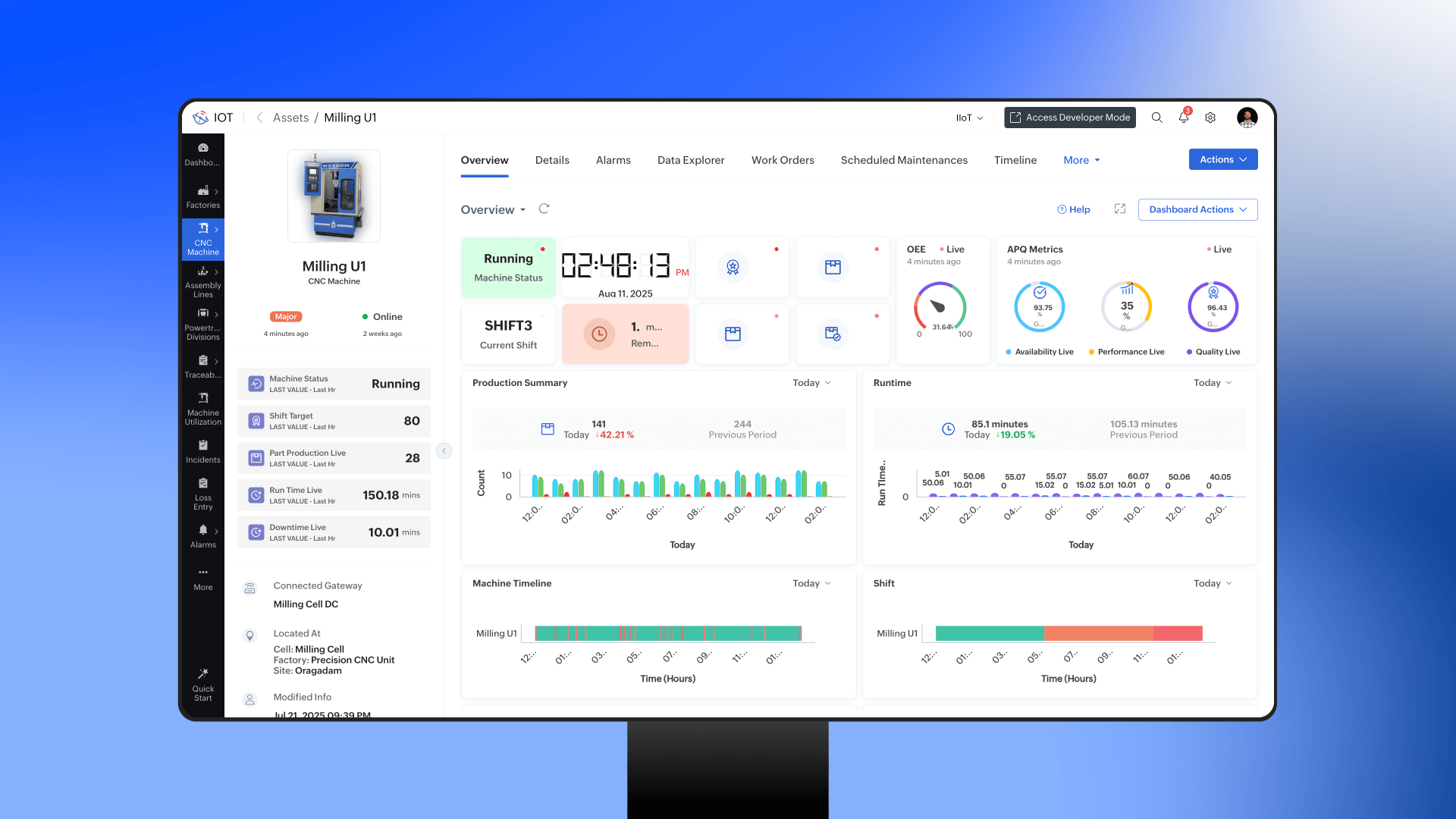
Zoho IoT's Industrial IoT includes prebuilt modules and toolkits designed from the ground up for rapid deployment and intuitive operation.
- Production Scheduling that dynamically optimizes shift planning and adapts to real-time status changes on the line.
- Work Order Management that seamlessly digitizes job instructions and synchronizes with ERP systems.
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) Tracking to monitor performance, availability, and quality metrics in real time.
- Downtime Analysis that automatically categorizes stoppages, sending customized alerts and suggestions for immediate resolution.
- Tool Life Monitoring to avert wear-based failures, optimize maintenance, and preserve capital investments.
- No-Code Dashboards enabling anyone to visualize performance, monitor trends, and trigger automated actions instantly.
Why Manufacturers Choose Zoho IoT
Manufacturers turn to Zoho IoT's industrial IoT solution for its balanced approach as it offers an affordable starting point, high-end functionality, and the flexibility to scale. With our intuitive low-code platform, both technical and non-technical users can drive value, iterate fast, and tap into Zoho’s extensive cloud and industrial app ecosystem.
Whether you’re starting small or scaling enterprise-wide, Zoho IoT helps you unlock real-time insights, boost efficiency, and drive measurable ROI. Book a demo today or start exploring our platform to see the difference first-hand.