- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Hyperautomation guide: Benefits, strategies, and examples
Hyperautomation guide: Benefits, strategies, and examples
- Last Updated : November 25, 2025
- 329 Views
- 10 Min Read
You've automated some processes and your team uses various tools for repetitive tasks; but you're still dealing with manual handoffs, disconnected systems, and workflows that need human intervention at multiple points. Is there a better way?
Highlights
- Hyperautomation is a business approach that combines AI, RPA, low-code platforms, and integration tools to automate end-to-end processes across your organization.
Hyperautomation systems manage complete processes involving decision-making, exceptions, and multiple systems working together.
Successful hyperautomation requires AI for intelligence, RPA for legacy system interaction, low-code for custom applications, and integration platforms to connect everything.
You need to map current workflows, identify automation opportunities, and prioritize based on business impact before building hyperautomation solutions.
Begin with specifichigh-value processes, prove results, and then expand, rather than attempting organization-wide changes simultaneously.
Hyperautomation solves these challenges by combining multiple technologies to automate entire workflows instead of just individual tasks. In fact, data shows businesses implementing generative AI with automation can experience yearly productivity increases of 0.5–3.4%.
In this article, we'll explore in detail what hyperautomation is, including its importance, key technological components, implementation tips, and use case examples. By the end of the guide, you’ll know exactly how to implement hyperautomation for your organization.
What is hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is a business strategy to automate as many processes as possible by combining multiple technologies. It involves using AI, robotic process automation (RPA), low-code platforms, and integration tools together to handle complete workflows.
The main purpose of hyperautomation is to connect automation across departments and systems so work flows smoothly without constant manual intervention. You're creating an automation ecosystem where different technologies handle what they do best.
For example, a logistics company receives customer orders via email, phone, and its website. Traditional automation might extract order details from emails, but hyperautomation processes orders from all channels, checks inventory across warehouses, calculates optimal shipping routes, generates pick lists, updates tracking systems, sends customer notifications, and triggers billing. Human staff only get involved when the system identifies exceptions that need judgment.
What are the key benefits of hyperautomation?
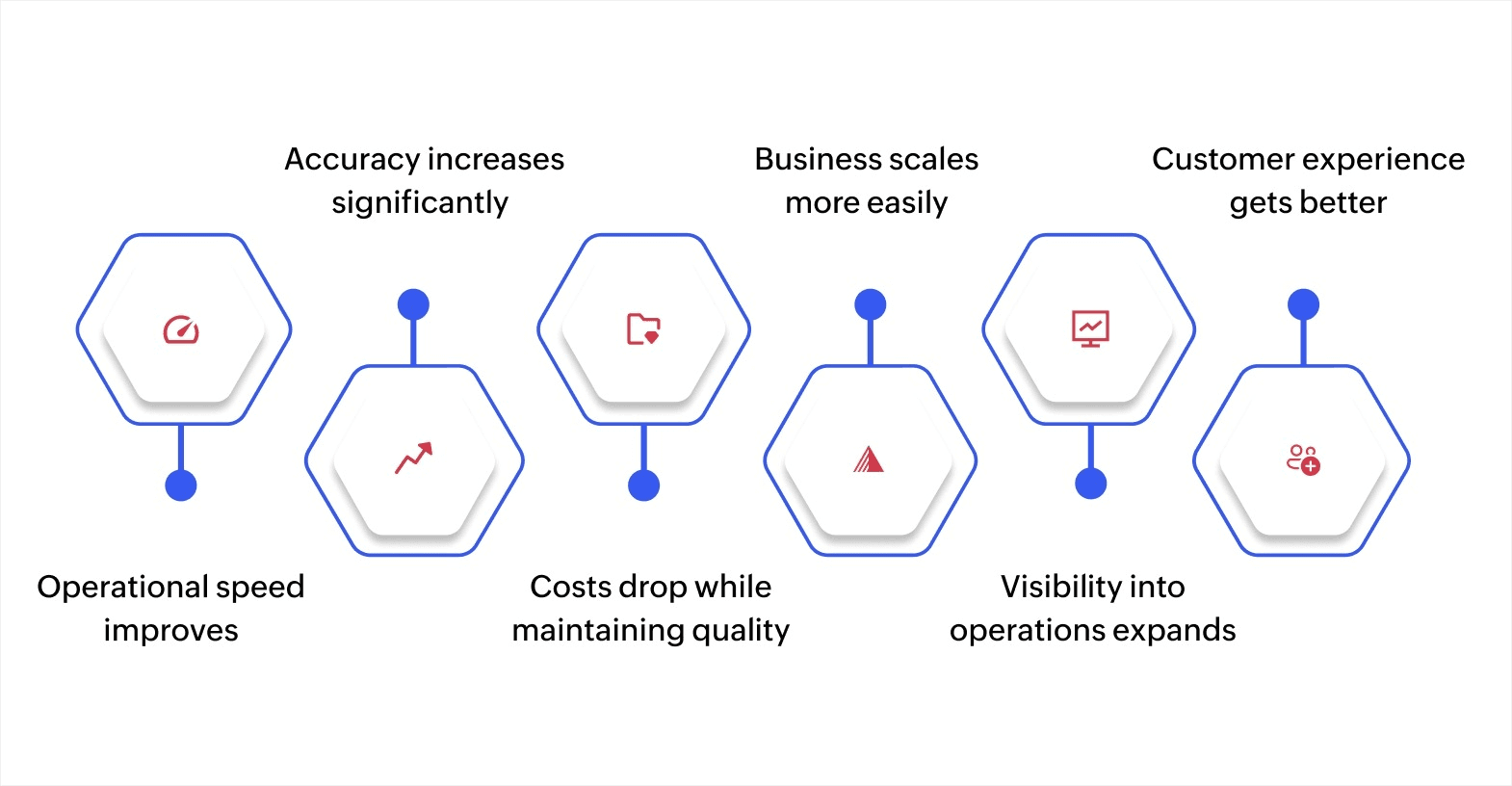
Research shows that 70% of work activities today are suitable for automation, with estimates suggesting that almost half of all work will be performed by automated systems over the next two decades. Organizations moving forward with hyperautomation now gain a considerable advantage.
Operational speed improves
With hyperautomation, processes that took days or weeks are completed in hours or minutes. Customer requests get handled faster. Orders ship sooner. Your business responds to opportunities and issues without delays from manual handoffs.
Accuracy increases significantly
Manual work introduces errors from typos, missed steps, and fatigue. Automated processes execute the same way every time. Data moves between systems without transcription mistakes. Compliance rules get applied consistently.
Costs drop while maintaining quality
You handle more volume without adding staff proportionally. People shift from repetitive tasks to work that requires judgment and creativity. Systems run 24/7 without overtime costs or shift scheduling.
Business scales more easily
Manual processes create bottlenecks when volume increases. Automated workflows handle 100 transactions or 10,000 with the same reliability. You grow revenue without increasing operational complexity.
Visibility into operations expands
Manual processes hide where work sits—and they're what cause delays. Hyperautomation creates data trails showing exactly how your business operates, where bottlenecks exist, and what needs improvement.
Customer experience gets better
Faster response times, fewer errors, and consistent service quality improve how customers perceive your business. Automated notifications keep them informed without staff having to remember to send updates.
What technologies power hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation combines several technologies, each serving a specific role. To truly automate complete processes, you need multiple tools working in sync.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
AI handles decision-making in your automated workflows. It classifies documents, extracts information from unstructured data, predicts outcomes, and manages exceptions that don't follow standard rules.
For instance, AI reads customer emails, identifies what they need, and routes requests to the right team or responds automatically to common questions. Machine learning improves these decisions over time by learning from patterns in your data.
Robotic process automation
RPA bots interact with applications the way humans do—by clicking buttons, entering data, and moving information between systems. This capability is valuable for legacy systems that lack APIs. The bots work continuously without breaks and handle high-volume repetitive tasks.
For example, an RPA bot logs in to your supplier portal, downloads invoices, extracts key information, and enters it into your ERP system.
Low-code development platforms
Low-code platforms let you build custom applications and workflows without extensive programming. They're how you create the specific solutions your business needs quickly. Business users and citizen developers can build automation solutions without waiting for IT resources.
For instance, you can build a custom approval workflow for capital expenditure requests that routes to different managers based on amount and department.
Process mining and discovery
Process mining tools analyze your systems to show exactly how work flows through your organization. They identify where delays occur and which processes are good candidates for automation. This data-driven approach ensures you automate the right things. The tools create visual maps of your actual processes, not just what you think happens.
Integration platforms
Your business runs on multiple systems with customer data in your CRM, orders in your ERP, and communications in email. Integration platforms connect these systems so data flows automatically without manual transfers.
This connected ecosystem is what hyperautomation requires. APIs and webhooks enable real-time data synchronization across all your business applications.
Business process management software
BPM tools help you design, execute, and optimize workflows. They provide the framework for orchestrating complex processes that span multiple departments and systems. Workflows ensure work moves from one step to the next with proper approvals, notifications, and exception handling built in.
How do you implement hyperautomation at your organization?
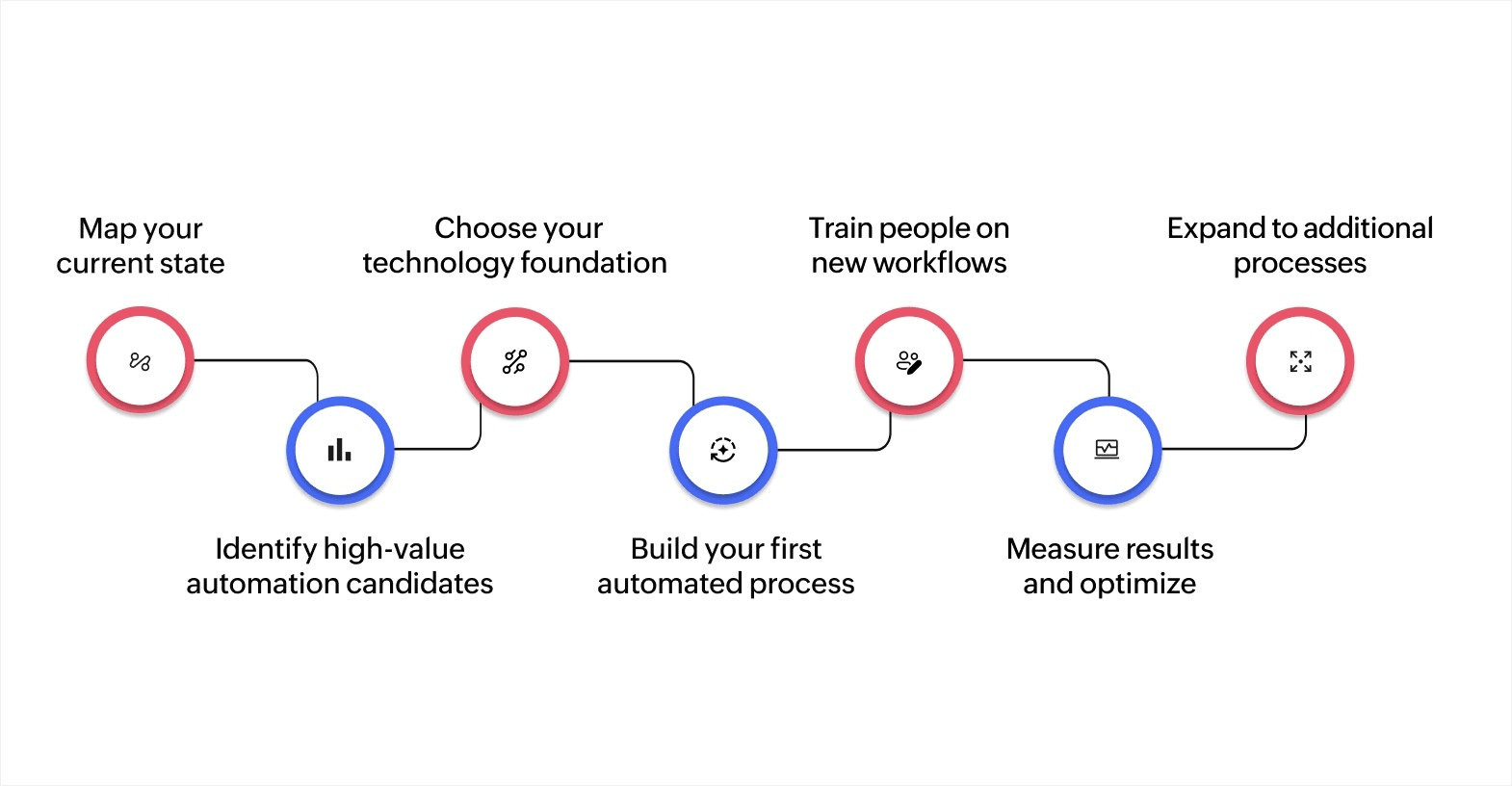
Starting hyperautomation can feel overwhelming when you have hundreds of processes and limited resources. A strategic approach works better than attempting organization-wide changes simultaneously.
1. Map your current state
You need to see how work actually flows through your organization. Document your key processes by talking to people who do the work daily. Ask questions like:
Which steps are manual?
Where do handoffs occur?
What takes the most time?
Where do errors happen most often?
This mapping reveals automation opportunities. Some companies also use process mining software to analyze system logs and automatically create accurate process maps.
2. Identify high-value automation candidates
Not all processes benefit equally from automation. Look for workflows that are high-volume, repetitive, rule-based, and time-consuming. Calculate potential impact by considering time saved, error reduction, and customer experience improvements.
For instance, employee onboarding, invoice processing, and customer service ticket routing often delivers quick returns because they happen frequently and follow predictable patterns.
3. Choose your technology foundation
Your platform choice determines what you can build and how fast you can move. You need AI capabilities, workflow automation, strong integration options, and scalability. Platforms like Zoho Creator provide these capabilities together rather than forcing you to integrate multiple vendor solutions.
Look for low-code options that let business users contribute to building automation instead of waiting for developer resources.
4. Build your first automated process
Start with one complete workflow from beginning to end. Build it, test it thoroughly with actual users, and refine it based on their feedback. This proves the concept and helps you learn what works in your environment.
For instance, a manufacturing company can automate its quote-to-order process, while a services firm might automate project intake and resource allocation.
5. Train people on new workflows
Technology only succeeds when people use it correctly. Show your team how automation makes their work easier by handling tedious tasks.
Address concerns about job security by explaining how automation enables them to focus on tasks that require human judgment and creativity. Document new processes clearly and provide support during the transition.
6. Measure results and optimize
Track specific metrics for your automated processes, like completion time, error rates, cost per transaction, and user satisfaction. Use this data to power continuous improvement.
What works well?
What needs adjustment?
Where should you automate next?
Share results with stakeholders to build support for expanding hyperautomation across more processes.
7. Expand to additional processes
Once you've proven success, create a roadmap for automating more workflows. Prioritize based on business impact, technical feasibility, and strategic alignment.
Build internal expertise so your team can handle automation projects independently, without relying entirely on external consultants or vendors.
What are common hyperautomation use cases and examples?
Hyperautomation applies across industries and business functions. These examples show how different organizations use it to handle complex workflows:
Customer service operations
Intelligent request routing: AI analyzes incoming requests from email, chat, and phone, categorizes them by type and urgency, then routes to the right team with relevant customer history attached.
Automated resolution for common issues: Chatbots and knowledge bases handle routine requests like password resets, order status, and account updates without human involvement.
Proactive service delivery: Systems monitor customer usage patterns, identify potential issues, and reach out with solutions before customers realize there's a problem.
Finance and accounting workflows
End-to-end invoice processing: Systems receive invoices from any channel, extract data using AI, match to purchase orders, route for approval based on business rules, schedule payments, and update accounting records automatically.
Expense management automation: Employees submit expenses through mobile apps, AI validates receipts and checks policy compliance, workflows route to managers for approval, and reimbursement happens without manual review for standard items.
Financial close acceleration: Month-end processes that took weeks now complete in days as systems automatically reconcile accounts, consolidate data from subsidiaries, apply accounting rules, and generate reports.
Supply chain and logistics
Inventory optimization: Systems monitor stock levels across locations, predict demand using historical patterns and market signals, and automatically generate purchase orders when inventory drops below thresholds.
Order fulfillment orchestration: Customer orders trigger automated workflows that check inventory, calculate optimal shipping routes, generate pick lists for warehouse staff, update tracking systems, and send notifications at each stage.
Supplier management: Platforms automate supplier onboarding, track performance metrics, manage contracts and renewals, and flag issues like late deliveries or quality problems for procurement teams to address.
Human resources management
Employee onboarding automation: New hire workflows provision accounts, assign equipment, schedule training, send welcome materials, and guide employees through their first weeks without HR staff coordinating each step manually.
Time and attendance processing: Systems track hours worked, calculate overtime, apply business rules for different employee types, route exceptions for approval, and feed clean data to payroll.
Performance review orchestration: Workflows schedule review cycles, send reminders, collect feedback from multiple sources, compile results, and ensure managers complete reviews on time.
Healthcare operations
Patient intake and scheduling: Systems handle appointment booking, insurance verification, medical history collection, and pre-visit preparation without staff coordinating each step manually.
Claims processing automation: AI extracts information from medical records, matches procedures to billing codes, checks insurance coverage, submits claims electronically, tracks statuses, and handles resubmissions when needed.
Medication management: Workflows track prescriptions, send refill reminders to patients, route approval requests to physicians, coordinate with pharmacies, and maintain accurate medication lists.
Build hyperautomation capability with Zoho Creator
Hyperautomation is essential to drive growth—but the real challenge is implementing it without the complexity and cost of traditional enterprise platforms that require large IT teams and long deployment cycles.
Zoho Creator is an AI-powered low-code application development platform that makes hyperautomation accessible. You get enterprise automation capabilities with the speed and affordability that growing businesses need.
deSIAM, a manufacturing company, used Zoho Creator to build custom applications for its operations, significantly reducing labor costs by 50%. The platform gave them the flexibility to automate processes exactly how their business needed, without forcing them into rigid prebuilt solutions. Read deSIAM's complete story.
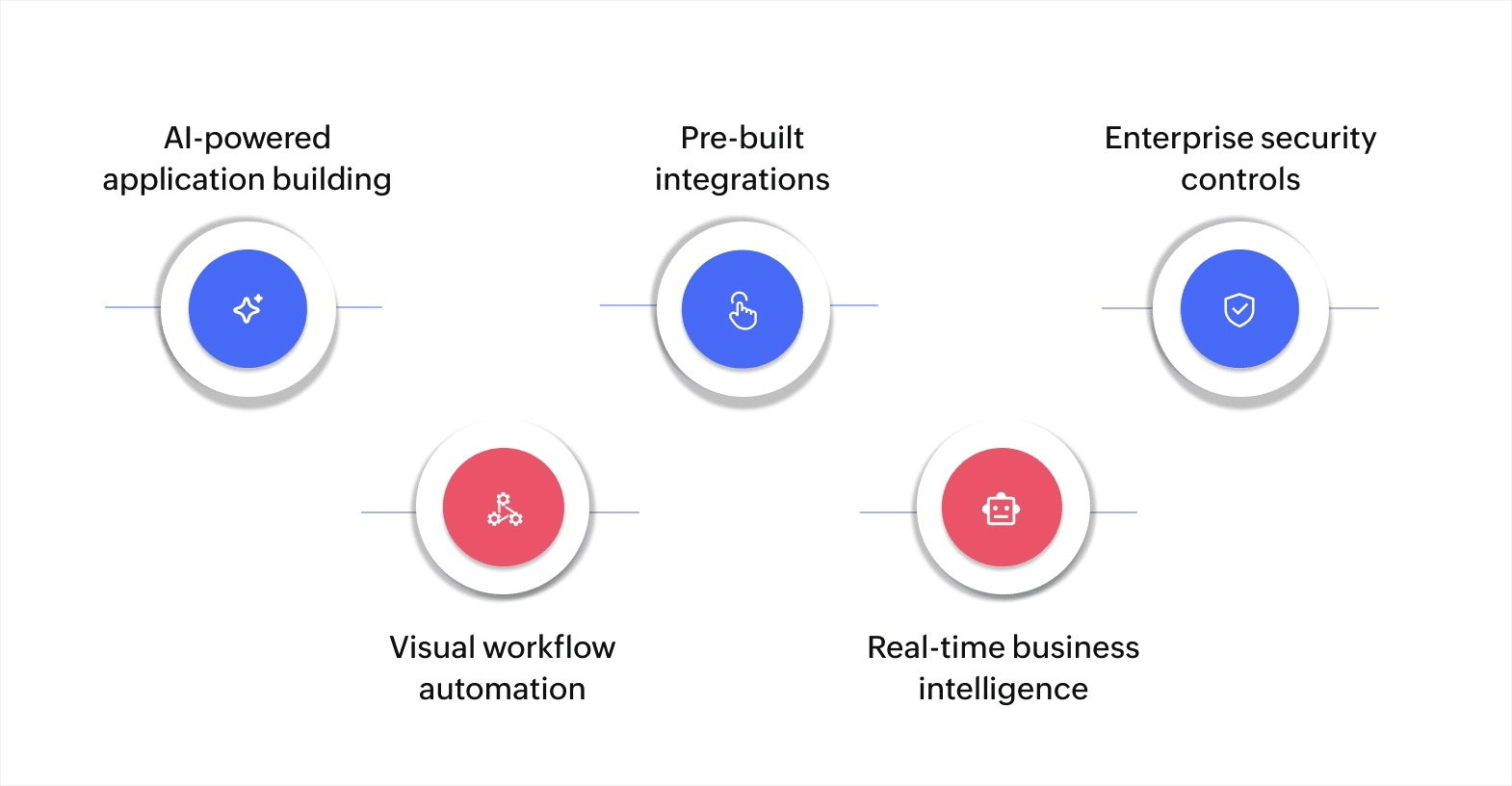
Here's how Zoho Creator enables your hyperautomation strategy:
AI-powered application building: Use Zia, Zoho's AI assistant, to build applications faster by describing what you need in plain language and having AI help create forms, workflows, and reports.
Visual workflow automation: Design complex multi-step processes using drag-and-drop tools with approval chains, conditional logic, and automated actions without writing code.
Prebuilt integrations: Connect with existing tools like Salesforce, QuickBooks, Google Workspace, Slack, and hundreds of other applications using preconfigured connectors or REST APIs for custom integrations.
Real-time business intelligence: Get visibility into automated processes with customizable dashboards. Easily track performance to identify optimization opportunities.
Enterprise security controls: Your data is protected with encryption, role-based access controls, audit trails, and compliance with global standards.
"With Zoho Creator handling all our paperwork, we can finally focus on what we do best: making, marketing, and selling our products. Administration tasks are no longer a burden."
— Hervé Haurie, Managing Partner, deSIAM
Companies are increasingly implementing hyperautomation as new tools make the process faster and easier—but the advantage goes to businesses that start now rather than waiting for the perfect moment.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between traditional automation and hyperautomation?
Traditional automation handles individual tasks like data entry or report generation. Hyperautomation is a strategy that automates complete end-to-end processes using multiple technologies, including AI, RPA, and low-code platforms, working together to handle complex workflows with minimal human intervention.
2. Do I need to replace existing systems to implement hyperautomation?
No, hyperautomation works with your current systems through integrations and APIs. Technologies like RPA can interact with legacy applications without requiring changes to those systems. The goal is connecting and orchestrating your existing tools, not replacing them.
3. What processes should I automate first?
Start with processes that are repetitive, high-volume, rule-based, and time-consuming. Common starting points include invoice processing, employee onboarding, customer service requests, and report generation. Choose processes where success will be visible and demonstrable to build organizational support for expanding automation.
4. What skills do I need to implement hyperautomation?
You need business process knowledge, basic technical capabilities, and change management skills. Low-code platforms reduce coding expertise requirements, allowing business analysts and citizen developers to build automation solutions. For complex integrations, having IT support helps, but many projects succeed without dedicated development resources.
5. How do you measure hyperautomation success?
Track metrics like process completion time, error rates, cost per transaction, employee time saved, and customer satisfaction scores. The specific metrics depend on your objectives. Most organizations focus on efficiency improvements, error reduction, and return on investment calculated from cost savings and revenue impact.
 Ann Elizabeth Sam
Ann Elizabeth SamHey! I'm Ann, and I work as a content writer at Zoho Creator. I'm exploring the SaaS world through various forms of content creation. Outside of work, I love dancing and would give up anything to read a good murder mystery.



