- HOME
- All Products
- Analyzing Google Workspace's downtime against Zoho Workplace's downtime
Analyzing Google Workspace's downtime against Zoho Workplace's downtime
- Published : May 7, 2024
- Last Updated : May 7, 2024
- 1.8K Views
- 8 Min Read
In our comprehensive series on the financial implications of selecting between Zoho Workplace and Google Workspace for SMEs, this article takes a deep dive into a vital but often overlooked aspect: the resilience and reliability of workplace applications like email, team chat, office tools, and virtual meetings.
In this article, we’ll explore the historical downtime records of Zoho Workplace and Google Workspace and delve into the nuances of how each platform addresses the root causes of outages, their transparency in communicating with users during such events, and the robustness of their recovery processes. We'll assess the preventive strategies each employs to mitigate future risks, including infrastructure investments and software updates, and consider evaluations from third-party benchmarks to provide an unbiased view of their operational resilience.
The impact of downtime
Downtime drastically impacts an organization's productivity and bottom line, affecting both direct and indirect financial aspects, along with reputational harm. When they’re down, key applications like email and cloud storage disrupt critical operations and communications directly, leading to immediate productivity losses and potential revenue declines. Indirectly, the diversion of resources to identify and fix downtime issues stalls innovation and growth efforts, compounding productivity losses.
Moreover, downtime strains support teams, stretching their capabilities and diverting their focus from proactive improvements to reactive troubleshooting, further impacting organizational efficiency. The reputational damage from frequent or extended downtime can weaken customer trust and loyalty, leading to long-term financial and competitive setbacks.
To estimate the monetary value of downtime for each application and its total financial impact, we can create a formula that considers various factors.
Assumptions for calculation
Average revenue per employee (ARPE): This value represents the average revenue generated per employee per minute. It's a crucial factor because downtime directly impacts employee productivity and, consequently, revenue generation.
Criticality factor (CF): This is a multiplier that reflects the urgency level and the additional stress of customer satisfaction impact on the support team during downtime. External-facing applications and those critical for immediate business operations have higher urgency factors.
Cost of support (CoS): The CoS during application downtime encapsulates the expenses incurred beyond direct productivity losses. It includes mobilizing IT and technical support for diagnostics and resolution, data recovery, and to manage increased inquiries.
Formula
The formula to estimate the financial impact of downtime integrates the employees’ reduced productivity due to downtime and the CoS.
Financial impact of downtime = Reduced employee productivity due to downtime + Cost of support during downtime
1. Reduced employee productivity due to downtime involves downtime duration with factors like the ARPE and the CF.
Reduced productivity = Reduced downtime duration × Impacted workforce * Productivity impact * ARPE * CF
Downtime duration: The total time the application is unavailable until recovery and restoration.
ARPE (Average Revenue Per Employee): Represents the revenue generated by an employee per minute, directly linking employee productivity to revenue. Let's assume an ARPE value of $0.50 per minute. This represents the average revenue generated by an employee per minute and directly links employee productivity to revenue generation.
CF (Criticality Factor): This multiplier indicates the application's criticality, considering customer satisfaction and the urgency of restoration.
Assumptions:
| High criticality | Moderate criticality | Low criticality | |
| Criticality factor | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Applications | Email, video conferencing (Meeting/Webinar), presentation tools (PPT) | Team chat, office tools (Docs, Sheets), cloud storage, calendar | Task management, social intranet (despite high usage, considering its internal focus) |
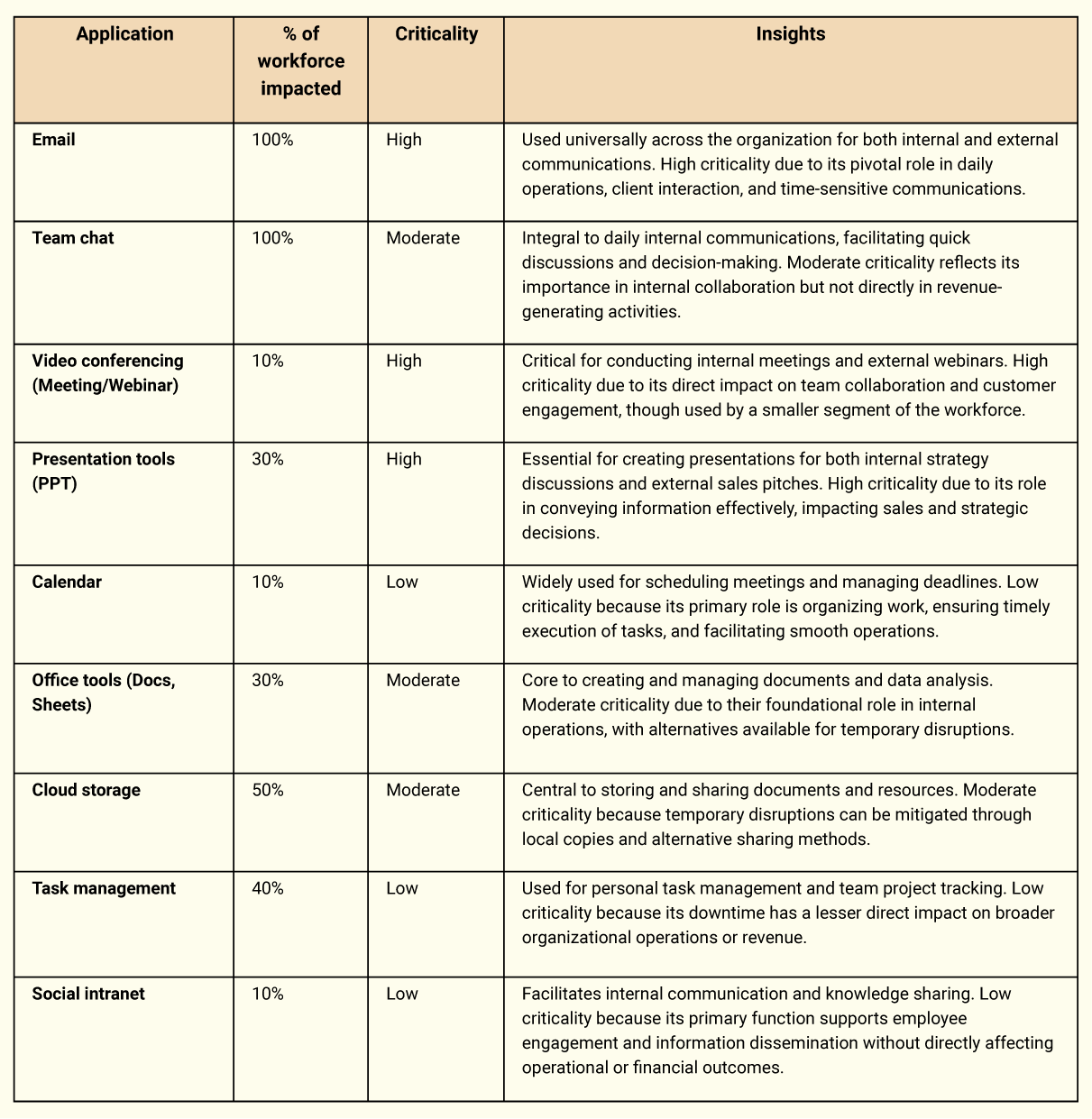
The table below gives the financial implications of downtime for key workplace applications, considering their usage across the workforce and their criticality to business operations. It provides a detailed view of how each application's availability directly influences organizational efficiency, internal collaboration, and external communications.
2. Cost of Support (CoS) for each application involves considering the percentage of the workforce impacted by the application and the application's criticality; we will use the following formula:
CoS per app = Hourly wage of IT staff × Reduced downtime hours × IT workload ratio + Impacted workforce x Number of IT staff (based on criticality) x Percentage of downtime requiring IT support x Hourly wage of support staff
Assumptions:
Hourly wage of IT staff = $60 (assuming each IT staff member is paid $60 per hour)
Number of IT staff involved = x (for applications with high criticality, a 100% likelihood of IT intervention is assumed with 3 support staff needed. Moderate criticality assumes a 50% likelihood with 2 support staff, and low criticality assumes a 20% likelihood with 1 support staff.)
IT workload ratio = 1.5 (indicating IT work often exceeds the actual downtime duration)
Percentage of downtime requiring IT support = 20% (or 0.2, assuming 20% of downtime incidents require IT intervention)
Criticality factor: High = 2.0, Moderate = 1.2, Low = 0.8 (based on the application's criticality)
Why SMEs are switching to Zoho Workplace
SMEs are increasingly scrutinizing the reliability of their workplace productivity platforms. For an organization that commits to 99.9% uptime SLA, it’s equal to 8 hours and 45 minutes of “allowed” downtime per year. According to Ponomon’s study, the average cost of downtime per minute for small businesses is $427, and $9,000 for larger enterprises.
Google Workspace encountered a substantial total of 22,564 minutes (approximately 376 hours) of global downtime, over 27 hours of service disruption, and over 9 hours of service outage in the last 12 months affecting various applications ranging from Gmail and Google Calendar to Google Meet and Google Docs. On the other hand, Zoho Workplace demonstrated remarkable resilience with a significantly lower total downtime of just 696 minutes (approximately 12 hours) across its suite of applications, including Zoho Mail, Zoho Sheet, and Zoho Cliq, among others.
In the last few years, Google Workspace has experienced several notable downtime incidents that have had significant impacts on its users:
December 2020 outage: This widespread outage affected multiple Google services, including YouTube, Google Play Store, Gmail, Google Assistant, YouTube Music, and Google Drive. Users globally were unable to access these services, and the cause of the outage was not immediately disclosed. The downtime was particularly alarming due to its broad scope, affecting almost all Google services simultaneously.
June 5, 2023 service disruption: This incident involved multiple Google services, including Gmail, Google Docs, and YouTube, indicating a recurring vulnerability in Google's infrastructure that led to disruptions in essential communication and collaboration tools. Although the exact duration and root cause of this outage are not detailed, such incidents highlight the challenges faced by Google in maintaining continuity and transparency during unexpected service disruptions.
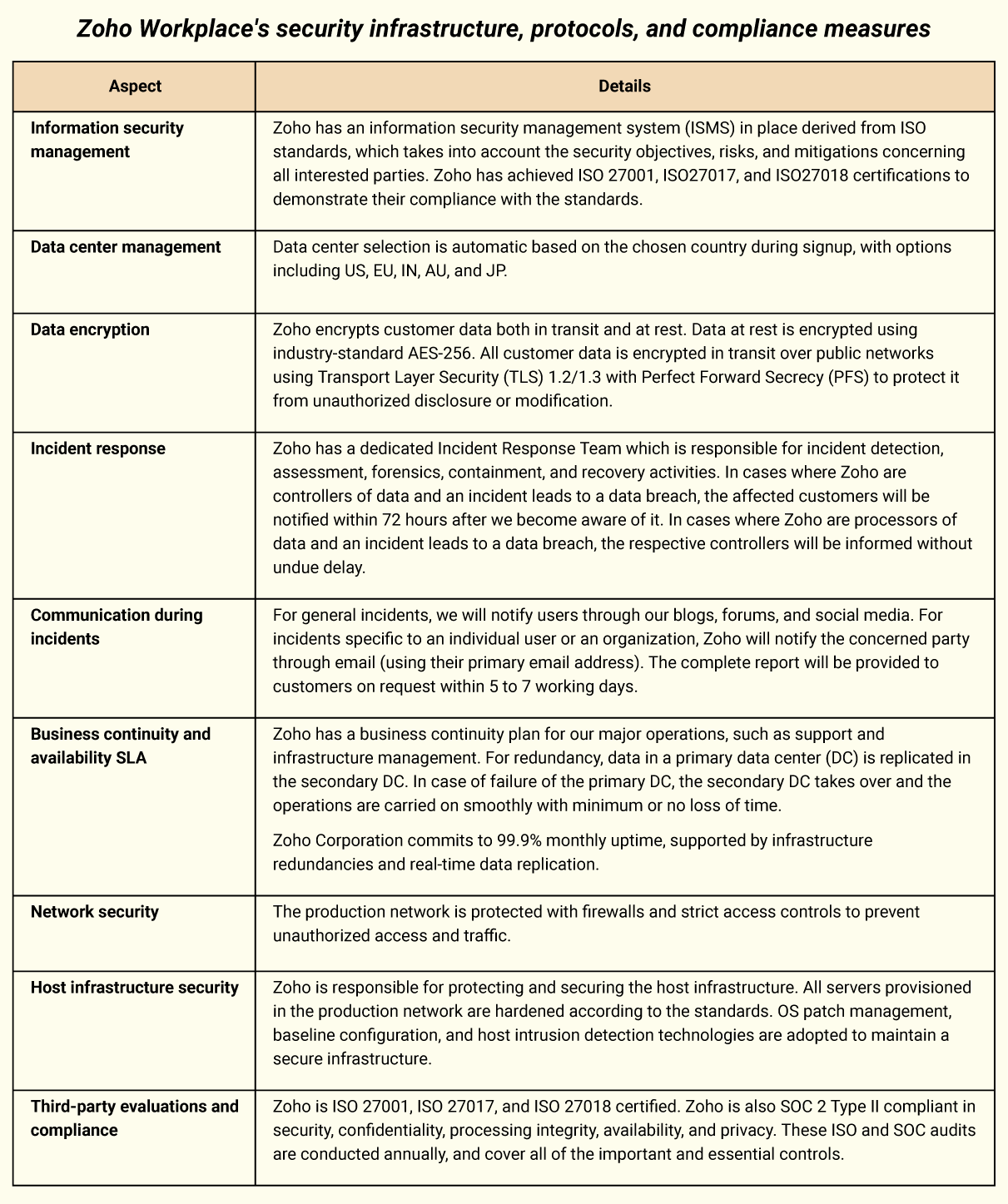
Zoho Workplace's security infrastructure, protocols, and compliance measures
Downtime comparison
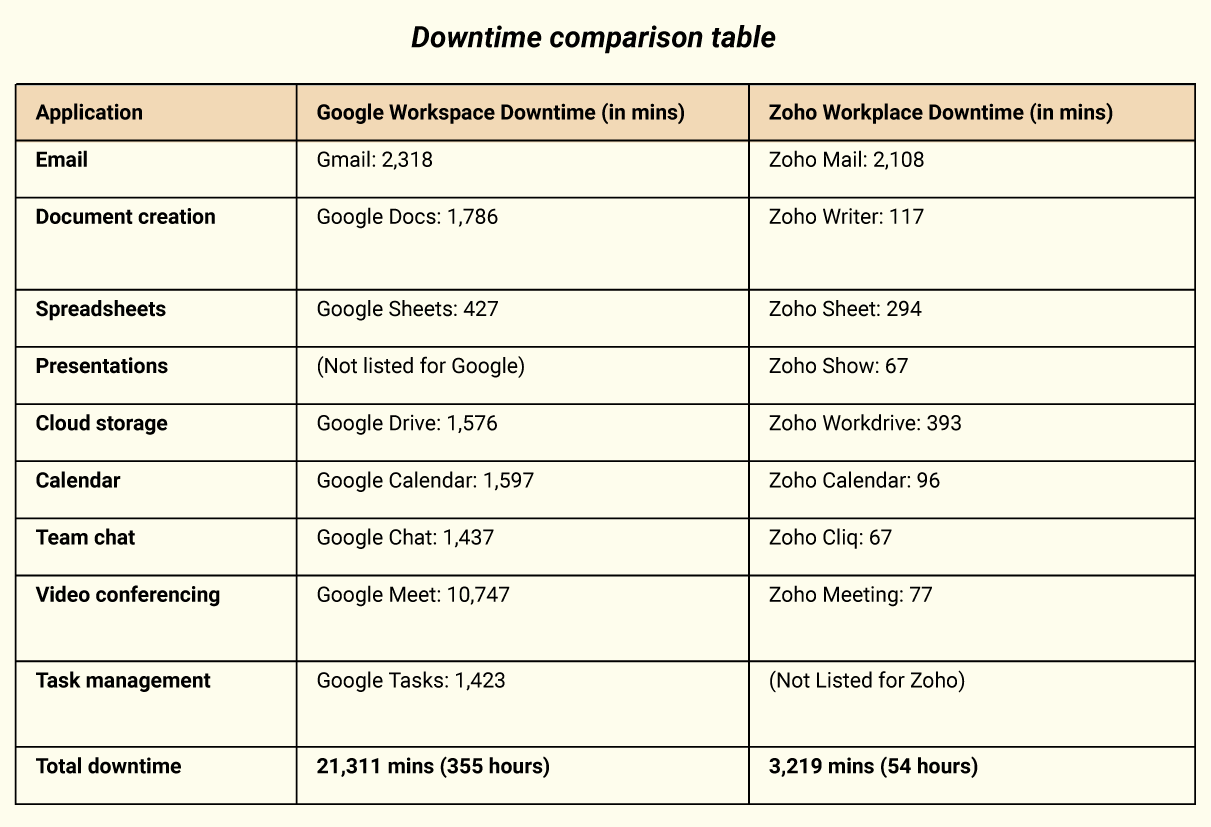
This data is based on the global status pages of Google Workspace and Zoho Workplace from March 2023 to February 2024.
Financial impact calculation
To conduct a financial analysis of the transition from Google Workspace to Zoho Workplace for a composite organization, we'll integrate insights on application usage and criticality with the historical downtime data. The analysis will estimate the financial impact of reduced downtime by transitioning to Zoho Workplace, considering an organization with 1,000 employees. The downtime comparison table displays global downtime data. For analysis purposes within the context of a composite organization, which we're considering as a region in the US, we’ll assume that 20% of the global downtime data represents the downtime for the US region.
Composite organization assumptions:
Employees: 1,000
ARPE (Average Revenue Per Employee): $0.50 per minute
Criticality Factor (CF): High (2.0), Moderate (1.2), Low (0.8)
Cost of Support (CoS): $60 per hour per IT staff member
Formula for financial impact:
Financial impact of reduced downtime = Reduced employee productivity due to downtime + Cost of support
Reduced productivity = Reduced downtime duration × Impacted workforce * Productivity impact * ARPE * CF
Financial impact by app (USD) due to reduced productivity
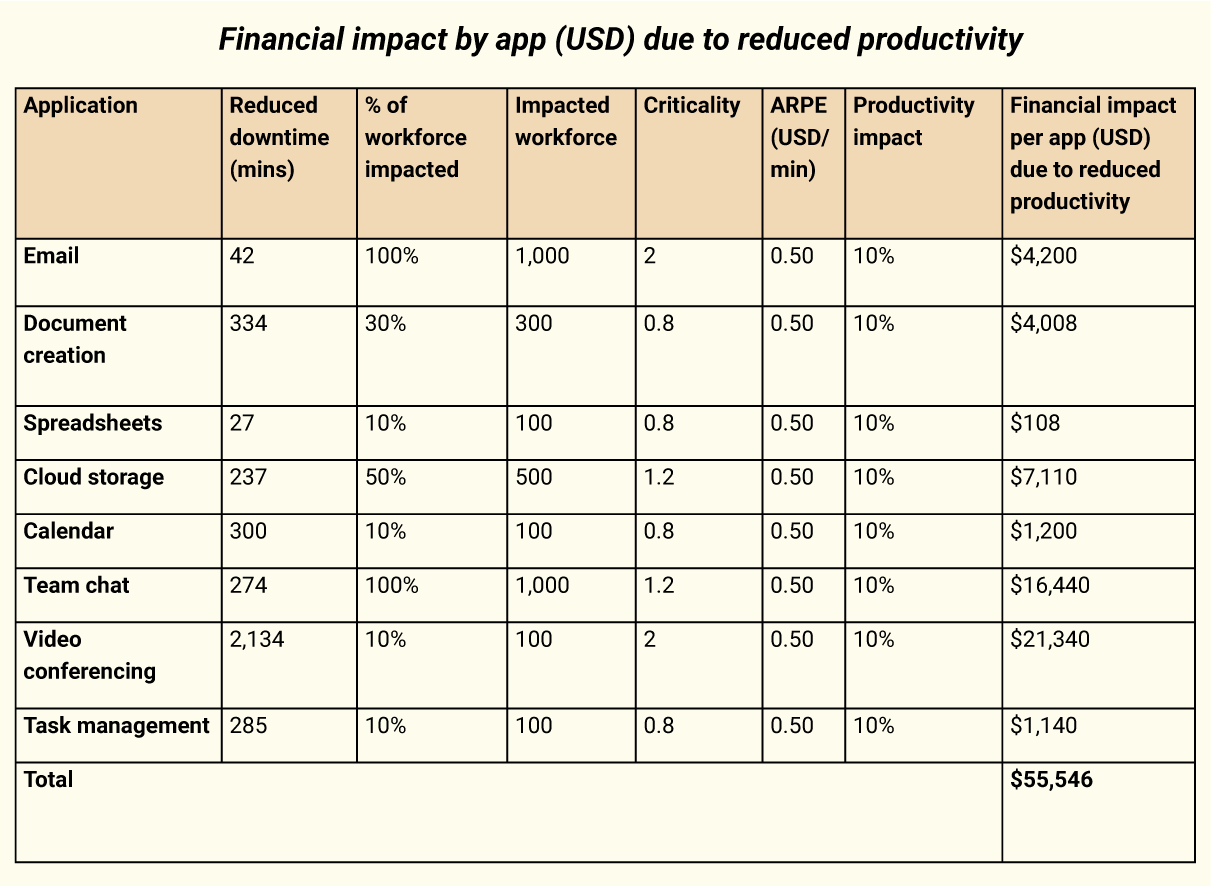
Total impact by app (USD) due to reduced productivity = $55,546
Notes:
Reduced downtime (in minutes) represents the difference in downtime minutes between Google Workspace and Zoho Workplace for each application in the US region, which is assumed to be 20% of the global downtime.
The productivity impact has been adjusted to account for the estimated 10% of the impacted employees' productivity affected by downtime.
The adjusted financial impact per app (USD) is calculated considering the reduced downtime, ARPE, criticality factor, percentage of the workforce affected, and the productivity impact.
Financial impact by app (USD) due to cost of support
CoS calculation table with new assumptions:
CoS per app = Hourly wage of IT staff × Reduced downtime hours × IT workload ratio + Impacted workforce x Number of IT staff (based on criticality) x Percentage of downtime requiring IT support x Hourly wage of support staff
Criticality and IT support: For applications with high criticality, a 100% likelihood of IT intervention is assumed with 3 support staff needed. Moderate criticality assumes a 50% likelihood with 2 support staff, and low criticality assumes a 20% likelihood with 1 support staff.
Hourly wage of IT staff: Assumed to be $60 for each IT staff member.
IT workload ratio: Set at 1.5 to account for the extended duration of IT work beyond the actual downtime.
Reduced downtime: Represents the difference in downtime minutes between Google Workspace and Zoho Workplace for each application.
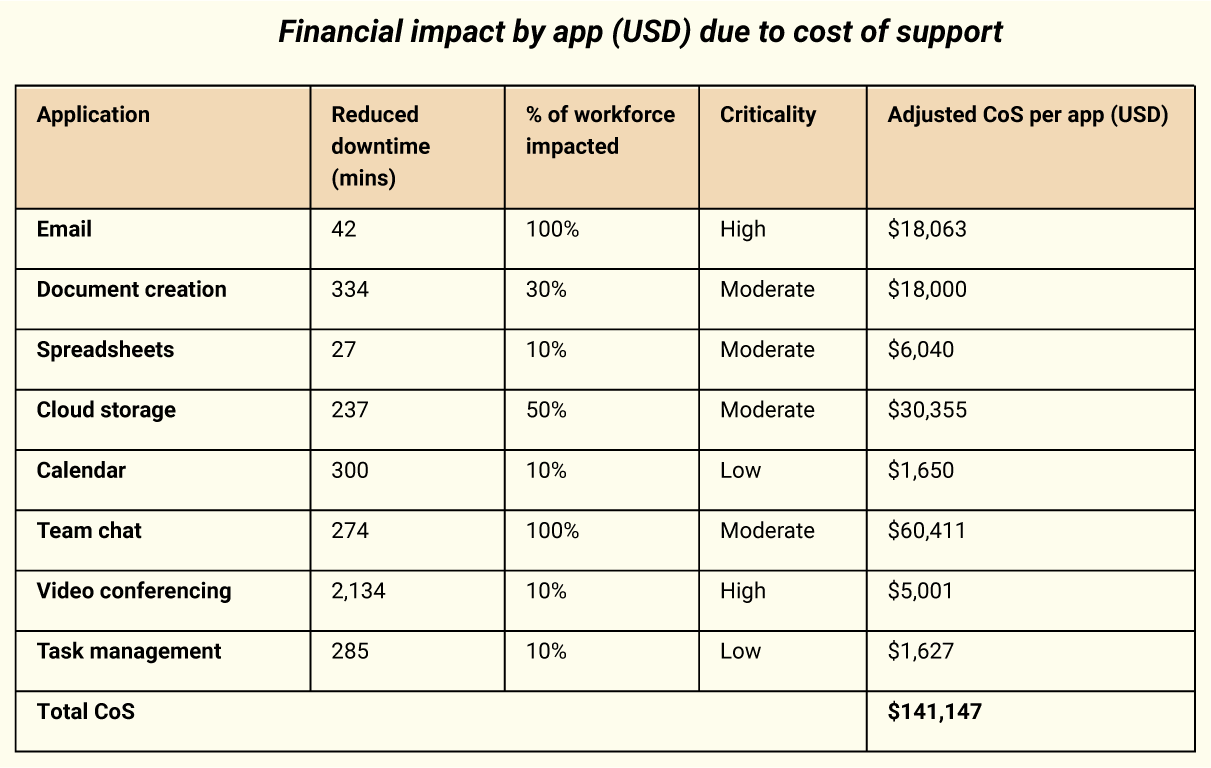
Financial impact of downtime = Reduced employee productivity due to downtime + Cost of support = $55,546 + $141,147 = $196,693
Conclusion
The comparison between Zoho Workplace and Google Workspace reveals significant disparities in downtime incidents, with Zoho demonstrating remarkable resilience. Downtime not only affects productivity but also incurs substantial financial costs, emphasizing the criticality of selecting a reliable productivity platform.
Zoho's proactive approach to security, robust incident response mechanisms, and commitment to transparency provide SMEs with assurance in their workplace productivity tools. The financial analysis considered various factors such as downtime duration, workforce impact, criticality factors, and the cost of IT support to estimate the substantial benefits of transitioning to Zoho Workplace. With an estimated total financial impact of $196,693 due to reduced downtime, organizations can realize tangible cost savings and operational efficiency gains.
As SMEs increasingly prioritize reliability and operational resilience, Zoho Workplace emerges as a compelling choice, offering not just productivity tools but also peace of mind and significant cost savings.
In the upcoming discussions, we'll explore additional factors and metrics to better quantify the financial benefits in adopting Google Workspace over Zoho Workplace, offering insights specifically tailored to SMEs.
Disclaimer
All names and marks mentioned here remain the property of their original owners. The statistics mentioned are as published by the named competitors on their website(s) on the date(s) shown and are subject to change without notice. The information on this webpage is not validated and is for general information purposes only. Zoho disclaims liability for any errors, omissions, or losses consequential upon any reliance on information contained here.
This article is co-authored by Sandeep Kotla and Vignesh S.
Sandeep is an accomplished inbound marketer at Zoho Corporation, specializing in digital workplace strategies, digital transformation initiatives, and enhancing employee experiences. Previously, he handled analyst relations and corporate marketing for Manage Engine (a division of Zoho Corp) and its suite of IT management products. He currently spends most of his time re-imagining and writing about how work gets done in large organizations, reading numerous newsletters, and Marie Kondo-ing his inbox.
Vignesh works as a Marketing Analyst at Zoho Corporation, specializing in content initiatives and digital workplace strategies. He's a passionate creator with a penchant for marketing and growth. In his free time, you can see him shuffling between books, movies, music, sports, and traveling, not necessarily in the same order.