- HOME
- Payroll administration
- What are allowances in salary? Allowance types and examples
What are allowances in salary? Allowance types and examples
It is an incredible feeling to expand your teams and watch your business grow. However, before you start hiring, there's an inevitable task to check off your list: creating a comprehensive salary structure for the roles you're looking to fill.
Crafting a diverse salary structure that aligns with labour laws and caters to the varied needs of employees is not an easy task. To help you along your hiring journey, here is a beginner-friendly guide on one of the significant components of an employees' CTC: allowances.

Allowance definition and meaning
An allowance refers to the amount given by an employer to an employee for meeting certain expenses. They're an additional payment paid as part of the employees' monthly salary, apart from their basic pay. Allowances are commonly provided for expenses such as house rent, travel, telephone, and children's education.
For example, organizations may provide conveyance allowance to sales representatives to cover their travel expenses to meet a client. Similarly, there are different allowances you can offer your employees based on their specific roles within the organization.
Types of allowances
Allowances can be broadly categorized into three types based on their tax implications: taxable, partially taxable, and non-taxable.
Taxable allowance
Taxable allowances are those allowances that are fully subject to income tax. When an employee receives a taxable allowance, the entire amount is added to their taxable income, and the employee is liable to pay tax based on their applicable slab rates.
Examples of taxable allowances include dearness allowance, overtime allowance, and city compensatory allowance.
Partially taxable allowance
These allowances are subject to certain tax exemptions up to a certain limit, beyond which the excess amount becomes taxable.
Conveyance allowance, children education allowance, and research allowance are some of the allowances exempt from tax subject to the limit set by the government.
Non-taxable allowance
Non-taxable allowances, also known as tax-free allowances, are allowances that are fully exempt from income tax. The amount received as non-taxable allowances is not considered when calculating an employee's income tax.
Allowances received by government employees working overseas and Judges of the High Court and Supreme Court are not calculated for taxes. Per diem allowances, given to private sector employees for business trips, are tax-exempt provided the entire amount is spent.
Examples of allowances
Besides basic pay, allowances make up the largest portion of your employees' salary. Ensure you provide them with the ones they can take full advantage of while you remain compliant with labour laws. Here are 12 examples of allowances you can offer along with their calculation and taxation rules.
Dearness allowance
Dearness allowance (DA) is paid mostly to public sector employees to cover their cost of living expenses and reduce the impact of inflation on them.
Since DA is related to living costs, the actual amount varies for employees in different locations—urban, semi-urban, and rural. The amount received is treated as taxable income and is subject to taxation.
DA is typically calculated as a percentage of the employees' basic salary. To determine this percentage, the government sets "DA rates" based on the All-India Consumer Price Index (AICPI).
- AICPI is a metric that measures the changes in the price of goods and services purchased by households over a period of time. This number varies from one location to another. The latest CPI can be found here.
- DA rates are determined and adjusted twice a year by the government to reflect the changes in the AICPI.
The central government has announced a hike in DA rates from 42% to 46% of the employees' basic salary effective from 1st of July, 2023.
DA calculation formula for central government employees
| Dearness allowance (%) = {(Average of AICPI (Base year 2001 = 100) for the past 12 months – 115.76)/115.76}*100 |
DA calculation formula for public sector employees
| Dearness allowance (%) = {(Average of AICPI (Base year 2001=100) for the past 3 months - 126.33)/126.33}*100 |
Learn in-detail about Dearness Allowance (DA).
Conveyance allowance
Conveyance allowance is provided to cover the commuting expenses while performing office duties within the city. It aims to reimburse fuel expenses, public transportation fares, and other costs associated with travel.
The calculation of the conveyance allowance can vary based on the company's pay policies. It may be a fixed amount or a percentage of the employee's basic salary.
The amount received is partially exempt from tax in the old tax regime, subject to the extent of expenditure. Any amount received in excess is taxed according to the income tax slab the employee falls under.
Learn more about conveyance allowance.
Transport allowance
Transport allowance is offered to employees to compensate the expenses incurred during commuting between their residence and workplace.
Generally, employers pay this allowance only if they don't provide transportation facilities for their employees. The amount can be a fixed amount or a percentage of the employee's basic salary. There's no limit on how much you can offer as transport allowance to your employees.
Transport allowance is fully taxable, and the amount received is added to the employees' taxable income. However, for differently-abled individuals, the tax exemption limit is ₹ 3,200 per month.
Learn in-detail about transport allowance.
Traveling allowance
Traveling allowances are provided to compensate the expenses made by employees during official business travel. It includes the price of travel tickets, accommodation, meals, and transportation.
It can be paid as a fixed amount or as a percentage of the basic salary for employees whose role requires them to travel from one city to another.
The amount received is exempt from tax in both the old tax and new tax regimes, provided the employee submits valid bills and proofs for the expenses.
Leave travel allowance
Leave travel allowance (LTA) or leave travel concession (LTC) is included in an employee's CTC to cover the expenses incurred when they undertake travel within the country for vacation purposes.
Employees become eligible for LTA if it is included in their offer letter or if it's part of the company's policy. Eligible individuals can claim this amount by submitting their travel tickets.
The claimed LTA amount is fully exempt from taxes in the old tax regime, provided the employee satisfies the following conditions.
- Either the employee or his dependents have traveled to a place within India.
- The employee has not claimed LTA more than twice in a block of four calendar years.
- If the employee has traveled by air, the LTA exemption is limited to the economy fare of the national carrier.
- If they have traveled by rail, the amount is based on the first-class fare for the shortest route.
The unclaimed amount is either carried forward to the next year or encashed at the end of the financial year based on the company's pay structure.
Learn more about leave travel allowance.
House rent allowance
House rent allowance, or HRA, is given to employees to help them meet the cost of renting accommodations.
The amount is calculated as a percentage of the basic pay, with variations based on the city of residence (metro or non-metro).
- HRA is 50% of the basic pay if the employee resides in any one of the four metropolitan cities: Chennai, Delhi, Mumbai, or Kolkata.
- It is 40% of the basic pay for employees residing in other parts of the country.
The amount received as HRA is fully taxable if the employee lives in his own house or does not pay any rent.
For the employees living in rented homes, the least of the following three amounts is eligible for tax exemption in the old tax regime.
- Actual HRA received from the employer
- 50% of the employee's basic salary (or 40% for non-metro cities)
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of the employee's basic salary
Any excess amount of HRA received beyond the eligible exemption is taxable in the hands of the employee.
Learn in-detail about House Rent Allowance (HRA).
Overtime allowance
Overtime allowance, or overtime pay, is a variable payment made by employers to employees for working beyond their regular working hours.
The amount is calculated based on the number of extra hours worked by the employee. The actual pay may vary depending on the laws governing the establishment and the company's policies. For instance, factory workers who spend over 9 hours in a day or over 48 hours in a week get double their regular wage for the overtime work.
The amount received is considered a part of the employee's taxable income and is subject to taxation.
Learn more about overtime allowance.
Children education allowance
As the name suggests, children education allowance is paid to employees to meet the educational expenses of their children.
It is usually paid by the government to its employees as a fixed amount every month to ease their financial burden. The allowance is exempt from taxes up to ₹100 per child, for a maximum of two children in the old tax regime. Any amount given in excess of that will be taxable.
Get to know everything you need to know about Children Education Allowance (CEA).
Medical allowance
This is a fixed amount provided monthly to employees to cover medical expenses, including consultations, medications, and treatments for themselves and their families.
The amount received is fully taxable and is included in the employees' taxable income.
Learn in-detail about medical allowance.
Entertainment allowance
Employees receive entertainment allowance to compensate the money they spend on meals, beverages, and hotel stays for the company's clients.
The amount provided to an employee is determined by the employer and is based on the nature of the employee's job role and responsibilities.
Entertainment allowance is completely taxable for employees working in private companies. For government employees, the amount is partially exempt from tax.
Sumptuary allowance
This allowance is offered to personnel within the central government to compensate for the costs associated with hosting visitors at their workplace.
The amount to be received as sumptuary allowance differs for authorities in different grades. For instance, cabinet ministers receive ₹2,000 per month, whereas deputy ministers receive up to ₹600 per month as sumptuary allowance.
City compensatory allowance
City compensatory allowance (CCA) is provided to employees working in cities to compensate for the increased expenses associated with residing in those cities. It is typically reserved for Tier-1 urban areas with some employers extending it to Tier-2 cities.
There is no fixed rate for the CCA component in salary; the amount is determined by the employer based on living costs and industry norms.
Any amount received as CCA is subject to income tax deduction based on the employee's income tax slab.
Allowances in salary structure
Now that you're aware of the various allowances you can offer, it's essential to understand how they collectively contribute to an employee's CTC.
CTC can be broadly broken down as a sum of the basic salary, allowances, and benefits. Typically, basic pay accounts for 50% of the total CTC, with benefits including social security deductions like PF and ESI.
Let's look at how the allowances you offer determine the total compensation of your employees with the help of a sample salary structure.
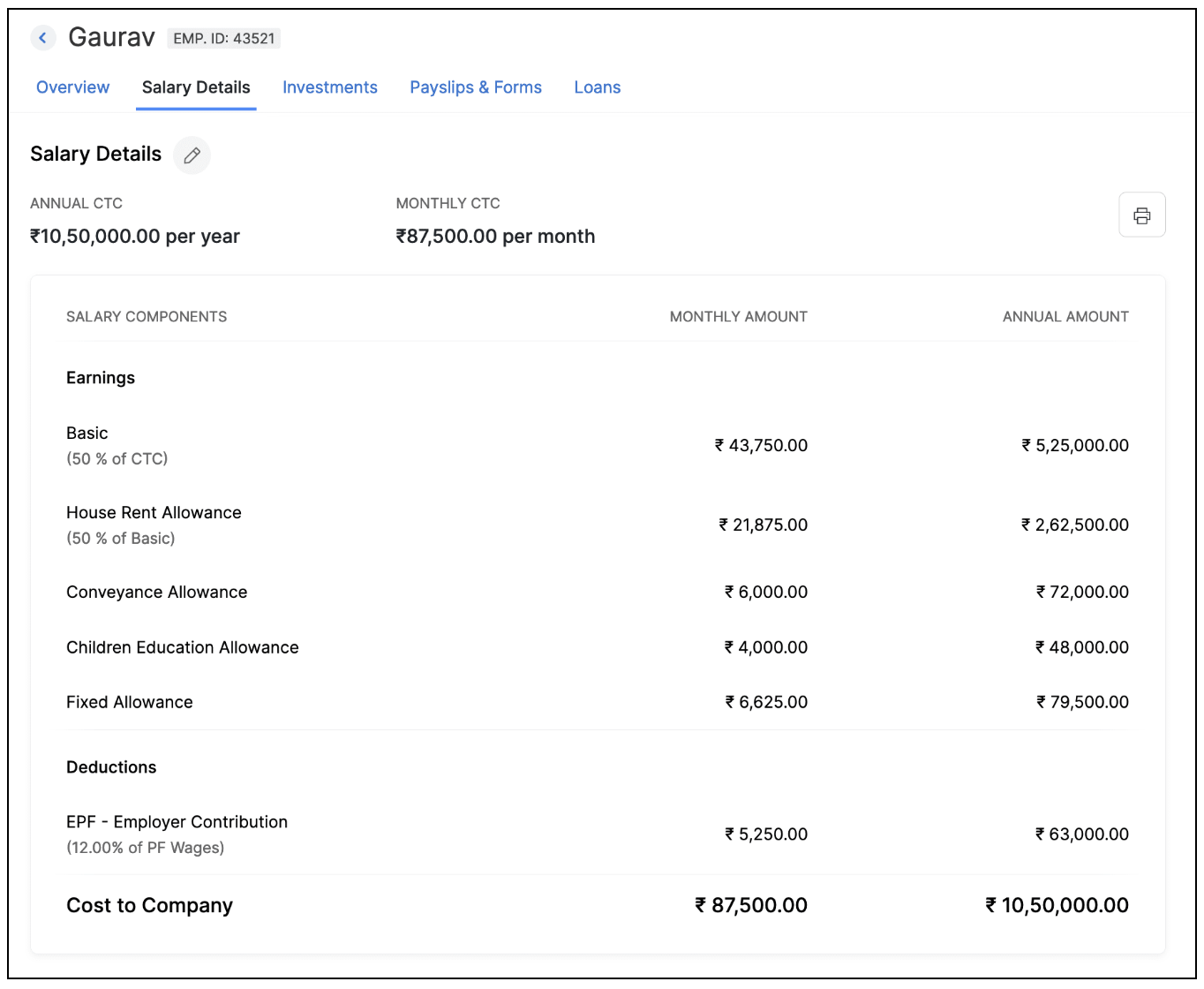
Sample salary structure in Zoho Payroll
Frequently asked questions on allowances
1. What are the difference between allowances and perquisites?
Allowances and perquisites are both forms of additional benefits or payments provided by employers to employees, but they differ in their nature and purpose.
| Allowances | Perquisites |
| Allowances are provided to cover certain expenses made by employees during their course of employment. | Perquisites, or perks, are benefits given to employees to enhance their compensation package and improve job satisfaction. |
| Examples of allowances include dearness allowance, conveyance allowance, and house rent allowance. | Examples of perquisites include company-provided cars, laptops, and accommodation facilities. |
| These are added to employees' salaries and influence their take-home pay | These are provided beyond the employees' salaries and do not have any effect on employees' take-home pay. |
2. Which allowances are exempt from income tax?
Allowances received by certain government employees, Judges of the High Court and Supreme Court are completely exempt from taxation.
Partially-taxable allowances, such as conveyance allowance and daily allowance, received by both public sector and private sector employees, are exempt from income tax to the extent of the actual expenses.
3. What is the special allowance in salary?
The special allowance is a component of an employee's salary structure provided by employers to offer additional compensation beyond their basic salary.
It is a flexible amount that can be adjusted based on the employee's role, responsibilities, and performance. Some organizations offer special allowance as a bonus to high-performing employees or as a fixed amount to cover the expenses they incur.
References
- The Income Tax Act of 1951
- Allowances chart by the Income Tax department
- Salaried employees' benefits chart by the Income Tax department
- The Salaries and Allowances of Ministers Act




