What is kanban?
The term kanban, originally from Japan, translates to “visual card”. It was initially developed to manage work, regulate inventory, and optimize production in the Japanese automotive industry.
At its core, kanban is all about visualizing work, limiting work in progress (WIP), and enhancing workflow to improve productivity. Kanban, since its initial development, has evolved into a versatile tool that can be implemented in numerous industries, from software development to healthcare, and even in everyday life.
Imagine walking into a team’s workplace where every task is depicted by a card on a board. The board is divided into columns, and each column represents a stage in their workflow. As a task progresses from ideation/inception to completion, the respective card moves across the board, providing a clear visual representation of the task status at any given moment. This simple method helps teams identify bottlenecks, balance workloads, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
From the factory floors of Japan to revolutionizing how modern businesses manage work, kanban has become a cornerstone of project managers, team leads, and innovators to build a successful business with thriving teams.
Kanban vs. scrum
Kanban and scrum are both agile methodologies used to improve project management and workflow efficiency, but they have distinct differences.
KANBAN
SCRUM
Visualizes and continuously improves workflow
Divides work into fixed time periods called sprints
Usually lasts for the lifetime of the project/product
Lasts for two to four weeks
Focuses on the continuous progression of work through phases
Focuses on completing a specific set of tasks within a fixed period
Perfect for teams with shifting workloads and regular modifications who wish to streamline operations without significant process changes
Ideal for teams with predetermined positions, like product owner, scrum master, and development team members
Helps identify bottlenecks and improve efficiency over time
Ensures that the project stays on track and meets the desired outcomes
Flexible framework
Agile framework
Both scrum and kanban methodologies aim to enhance productivity and adaptability. You'll choose which one to implement based on your goals, team dynamics, working style, and the flexibility you need.
If you’re new to kanban, you can explore this easy-to-use and intuitive kanban view in Zoho Tables with a free 15-day trial.
Understanding how the kanban method works
The very first step in kanban is to visualize the existing workflow. Each task is represented as a card on the kanban board, with columns indicating each stage of the workflow. These stages are typically “to-do”, “doing”, and “done”.
By limiting the number of tasks in progress at any one time, kanban helps teams focus on completing current work before starting anything new, leading to smoother workflow and better resource allocation.
Core practices of the kanban method
Visualize the workflow
Create a visual representation of your workflow using a kanban board. This helps teams see the flow of work and identify bottlenecks.
Limit work in progress (WIP)
Set limits on the number of tasks that can be in progress at a time. This prevents overloading team members and reduces multitasking.
Make processes explicit
Clearly define and communicate the rules and policies that govern your workflow. This includes criteria for moving tasks between stages, WIP limits, and definitions of “done”. This helps ensure consistency and transparency.
Implement feedback loops
Establish regular feedback mechanisms to review and improve the workflow. This can include daily update meetings and review meetings. This helps teams continuously improve their processes and adapt to changing conditions.
Manage flow
Focus on ensuring that work moves smoothly and efficiently through the workflow. Monitor the work and improve the flow whenever required.
Improve collaboratively, evolve experimentally
Foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging team members to suggest and implement progressive and practical changes. Experiment with new ideas and measure their impact.
Key components of kanban
A kanban board typically includes the following components:
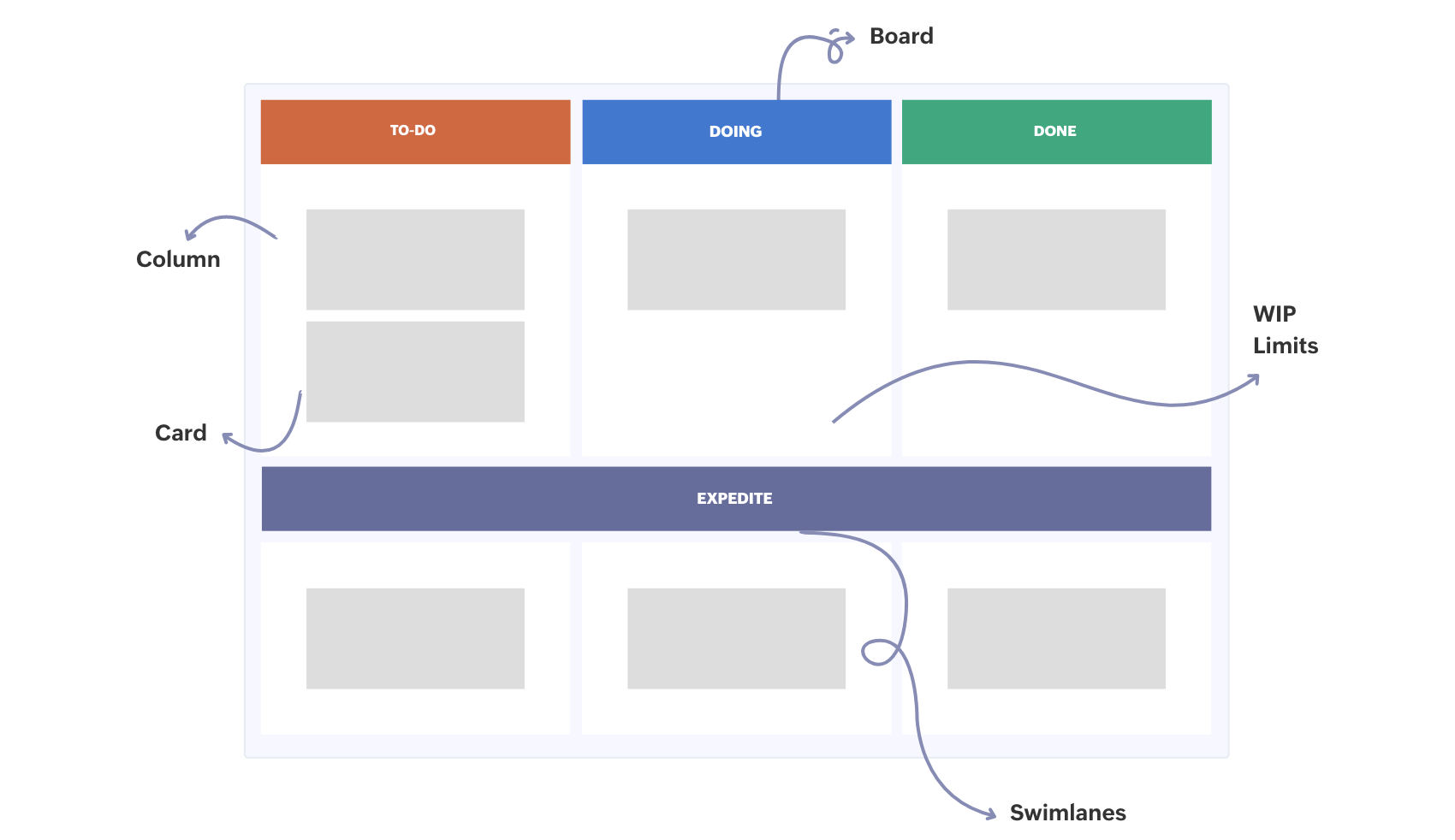
Columns
Columns represent different stages of the workflow, like “Backlogs”, “To Do”, “In Progress”, “Review”, and “Done”. Each column visualizes a phase in the lifecycle of a task.
Cards
Cards represent individual tasks or work items. Each card includes details like task name, description, owner, deadline, and relevant notes. Cards move through columns as the task progresses.
Swimlanes
Swimlanes are horizontal rows that separate different types of work, projects, or teams on the same board. This helps organize tasks and distinguish between various work streams.
WIP limits
Work in progress limits, also known as WIP limits, are constraints set on the maximum numbers of tasks allowed in a particular column at a time. WIP limits help prevent overloading and ensure a smooth workflow.
Board
The physical or digital space where the the kanban flow is displayed is called a kanban board. It acts as the central hub for visualizing and managing the workflow.
Kanban at work
The versatility of the kanban method makes it a valuable tool in a wide range of industries:
In manufacturing, it’s used to ensure just-in-time production and reduce waste.
Software developers use it to enhance collaboration, speed up delivery, and improve product quality.
Healthcare professionals use kanban to streamline patient care processes and manage supply chains.
Marketing teams use kanban to organize campaigns, track content creation, and manage deadlines.
Human resources uses kanban to manage recruitment processes, track onboarding, and oversee employee training.
Education institutions organize curriculum planning and administrative tasks using kanban boards.
In the retail industry, kanban is used to manage inventory, track sales processes, and organize supply chains to reduce stockouts and improve customer satisfaction.
Kanban is used in construction and real estate to coordinate tasks, manage project timelines, and oversee resource allocation to improve project visibility.
Event planners use kanban to organize tasks, track progress, and manage deadlines. This enhances coordination and ensures smooth execution.
Kanban beyond work
The simplicity of implementing the kanban method also makes it a practical tool to manage everyday life for millions of people who love organizing their chores and improving personal productivity. From meal planning to fitness goals, home renovation projects to event planning, financial management to travel planning, the kanban method can significantly enhance the organization and efficiency of daily activities.
In short, using a kanban board ensures tasks are evenly distributed and completed on time, whether it’s at work or at home.
Creating a kanban board in Zoho Tables
Zoho Tables is collaborative work management software that helps plan and track work, streamline and automate workflows, organize and visualize work data, and collaborate contextually.
While views like grid, calendar, and gallery help visualize data the way it makes sense to you, built into every single table is a kanban view, to give you a visual representation of your workflow. This ensures that, regardless of your project or task management style, you can seamlessly track progress, manage tasks, and enhance team collaboration with a powerful kanban view right at your fingertips. Check it out now!
Kanban view in Zoho Tables also has powerful sort, filter, and color customizations. When applied, these customizations will apply only to the view you’re working with and won’t affect any other views. You can also create multiple kanban views in a single table.
With Zoho Tables, when you create a kanban board, data is automatically populated from the grid view, which is perfect if you’re new to the kanban method.
Learn more about how kanban view works in Zoho Tables


