- HOME
- Taxes and compliance
- What is an Income Tax Return (ITR)? How to file an ITR online?
What is an Income Tax Return (ITR)? How to file an ITR online?
The Income Tax Department of India levies a tax on inidviduals' earnings according to the slab they fall under. Every citizen, whether they're an individual, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), or an association, has to pay a certain amount of tax based on their annual income. Taxpayers can claim rebates, deductions, and exemptions on taxable income and should pay tax on the rest of the amount for every financial year.
Taxpayers and applicable individuals are also required to file an income tax return (ITR) for their income before the last date as specified by the Central Government. As per Section 139 of the Income Tax Act, every person whose annual income is above ₹2,50,000 is obligated to file an income tax return.
We understand that filing an income tax return can be a challenging task, but doing so will be beneficial. You can claim certain refunds on tax deducted at the source, make visa or loan processing easier, and carry forward business losses to the subsequent year by filing an ITR. Learn what an income tax return is, why we file an ITR, and how to file a return online and offline in this step-by-step guide.

What is an income tax return?
An income tax return, or ITR, is an official record submitted to the Income Tax Department that contains a person's annual income and the taxes paid on such income. It is filed once every financial year, which starts from the 1st of April of the current year and ends on the 31st of March of the following year.
Tax liability is calculated based on the person's total income. A person's annual income can be from various sources such as:
- Income from salary
- Income from interest on deposits
- Profit and gains from a business or profession
- Income from house property
- Income from dividend, capital gains, family pension
- One-time income (winnings from lotteries, horse race, etc.)
An ITR is a worksheet that shows a person's tax liability. If a person has paid more than what they're liable for, it will be reflected on the ITR and they can claim a refund from the Income Tax Department.
Who should file an income tax return?
As per the income tax laws, ITR filing is mandatory for individuals and businesses if they meet certain criteria.
The following individuals whose gross total income exceeds the basic exemption limit must file an ITR:
| Particulars | Taxable income |
| Below the age of 60 | Above ₹ 2,50,000 |
| Senior citizens (between 60 and 80 years of age) | Above ₹ 3,00,000 |
| Super senior citizens (above 80 years of age) | Above ₹ 5,00,000 |
There are certain scenarios where ITR filing is mandatory for individuals even if their gross total income is below the basic exemption limit. You have to file a return if:
- You have spent more than ₹2 lakh for an international trip.
- Your bank account's cash deposits and withdrawals exceed ₹10 lakh in a financial year.
- You have deposited an aggregate of ₹1 crore in your current bank accounts.
- You have spent more than ₹1 lakh in electricity bills in one financial year.
- You run a registered company or firm. (Note: You have to file a return of income irrespective of whether you have made profit or loss throughout the year.)
- You have assets or financial entities located outside India.
- You're a non-resident Indian who accrued more than ₹2.5 lakh in India in a fiscal year.
ITR filing is voluntary for individuals whose gross total income is below ₹2.5 lakh and do not meet any of the above criteria.
Why should you file an income tax return?
Here are six reasons why you should file an income tax return every year.
1. Have an official record of your income
For self-employed individuals who do not have Form 16, this can be used as a proof of income. ITR documents are also accepted as a proof of address by the government.
2. Claim a refund on TDS
Individuals who file an ITR within the stipulated time can claim a refund if the tax deducted at the source exceeds their actual tax liability. Learn more about income tax refunds, and how to claim and check an ITR refund status here.
3. Process loan, credit card, and visa application easier
When you're applying for a loan or credit card, banks usually ask for the previous three years' ITRs as proof of income. Likewise, embassy officials also ask for your ITR to approve visas. This is done by officials to assess your financial situation. Having proper returns increases your chances of getting loans and visas.
4. Carry forward business losses
If you run a business, it'll be beneficial for you to file return regularly and carry forward any losses. This helps you claim adjustments in the future as losses not recorded in returns can't be shown as an exemption in the subsequent year.
5. Avoid penalties and late filing fees
The Income Tax Department can impose a penalty of up to ₹5,000 for delayed filing or non-filing of an ITR. An additional penal interest on the unpaid tax liability will also be levied if you're filing return after the due date.
6. Contribute to nation building
Paying taxes contributes to the development of a country. By filing an ITR, you're being accountable and fulfilling your duty as a citizen.
Documents required to file an ITR
For salaried employees
- PAN
- Aadhaar
- Form 16 issued by the employer
- Month-wise pay slips/salary slips
- Form 26 AS from the income tax website- A consolidated annual statement of tax deducted/collected at the source, advance tax paid by the individual, and income tax refunds
- Home loan statements
- Rental income statement(s)
- Month-wise rent receipts in case house rent allowance is being claimed
- Bank statements for interest on savings and fixed deposit accounts
- Section 80 C investment documents, if any
For businesses
- PAN
- Aadhaar
- GST number, if registered under GST
- Rental income statement(s)
- Profit and loss statement for the financial year
- Balance sheet
- Audit report, if applicable
- Form 26AS from the income tax website
- Bank account statements
- Demat account statement, if applicable
- Interest certificates from banks and cooperative society, if applicable
- Section 80 C investment documents, if any
- Details of foreign assets
- Details of fixed assets, sale and cost of assets
Types of ITR forms
The IT department has notified 7 different ITR forms for individuals. The following infographic will help you understand the eligibility criteria for each of the forms.

Learn more about ITR forms for FY 2023-24 in our detailed guide.
How to file an income tax return
Individuals can file returns online or offline.
Filing ITR online
Note: Taxpayers can only file ITR 1 and ITR 4 forms online through the income tax e-filing portal.
- Go to the income tax e-filing portal https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal.
- Click on the login button present at the top right of the screen.
- Log in using your PAN/Aadhaar or other ID number and password.
- Log in using your PAN/Aadhaar or other ID number and password.
- Click on the e-File button. A dropdown will open.
- On the dropdown list, select Income Tax Return and then click File Income Tax Return.
- Select the assessment year and click online mode if you're a taxpayer and are filing ITR 1 or ITR 4.
- Read the instructions carefully and choose the ITR form applicable to you.
- After ascertaining the form, fill in all mandatory fields. Refer to your income and tax-related documents and fill in the details.
- Validate your return breakup, and confirm your return summary.
- Once you have completed filing the form, you have to choose the appropriate ITR verification option under the Taxes Paid and Verification column.
- Once you've verified your returns, click Preview and Submit button to check all the data you've entered.
- Click Submit to complete the process.
Filing ITR offline
All taxpayers can file return offline using the ITR Offline Utility. There are two major steps involved in filing return offline:
- Generate a JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) file using the Utility
- Upload the JSON file to the income tax portal
Here are steps to download the ITR Offline Utility and file an ITR offline.
Generate a JSON using the utility
1. Go to the income tax e-filing portal https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal.
2. Click on Downloads; a new page will open.
3. On the Downloads page, under Income Tax Return, select your assessment year.
4. Once done, choose the ITR form applicable to you and click Schema to download the appropriate utility.
Note: Individuals filing ITR 1 to ITR 4 can download the Common Offline Utility and file returns.
5. Upon clicking Schema, a zip folder will download on your device. Open the zip folder to install the utility.
6. Once the offline utility is installed, carefully fill in the relevant details based on your income and tax documents.
7. You can also download prefilled data from the ITR portal, import the data in the utility, and edit the fields, if required.
ITR e-filing portal >> Login >> E-file >> Income tax return >> Download pre-filled data
8. Check for the tax payable amount, if any, on the utility. Click Validate on the right side of the form to ensure all the mandatory fields are filled.
9. After validating, click on Generate JSON to convert the form to a JSON file.
10. Save the JSON file on your device.
Uploading the JSON file to the income tax portal
11. Go to the income tax e-filing portal https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal and log in using your credentials.
12. Click e-File. On the dropdown list, select Income Tax Return and click File Income Tax Return.
13. Choose your assessment year and select Offline as your mode of filing.
14. On the Select Filing Type dropdown, you'll need to mention the status of your return (original return, belated return, revised return, or a modified return).
15. Click on the ITR type applicable for you and mention if your returns require an audit under section 44AB.
16. Once you're done, click Continue. You'll be taken to the File Income Tax Return page.
17. Upload your filed ITR in JSON format using the Attach file button.
18. If there are no errors on the file, the page will display Validation Successful.
19. Click Proceed to Verification and verify your returns before the due date for a successful ITR submission.
Income tax return verification
As per the new guidelines, if you're filing ITR after 1st August, 2023, your return will be invalid if you do not verify it within 30 days.
Here's how you can verify income tax return online and offline:
- You can e-verify using a one-time password sent to your Aadhaar-registered mobile number or generate an Electronic Verification Code (EVC) through your pre-validated bank/demat account.
- Your ITR can be verified offline by generating an EVC via select bank ATM cards or by sending a signed ITR-V (acknowledgement document) to the tax department via normal or speed post services.
How to file a revised income tax return
Section 139(5) of the Income Tax Act allows individuals to rectify mistakes on their original income tax return by filing a revised return. There is no limit to the number of times an individual can file a revised return, but they must do so 3 months prior to the completion of the relevant assessment year.
Revised return can be filed easily by logging into the income tax e-filing portal and clicking File Revised Return on the dashboard. You'll need to select the assessment year again and fill in the form suitable for you. The new return will replace your original return upon successful submission of the revised return.
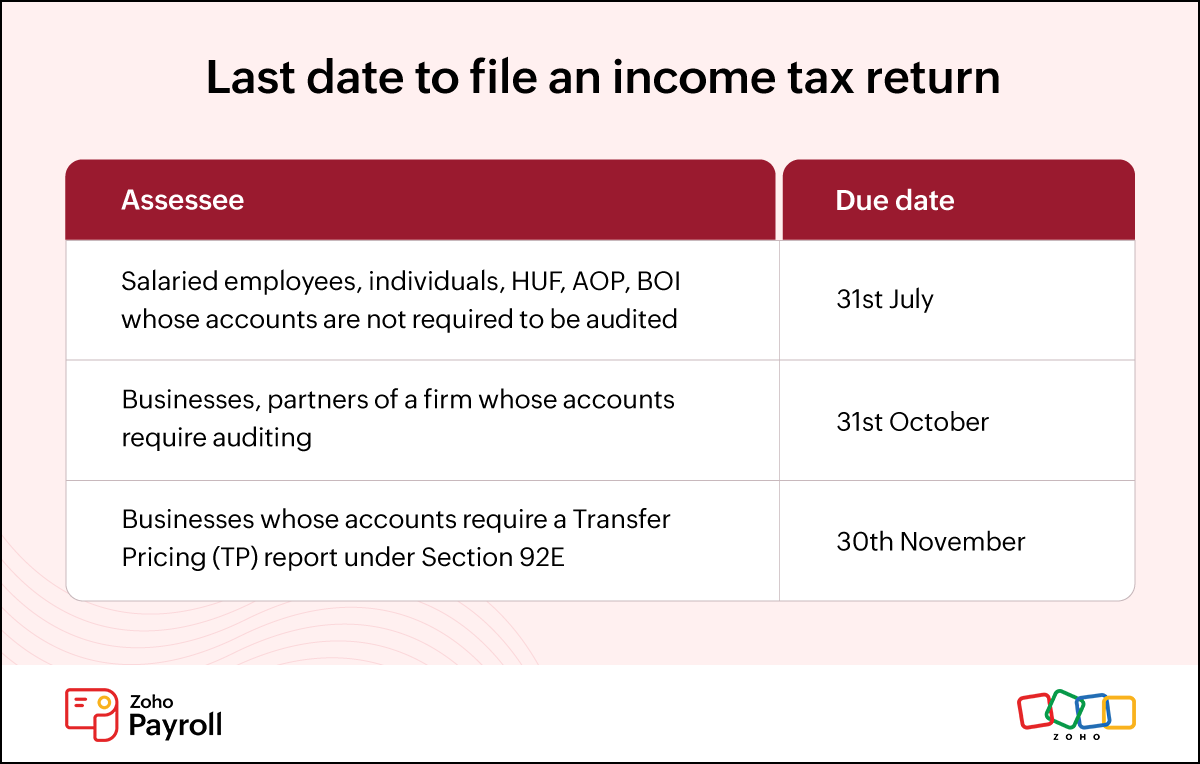
Last date to file an income tax return
The last date to file returns for individuals is set by the Income Tax Department. The due date differs based on the individual's income source and business type.
Penalty for non-filing of an income tax return
According to Section 234F of the Income Tax Act, a late filing fine of ₹5,000 will be levied on individuals who do not file a return before the due date. However, for individuals with gross income less than ₹5 lakh, the maximum penalty is ₹1,000. If you miss the ITR deadline, you will also have to pay interest of 1% per month on the unpaid tax amount.
For people who have income from a business or profession, loss adjustment in the subsequent financial year will be allowed only if you have filed a return before the deadline the previous year.
FAQs on Income Tax Return filing
1. What is Form 16? How do I get Form 16?
Form 16 is a certificate issued by an employer that contains information related to the employee's salary, income tax, and other deductions made at the source. Learn more about Form 16, its format, and the steps involved in generating it from our comprehensive guide on Form 16.
2. What is an ITR acknowledgment? How can I download an ITR acknowledgment?
An ITR acknowledgement or an ITR-V is a document generated by the Income Tax Department after a successful income tax return filing and verification. Users can download an ITR acknowledgement through the Income Tax e-filing portal.
- Log in to the e-filing portal using your credentials.
- Go to E-file >> Income Tax Returns.
- Select View Filed Returns and click Download Form. Your ITR acknowledgment document will download.
3. How can I check my ITR status?
Log in to the Income Tax Department's online portal using your PAN or other ID number and password. The status of your recently filed ITR will be displayed on the dashboard. Here are the different ITR filing statuses and their meanings:
- Submitted and pending verification: You filed an ITR and forgot to verify it. Follow these steps to verify your returns.
- Successfully verified: You submitted and verified an ITR, but it was not processed by the taxing authorities yet.
- Processed: Your ITR submission has been processed successfully by the Income Tax Department.
- Defective: The authorities found errors in your ITR. You'll receive a notice from the department to rectify the mistakes within a specified time limit.
- Case transferred to the assessing officer: The IT department transferred your ITR submission to the jurisdictional assessing officer. You will be contacted by the respective officer to provide details regarding your earnings and taxes.
4. What is the time limit for revising a return?
Individuals can file a revised return before the 31st of December of the relevant assessment year or before the completion of the assessment, whichever is earlier. For the current assessment year 2023-2024, the last date is 31st December, 2023.
5. What is Form 26AS? How do I download it?
Form 26AS is a crucial tax document that shows the tax deducted/collected at the source and the advance tax or self assessment tax paid to the government by the taxpayers. Besides the deduction details, the form also contains high-value transactions made by the users. You can view and download Form 26AS from the TRACES website or through net banking from any of the authorized banks.
Appendix
Hindu Undivided Family
As per Hindu law, the IT Act treats a Hindu Undivided Family as a separate entity formed by lineally descendants of a common ancestor. It includes wives and unmarried daughters of male descendants. A HUF cannot be created under a contract. A person, their spouse, and children can create a HUF and claim certain tax benefits.
LLP
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a corporate business vehicle formed by at least two partners. It contains elements of both a corporate structure and a partnership firm and allows flexibility in operation. The liability of each partner is limited to their shares as specified in the agreement filed during the creation of the LLP.
Association of Person
Association of Persons (AOP) is a group of people or entities (which includes LLPs, firms, and companies) who come together to achieve a common objective. For example, a company and an individual can join and form an AOP for a mutual benefit.
Body of Individuals (BOI)
Body of Individuals (BOI) are individuals who come together with the intention of earning income. Entities like companies and firms cannot join to form a BOI.
- Artificial juridical person
They are a public corporation established under the legislature having their own juristic principles. Universities and institutes are examples of artificial juridical person.
References
https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/help/e-filing-itr1-form-sahaj-faq
https://www.incometax.gov.in/iec/foportal/help/e-filing-itr2-form-faq




